 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Hate Crime, Term Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Term Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Over the past two decades, the world has experienced a rising trend in terrorism and mass shootings. The recent Christchurch killings in New Zealand highlight the increasing hate crime towards minority groups around the world. The most bizarre incidents of hate crimes are that both victim and offender share no common interest. The interest in this type of crime emanates from the lack of support from political, religious and government to resolve the issue affecting minority groups. Furthermore, a considerable number of Americans do not think that hate crime is a major issue that needs to be addressed (Ehrlich). The denial of culture and lack of proper reporting are the social factors leading to the prevalence of prejudice crime in society.
Carr, Haynes, and Schweppe, 2017 define a hate crime as a criminal felony against and individual founded by the perpetrators’ prejudice against gender, ethnicity, sexual orientation, religion or race. Recent statistics by the Federal Bureau of Investigation through its UCR flagship show a rising trend in hate crime in the United States. The agency gathered the data in 2017 present information regarding the areas of hate crime, victims, offenders, and offenses. The report indicates 7,106 hate crime incident reports where 8,493 victims were targeted. Furthermore, 60% of hate crime victims were targeted because of ethnicity, and race. A fifth of the victims became targets owing to their religious affiliation. Another 15.8% population was targeted for being gay or lesbian. According to the FBI reports, the hate crimes varied from physical assault, rape, robbery, vandalism, and murder.
The FBI conducted investigations in nine US major cities. The cities include New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston, and Philadelphia. Others such as San Antonio, San Diego, Dallas, and San Hose. The Center for Hate and Extremism reported 921 prejudice related crimes in the cities in 2016. New York City reported a rise in hate crimes by 6%, 173% in Houston, 13% in Los Angeles and 26% in Chicago according to the statistics. According to (Masood, 2019) data also revealed that gays, Jews, and African Americans topped the list of target groups in the city of Chicago. The graph below represents hate crimes as seen in the top 9 cities in the US.
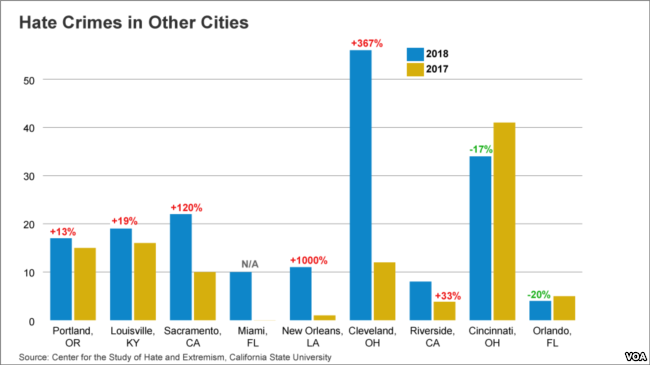
Source: Center for the Study of Hate and Extremism, California State University
New York indicated a rise in anti-Semitic attacks since a large percentage of the Jewish people inhabit the city. Data shows that 361 reported cases of hate crime targeted the Jewish community. In 189 incidences of anti-Jewish hate crime reported in 2018, 150 of the cases involved the exhibition of swastikas. The presented data within the 9 cities indicates that hate crime continues to rise (Masood, 2019). The most vulnerable group remain people with different sexual orientation, Blacks, and Jews.
I found two media articles highlighting the rise of hate crime in my city New York, particularly anti-Semitic attacks on the Jewish community. The CNN article reports three cases where victim, offender and the category of the hate crime occurred in New York. The articles reports of a video showing a 51-year-old Jewish being physically abused by three men. It appears the attackers randomly selected the Jewish man. The second incident of hate crime is a recorded street video showing a man holding a tree branch chasing an Orthodox Jewish man. The last incident reported an assailant pouncing and chocking an Orthodox Jewish man as he pinned him against a fence (Otternman, 2019). All three cases occurred in Crown Heights in 2018, rising alarm to the growing trend of anti-Semitic attacks in New York City. Of particular interest to the CNN report is that incidences reported in Crown Heights, Brooklyn specifically targeted Jews. By Feb 17th this year, police received 55 hate crime reports in New York city alone a rise by 72 % in 2018 (Otternman, 2019).
Another article by the Times of Israel emphasizes the anti-Semitic attacks in the city of New York. According to the article, there was a 22% increase in hate crime reports on the Jews living in New York. Out of the overall 352 incidences of hate crime, 183 were recorded to target the Jews community. The article also highlights the Brooklyn area as prone to hate crime incidences, nonetheless, hate crime against Muslims declined by about half while Jews hate crime rose by 22% in 2017 (JTA, 2018). The two news articles augur well with the FBI statistics which shows New York ranking high among hate crime incidences.
Impacts of Hate Crime
Hate crimes cause fundamental effects on victims that suffer emotional and physical abuse. Victims are also dominated by the perpetrators view on their identity. Offenders mostly see the victim as innately lesser and different. Hate crime offenders mostly go through an increased urge to inflict pain with the perception of reducing risk. Such perceptions of minimizing risk come from the social hostility targeting a primary element of the victims identify (Carr, Haynes & Schweppe, 2017). Identify elements include race, religion, sexual orientation, gender or disability.
According to (Carr, Haynes & Schweppe, 2017) argues that every hate crime generates a number of individuals indirectly affected. Separate members of the target group remotely go through their fear of victimization and suppression. Hate crime simply sends the message that the target group is perceived as abject, and often are susceptible to attacks (Carr, Haynes & Schweppe, 2017).
