 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Journal of Materials Engineering, Term Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Term Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Pore- Pressure Build Up, Dissipation, and Clay
Name
Clay is used in low permeability soil in order to allow the pile to gain capacity. The increase in capacity occurs as the pore pressure increased and dissipation occurs. Research has focused on the factors that use pile installations into clay material. The current paper analyzes pore pressure and dissipation, the gain in capacity, and the effect on the increase in gain on the pile. In addition, the paper examines how clay influences the pile driving process. Utilizing clay results in benefits, such as cost.
Keywords: Clay, Pore Pressure, Dissipation
Introduction
Clay has many uses as a material in the engineering field. One of the uses is pore pressure of loads in pile driving. Pore Pressure has been referred in engineering as the build-up or entrapment of fluid. The pressure increases because the fluid is unable to leave the pores. In addition, the pressure is dependent upon the depth and density of the surrounding material or type of soil. The increase in pore pressure is correlated with the instability of a load. Although the increase is pressure occurs, the pressure will eventually dissipate, thereby decreasing the pressure depending on the type of soil. For instance, the pile capacity has shown to increase with an increase in the strength of the soil. This has been observed in soils that have a low permeability, such as clay. (Chen et al.) For pile driving, it is essential to determine the amount of pore pressure that will occur before implementing pile driving. Engineers have developed programs that allow them to determine the amount of pore pressure, referred to as limit equilibrium stability. (WSDOT, 2010)
Engineers have undergone research in order to find the amount of time it takes for pile capacity, as well as obtain the amount of pressure resulting from piles. Engineers are also finding that the increase in porewater pressure combined with clay results in a decrease in soil strength; however, dissipation over time allows for the soil to consolidate and gain strength, as well as capacity. (Swan) The current paper examines the effect of piles that are driven into clay and the resulting capacity gain.
Pile foundations can be described as the structure that supports the given structure to the ground. Different types of material are used in piles, such as steel or concrete. (Abebe and Smith) Different types of soil react differently to piles and are categorized into two different materials, granular or clay. Granular soils tend to be non-cohesive and clay is cohesive; therefore, the strengths of these types vary. The capacity of the piles that are driven into the clay soils are therefore an important area in engineering research. Research has been conducted to determine the amount of stress the pile undergoes in clay. Through research, it has been noted that a pile can change the amount of stress in the soil significantly. (Randolph et al., 1979) has also been found that clay re-shapes the soil that is contained around the pile.
Clay allows piles to increase the capacity via friction. The areas in which clay is used are found in piles underneath rafts or mats. Different numbers of piles are; however, the number of piles is not a factor, the size and type of soil is the factor. (FM 5-134) When using clay, it is the pore pressure increase and dissipation that directly alter capacity gain.
Literature review
The changes in pore pressure and stress in clay were analyzed and it was found that an equation that is useful when stress is combined with pore fluid of a saturated soil type. The authors indicated that the formula was useful for charting the dissipation of the pore pressure after the cavity expands.
Formula (2) written above explains the total stress; however, it does not include pore pressure or the use of clay. In order to integrate these factors, calculations for the increase in the cavity were implemented. The results of this implementation illustrated that the pressure is limited once the cavity increases in size. (Carter et al., 1979) Another study focused on the effect of time of a pile when driven into clay. In the study, piles were driven into a clay deposit and a sand deposit. After the first week,
Chen (et al.) conducted a field research project to illustrate the effect of time on pile capacity when driven in clay. Two different piles were used, soft marine clay deposit and silty sand deposit. The results of the study showed that when utilizing clay, there was an increase in the pile capacity. (Figure 1) experiment illustrated that the pile driven in the clay exhibited an increase in pile capacity over time. The pile capacity increased due to strength from the reconsolidation of the surrounding soil. (Figure 3) In addition, the results of this study showed that the increase in pile capacity over time indicated that there could be a possible cost reduction due to the type of soil used. The higher the capacity, the less number of piles required. (Chen et al.)
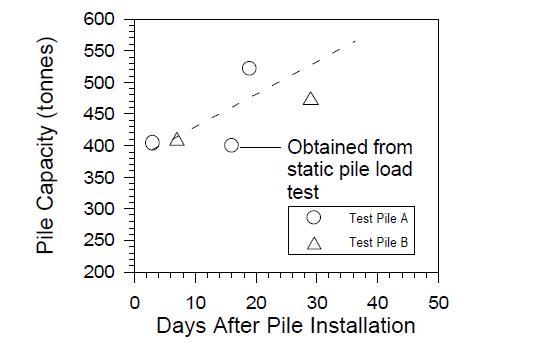
Figure 1. Pile capacity vs. time in clay. (Chen et al.)
