 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Making Management Decisions, Statistics Problem Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Statistics problem
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

The management team is very different in its decision-making approach. William Stevenson, the production manager, is risk averse. It is notable that he is adequately trained for his production manager post because he is trained as an engineer. The fact that he is conservative and risk-averse makes him unable to adventure in new business ventures. It is notable that MBC has not been doing well since the year 2009 and it is in fact recording losses. This does not mean that there are no opportunities that can be applied to help the company perform better.
Since MBC is the market leader at the moment, there should be strategies to ensure that it keeps this position. Every manager agrees that the number of employees is high since production has decreased to match with decrease in demand. It has been agreed that employees need to be decreased by 25%. However, demand has been reported to be increasing for the past three months. According to William, who is risk-averse, the decisions the management needs to take to solve its problems of making losses is to decrease production to reduce fixed costs and report profits
William applies Limited Procrastination decision making Style. In this style, one does not need to rush to decisions even if the situation needs to be resolved urgently. He fears to encounter risks that will be incapable to solve later and prefers to delay all decisions until all necessary factors are evaluated. This is the reason why William does not accept the decisions suggested by Harry and Imran. William might prevent MBC from making the right choices because of his risk-averse character in which he is out to resist any changes that involve taking risks. This can be mitigated by making William understand the benefits associated with the high-risk opportunities.
Harry Stevenson is the Marketing and the Managing Director of MBC. He is trained in business studies and considering his logical and systematic treatment of business problems, he can make decisions that are more informed. He does not necessary fear risks neither does he love taking them. As a result, he is risk neutral. He prefers opportunities that show moderate risks. There are two main options that the firm can take to solve its problems of losing profits. He prefers the option of focusing on UK market in which promotion will be increased buy costs cut. This option looks like a good choice for Harry bearing in mind that he likes making logical choices but does not like trying high-risk ventures.
Harry’s decision-making style is Systematic Style. In this style, the decision maker evaluates each possible option before making the decision. In this case, the decision maker does not consider risk ventures and is only interested in moderate risks. If the company goes by Harry’s option, it does not mean that the current situation is not improved. However, the improvement done is not at its maximum and thus may give room for competitors to win market share.
Harry’s decision can be changed by being encouraged by bee shown the benefits associated with risky ventures. Harry needs to understand that his decision is not a bad one but it is not the best option among the alternatives since more benefits are associated with the second option.
Risk taking is a factor that benefits an organization in most of the time. By risk, it means that the investor can lose everything or gain extraordinary profits. Imran Malik, the Director of Finance and Administration manager holds a masters degree in business. He can be seen as an entrepreneur because of his risk loving character. He understands that risky ventures have more returns and as a result, he has always loved taking risks.
Imram is for the idea of opening new markets, and enter UK markets. This option is seen as being risky because of the escalating foreign exchange rates. The increase in fixed costs is proposed to be very high at £50,000 and this means that the firm has to borrow in order to finance this venture. By taking Harry’s alternative, it means that the firm will be exposed to more debts and in case the option fails, the firm will be closed and still there will be debts to cover. The risks associated with this option can be lessened by doing further research in order to ensure that the management is more informed before making the final decision. This way, the best decision will be taken and the condition of the company will be improved.
The assumptions made in this case include (Lybrand 2):
- A 52-week year
- Other fixed costs remain constant with only the specified fixed costs changing
- Overhead costs are allocated on labor hour basis
- Overhead is fixed irrespective of the decision taken
- Labor hours overhead application method is the best base for our company
- Manufacturing capacity, production mix, sales prices and variable costs are constant
- Calculate the current total breakeven weekly quantity and production capacity utilization of barometers for MBC.
Break even is the point at which profit is equivalent to zero implying that the sales revenues equal to fixed cost and variable cost (total cost). The equation is (Cafferky and Wentworth 42);
Break even sales= total costs (fixed costs + variable costs)
In units, Breakeven point in units = Fixed expenses / Unit contribution margin;
Since the case includes, depreciation cost, the formula for calculating breakeven point changes to; Breakeven Point = (fixed costs – depreciation) / contribution margin per unit
Contribution Margin = Sales Revenue – Variable Cost
Fixed cost= £5,000, depreciation costs= £1,000, sales revenue per unit =£160 (90+70), variable costs= £85 (20+20+20+10+10+5)
Contribution margin = £160-£85= £75
Breakeven point in units= £4,000 (5,000-1,000)/ £75; = 53.33 units approximately 54 units.