Hate crime and social cohesion
Apart from the psychological and physical impacts on victims, hate crime can be understood as an assault on the whole society. According to (Carr, Haynes & Schweppe, 2017) crimes based on an individual’s identity pose more damage to society compared to other offenses without perceived intent. Hate crime portrays and mold relations between groups, hate crimes thus remain dangerous to the overall societal conscience because they can polarize individuals of a particular group, exposing societal differences. (Carr, Haynes & Schweppe, 2017) maintains that hate crime can also act as a channel which drives society apart; forcing groups alienate themselves and fuelling intergroup conflict. Therefore if not addressed the issue of hate crime and revenge can become a negative vicious cycle in the society (Carr, Haynes & Schweppe, 2017).
The theoretical basis of Hate Crime
Strain, doing difference, self-control, and authoritarian personality theories have been used to conceptualize why hate crime permeates society. The four theories help highlight the sociological aspects that act to generate enormous hatred towards and fear of minor identity communities (Walters, 2010)
Strain and doing difference theory
The two theories relate via emotional fear which is the perception that others may intrude into a dominant group socio-economic independence and identity. The fear thus triggers the hate towards the alleged ‘intruder’. The dominant group may or not feel the ‘strain’ of the encroachment direct, however, they remain inclined to ‘safeguarding’ their dominant identity and socio-economic power. The prevailing group might act to subjugate minorities that do not conform to their beliefs. The dominant group thus develops a fear of possibly losing their economic and social success to the ‘outlaws’ in the future (Walter, 2010). A common phrase used by white supremacists, for instance, is that the crime is not fuelled by hate for minority groups but their love for the Caucasian race. A phrase such as ‘my own kind’ features predominantly in white supremacists defense of the hate crime actions (Ehrlich, 2010)
Self-control Theory
Self-control theory on crime posits that people possess control over their action thus preventing them from falling into the lure of a chance to commit the crime. An individual’s capability to apply self-control is an attribute from early childhood. Failure to nurture self-control leads to the lure of self-gratification. Hate crime offenders possess no self-control thereby showing aspects of impulsivity and insensitivity. According to (Walters, 2010) they are individuals that take risks and do not considers others around them, self-gratification comes first. Individuals with low self-control have a low tolerance for others and are mostly unsociable.
Authoritarian Personality Theory
According to (Walters, 2010) psychological literature on crime attempts to explain hate crime through the Authoritarian Personality theory. The basis of the theory posits that parents often present themselves in a dismissive and overtly critical manner. Consequently, kids raised by such parents grow up knowing that power and control remain critical in human associations. Any frustration toward their upbringing is exerted towards vulnerable groups in order to relive a sense of control. An authoritarian personality remains the most convincing way of understanding the action of extremist’s perception against certain groups of people. Perpetrators of hate crime are likely to subscribe to outfits whose main objective is to inflict pain or harm on others that they perceive different or inferior (Walters, 2010). The act of the hate crime gives the individual an opportunity to exert authority over the victim
Conclusion
Hate crime continues to be witnessed in various forms across the globe. The UCR data provided by the FBI between 2004 and 2017 indicates that hate crime occurs mostly in New York City. Victims of such hate crimes are predominantly Jews or blacks. The implications of hate crime include both physical and psychological. Victims and members of the affected group constantly live in fear. Overall, hate crime threatens the fabric of society as it forces groups to isolate against each other. Different theories have been put forth to conceptualize crime based on prejudice. The Strain and ‘Doing Difference’ theories are based on emotional fear from the offender. In most cases, the perpetrators aim to protect their identity or socio-economic power based on the fear of encroachment by the minority group. Self-control theory posits that people with no self-control possess attributes such as intolerance to other people’s identity. The authorial personality theory argues that children raised by dominant and strict parent grow up to understand that control and dominance are a sign of power. White supremacists, for instance, hold the belief that their race is much superior to others. The minority group must, therefore, be subjugated.
References
Carr, J., Haynes, A., & Schweppe, J. (2017). Hate crime: an overview of significance and relevance to Irish sociology. Irish Journal of Sociology, 25(1), 73-83.
Ehrlich, H. J. (2010). Hate Crimes and Ethnoviolence: The History, Current Affairs, and Future of Discrimination in America. Sydney, Australia: ReadHowYouWant.com.
J.TA (2018, December 28). Hate crimes in New York, 2018: Jews targeted more than all other groups combined. The Times of Israel. Retrieved from https://www.timesofisrael.com/hate-crimes-in-new-york-2018-jews-targeted-more-than-all-other-groups-combined/
Masood, F. (2019, January 31).Hate Crimes in Major US Cities Rise for Fifth Year in a Row, Data Show.. Retrieved from https://www.voanews.com/a/hate-crimes-in-major-us-cities-rise-for-fifth-year-in-a-row-data-show/4767616.html
Otterman, S (2019, February 18). Anti-Semitic Attacks Fuel Continuing Rise in Hate Crimes in New York. The New York Times (2019, February 19). Retrieved from https://www.nytimes.com/2019/02/18/nyregion/anti-semitism-brooklyn-new-york.html
Walters, M. A. (2010). A General Theories of Hate Crime? Strain, Doing Difference and Self Control. Critical Criminology, 19(4), 313-330

Stuck with your Term Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