Other useful research for utilizing clay has been used for projects in areas of seismic activity, such as California bridges. Pestana (et al., 2002) found that piles used in marine clay created a high pore pressure, which dissipated over time and consolidated the soil. (Figure 2)
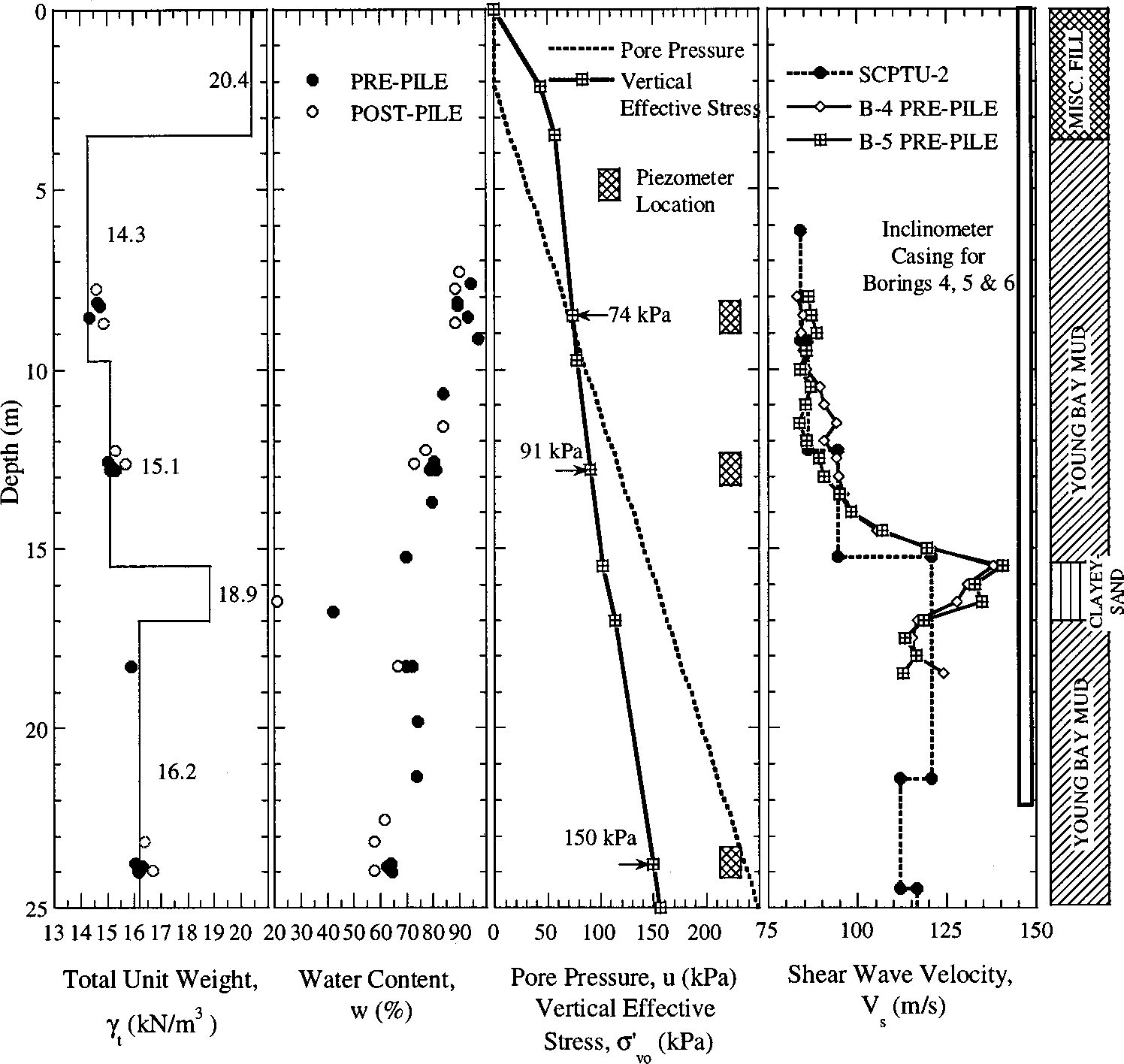
Figure 2. Soil profile of pore pressure and stress. (Hunt et al., 2002)
Other studies conducted by Gavin et al, (2010), found that piles driven into soft silt clay increased the stress and pore pressure. In addition, research conducted by Marchetti (et al., 1986) support the notion that when piles are driven into clay, the pore pressure increases at the pile-clay interface, as illustrated in Figure 3.