Capacity utilization (%) = actual output per week x 100%/ maximum possible output per week
= 60% x 200×100%/ 200 = 120/200 = 0.6 or 60%.
- Calculate the current breakeven weekly quantity and production capacity utilization of Household and Commercial barometers for MBC.
Breakeven Point = (fixed costs – depreciation) / contribution margin per unit
Contribution Margin = Sales Revenue – Variable Cost
- Breakeven point in units of Household barometers;
Contribution margin per unit household barometer = £70- £35 (20+10+5) = £35
Breakeven point in units= £ 4,000 (5,000-1,000/ £35 = 114.29, approximately 115 units.
- Breakeven point in units of Commercial barometers:
Contribution margin per unit commercial barometer= £90- £ 50 (20+20+10) = £40
Breakeven point in units = £4,000 (5,000-1,000)/ £40= 100 units
- Do you agree with the basis of allocating the fixed overhead? Could this be improved?
Overhead costs are allocated through a number of ways including direct labor hours, direct labor cost, machine hours, and revenues among others. It is the decision of the management to decide on the best overhead allocation system to apply. This depends on a number of factors. For instance, with a labor-intensive company, it is advisable to use direct labor cost of direct labor hours (Lybrand 4). On contrary, for a capital-intensive company, it is advisable to use machine hours. At MBC, fixed overheads are allocated using labor hours. This method is reliable and practical because the two products have different usage of labor hours associated with them.
However, the method needs to be changed to labor-cost basis because the two products have different labor costs just as they have different sales revenues. In addition, labor cost associated with each product can be equated to revenues realized from each product. By this, it means that the product with high selling price has high labor cost. This way, the method of allocating fixed overhead will be more reliable because more fixed overhead will be allocated to the product with high returns.
It should be noted that by poor fixed overheads allocation, an investor might discontinues a product on wrong basis because the product might prove to be incurring losses. It should be ensured that the method used to allocate fixed overheads allocates low values to the products, which have low selling products and vice versa.
- Briefly explain the limitations of breakeven analysis for decision making
In breakeven analysis method, there are a number of limitations that a decision maker has to face. While there are different types of costs including, fixed, semi-fixed, and variable, breakeven analysis method assumes only two types of costs, fixed and variable. Variable costs depend on volume of production while in real, there are times in which variable costs increase at an increasing rater with increase in production. It is assumed that fixed costs remain constant over a certain volume of production. However, this is a limitation because fixed costs might change even without the change in production range.
The fact that it is assumed that per unit selling price is constant for all the entire volume is a limitation since prices are decided by market forced and change with demand changes. It is possible to conduct breakeven analysis for several products, which are been produced in varying mixes and therefore it is assumed that the company in consideration sells a single product of a constant mix of products.
It is assumed that costs are only affected by volumetric increase while in reality; there are other factors that affect costs such as changes of material costs, political instability, inflation, and scarcity of materials among others. Resource use and efficiency is constant over the specified period while in reality, this may change since resources such as materials efficiency is determined by quality and this may change when the firm is supplied with poor quality resources.
Compare the two decision options using the net present value (NPV) approach. Assume a five-year planning period and discount rates of 5% for Option 1 (UK focus) and 6% for Option 2 (EU expansion).
Option 1 (UK focus)
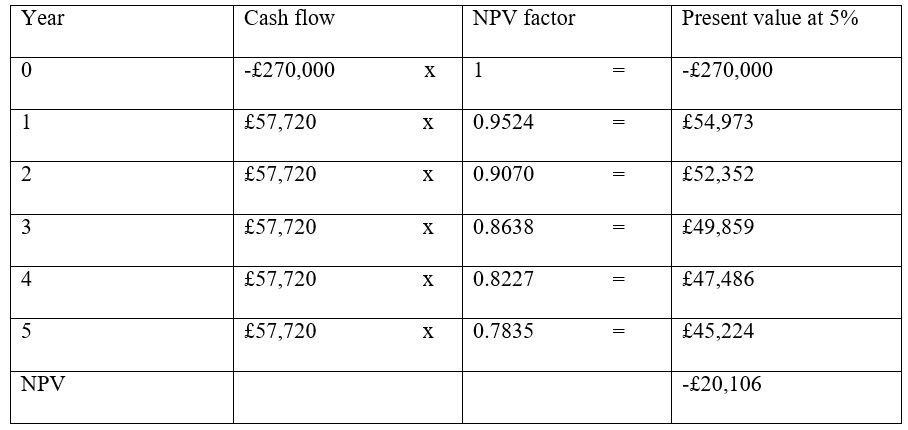
Current sales revenue from household barometers is £4,200 (70 x 60), while sales revenue from commercial barometers is £5,400 (90 x 60). Total current sales revenue =£9,600 x 52 weeks = £499,200.