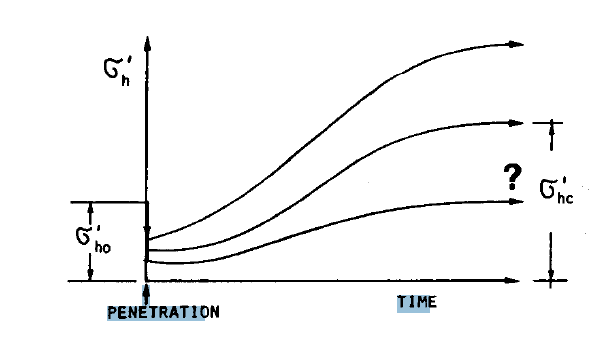
Figure 3. Effective Stress Interface after Pile Installation. (Marchetti et al., 1986)
The U.S. Department of Transportation has implemented models to illustrate the interaction of piles driving into materials, such as clay. The model pile monitors the pressure of the pile and simulates different types of conditions, such as soil. This type of model can be useful in obtaining the pile capacity for projects. The model also shows the dissipation of the pore pressure and is capable of determining the rate of the dissipation of pore pressure. Results from simulations using this model show that the use of clay should be used for pile foundations, especially in seismic areas. (Paikowsky and Hart, 2000)
The model also outputs data into a plot to show the best fit line for dissipation. (Figure 8)
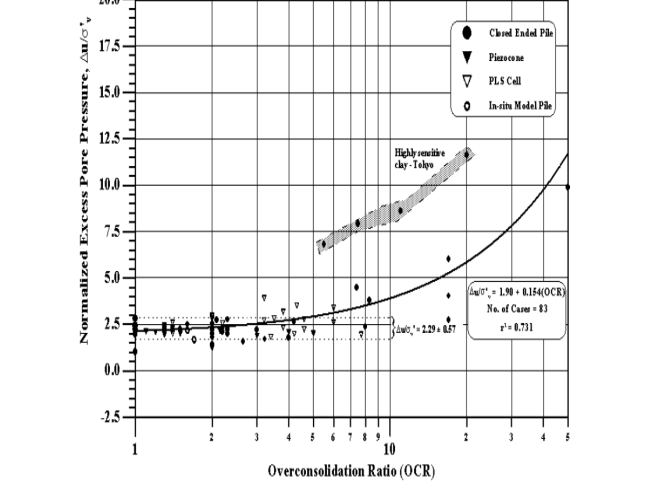
Figure 8. Model created for pore pressure and dissipation. (Paikowsky and Hart, 2000).
The increase in pore pressure and the subsequent occurrence of dissipation is a factor for piles driven in clay. Por pressure can result in an instable foujndation and the dissipation is therefore necessary. Much research has focused on factors after driven into clay. Models have also been created in order to facilitate the pile driving process, especially in seismic areas.
Conclusion
Overall, the engineering researchers continue analyze different models and methods in order to study the results of piles driven in clay, as well as the factors that occur after piles are driven into clay.
material. Factors such as pore pressure and dissipation are extremely important in this process. Research has shown that using clay is particularly important in areas of great seismic activity, such as in California.
Engineers have developed equations and calculations to help determine the capacity, pore pressure and dissipation in order to determine the need for clay. There have also been advances with the Department of Transportation supporting the use of clay driven piles as they are most effective for increasing pore pressure and dissipating over time. The purpose of this support is to help benefit costs. Further research should be applied to correlate the amount of cost savings related to using clay.
Acknowledgements
I would like to acknowledge my family for all of their support through this program.
References
[1] Ababe, A. And Smith, I.G. Ph.D. Pile Foundation Design: A Student Guide. School of the Built Environment, Napier University, Edinburgh.
[2] Carter, J.P., Randolph, M.F.. Wroth, C.P. (1979). Stress and Pore Pressure Changes in Clay During and After the Expansion of a Cylindrical Cavity. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics. 3(30):305-322.
[3] Chen, C.S., Liew, S.S., TAN, Y.C. Time Effects on the Bearing Capacity of Driven Piles. SSP Geotechnics Sdn Bhd, Malaysia.
[4] Hunt, C., Pestana, J.M., Bray, J.D. (2002). Effect of Pile Driving on Static and Dynamic Properties of Soft Clay. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering. pp. 13-24.
[5] Gavin, P.D.K. (2011). The Shaft Capacity of Displacement Piles in Clay: A State of the Art Review. Geotech Geol Eng . Spinger Science + Business Media B.V. 2011
[6] Gavin K, Gallagher D, Doherty P, Mccabe B (2010) Field investigation assessing the effect of installation method on the shaft resistance of piles in clay. Can Geotech J 47(7):730–741.
[7] Marchetti, S., Totani, G., Campanella, R.G., Robertson, P.K., Taddei, B. (1986). The DMT-obc Method for Piles Driven In Clay. Reprinted from Proceedings of In Situ. GT Div., AXE. pp765-768.
[8] Paikowsky, S.G. And Hart, L.J. (2000). Development and Field Testing of Multiple Deployment Model Pile (MDMP). U.S. Department of Transportation. Federal Highway Administration. Publication Number: FHWA-RD-99-194. 284pp.
[9] Pestana, J., Hunt, C., Bray, J. Soil Deformation and Excess Pore Pressure Field around a Closed-Ended Pile. ASCE. 128(1):1090-0241.
[10] SWAN, C.C. Changes in Soil During Pile Driving. Foundation Engineering. The University of Iowa. Web. Retrieved from: http://www.engineering.uiowa.edu/~swan/courses/53139/notes/changes-in-soil-during-pile-driving.pdf.
[11] Wsdot. (2010). Wsdot Geotechnical Design Manual M 46-03.01 pp.51.

Stuck with your Term Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