With option 1, fixed costs are decreased by 3% and this can be regarded an inflow, making the amount get to 3% of £5,000 = £150 x 52 weeks= £7,800
Annual cash inflow for the five years will be (10% of £499,200) + £7,800 = £57,720
Annual cash outflow = £ (5,000 x 52 weeks) + £10,000 = £270,000
NPV factors are = 1/ (1+r)n, where r is discount rate and n is time (Bragg 303).
NPVs, Year 0 = 0; year 1= 1/(1+0.05)1 = 0.9524; year 2 = 1/(1+0.05)2 = 0.9070; year 3 = 1/(1+0.05)3 = 0.8638; year 4 = 1/(1+0.05)4 = 0.8227; and year 5 = 1/(1+0.05)5 = 0.7835
Option 2 (EU expansion)
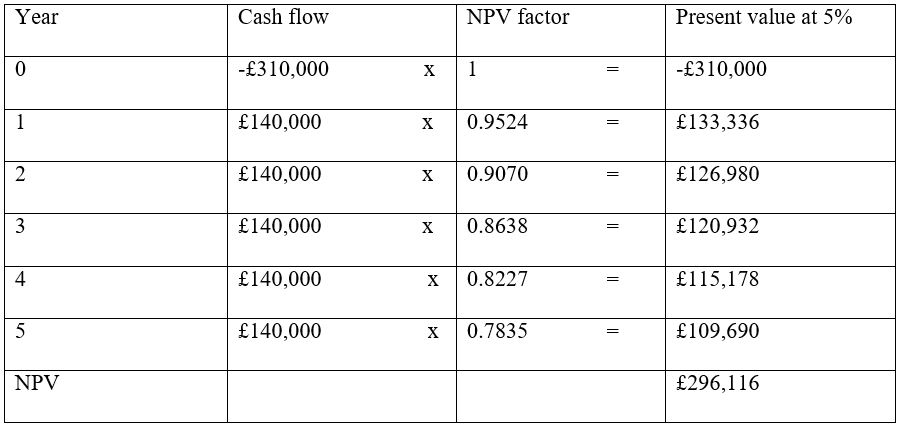
Annual cash flow for the five years is calculated as follows:
Annual Cash outflow = £50,000+ £ (5,000 x 52) = £310,000
Annual cash inflows = £140,000 (given)
Decision: the option to select should have a positive NPV. The decision should be select Option 2 (EU expansion)
Summarize your recommendations for MBC
Management decisions make or destroy a firm. Management decisions affect barely every functioning of the firm. They range from purchasing, employees, marketing research, employees’ selection, recruitment and motivation among others. Decisions made by management need to be strategic to ensure that they do not affect the functioning of the firm negatively. Considering the case of The Midland Barometer Company (MBC), located in Birmingham, and owned by William and Harry Stevenson, things are not going as planned. Imran Malik, Director of Finance and Administration manager, Harry, Marketing and the Managing Director, and William, as Production manager, hold the management positions. Management structure is informal with good deal of sharing ideas.
With informal decision-making, it is expected that the company perform successfully. It has reached a point in time when there in need for strategic decision-making to change the situation in the company. Although demand is growing in a slow pace, it is notable that the company is realizing losses. The company is also facing the threat of competitors outweighing it and winning the market when in reality, the company has been the market leader.
Considering the two alternatives, there is need for adequate research to ensure that the selected option will benefit the company. The financial resources of the company and being depleted and this means that the option taken should be able to repay any loan used to finance the venture.
With the two options to select from to better the situation at MBC, the management should pick on option 2 (EU expansion) because it has a positive NPV. The method is able to repay its debts unlike the first option that has a negative NPV.
Works cited
Aryasri, Daniels. Managerial Economics and Financial Analysis. London: Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2000. Print.
Bragg, Steven, M. Financial Analysis: A Controller’s Guide, Edition 2. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2007. Print.
Cafferky, Michael and Wentworth, Jon. Break Even Analysis. New York: Business Expert Press, 2010. Print.
Lybrand, Coopers, N. Breakeven Analysis: How to do it. New York: Coopers & Lybrand, 2002. Print.

Stuck with your Statistics problem?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

