 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, Term Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Term Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Abstract
The objective of this work is to answer the question of what is the underlying philosophical paradigm of the practice theory and why is it that this is the philosophical paradigm underlying this theory? This work will link the major assumptions of the theory to the ontological, axiological, and methodological assumptions of the epistemological paradigm as well as identify and describe what research studies have been used to test this theory. This work will answer as to what research methods these research studies used in testing the theory and discuss the scope of practice theory and its appropriateness for theory building and validation as well as answer how accurate the theory is an explaining the phenomenon.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Objective
The objective of this work is to answer the question of what is the underlying philosophical paradigm of the practice theory and why is it that this is the philosophical paradigm underlying this theory? This work will link the major assumptions of the theory to the ontological, axiological, and methodological assumptions of the epistemological paradigm as well as identify and describe what research studies have been used to test this theory. This work will answer as to what research methods these research studies used in testing the theory and discuss the scope of practice theory and its appropriateness for theory building and validation as well as answer how accurate the theory is an explaining the phenomenon.
Introduction
Abraham Maslow attempted to conduct a synthesis of a large volume of research on human motivation. Historically research had centered on factors that were related to biology, power or achievement in attempting to explain what serves to direct, sustain and motivate the behavior of humans. Maslow proposed a hierarchy of human needs, which had as its basis two types of needs and specifically:
- Deficiency needs; and
- Growth needs. (Huitt, 2001)
The first four levels of these needs are those as follows:
- Physiological – including thirst, hunger, and other comforts that are of a bodily nature;
- Safety needs – relating to the individual’s sense of danger;
- Belonging and Love – the needs for acceptance; and
- Esteem – related to the need to achieve and be recognized. (Huitt, 2007)
The following illustration depicts the conceptualization of Maslow in his ‘Hierarchy of Needs’.
Figure 1
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
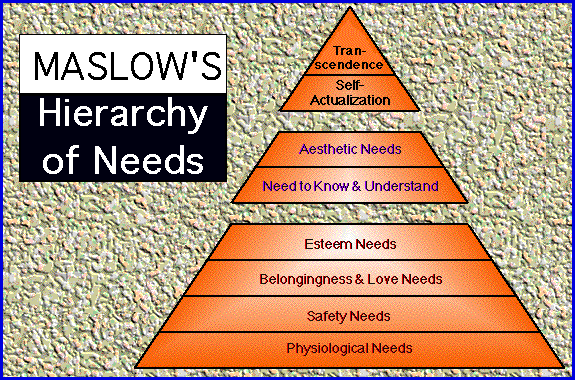
Source: (Huitt, 2007)
Maslow held that the human being is ready to act upon other needs for growth only when the deficiency needs are met. The initial conceptualization of Maslow was inclusive of only one growth need and that was the need for self-actualization. Self-actualization characteristics in the human being include that the individual is:
- problem-focused;
- Incorporates an ongoing newness in appreciating life;
- A concern for their personal growth; and
- The capacity to have peak experiences.
The initial position of Maslow is that as the individual becomes more self-actualized the individual possesses more wisdom.
Maslow – Theoretical Basis
Humanism is a paradigm reported to have emerged in the decade of the 1960s and which has as its focus the freedom, dignity, and potential of the human being. Stated as a central assumption of humanism is that “people act with intentionality and values” and that this is “in contrast to the behaviorist notion of operant conditioning which holds that all behavior is the result of the application of consequences…” (Learning-Theories, 2011)
It is the belief of Humanists that the individual must necessarily be studied as a whole since the individual experiences growth and development across the lifespan therefore “the study of the self, motivation, and goals are areas of particular interest.” (Learning-Theories, 2011) Abraham Maslow is reported to be considered as one of the founders of the Humanistic Approach and while Maslow is not as influential among therapists as is Carl Rogers, and additionally reported is that Maslow is generally better known due to his interest in the application of psychological principles to areas such as behavior in business settings.
The Humanistic approach is termed by Maslow as the ‘Third Force’, which emphasizes the difference of this approach from the Psychodynamic and Behaviorist Approaches. Maslow’s theory places an emphasis on motivation as the primary factor in comprehending the behavior of humans. Maslow emphasizes what he calls ‘peak experiences’ which are stated to be “moments in life which take us beyond our ordinary perception, thoughts and feelings” and is an experience which the individual is filled with energy somewhat similar to the “Zen concept of satori or ‘literally enlightenment’ which just as a peak experience happens without prior expectations and serves the transform the individual’s understanding of themselves and the world around them. (Learning-Theories, 2011)
Axiological and Ontological Assumptions
According to Maslow, “physiological survival is considered to be the most basic motivator of human behavior.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008) When the individual or the organism is dominated by physiological needs their behavior is therefore fundamentally different than when other needs motivate behavior. (Reid-Cunningham, 2008) Maslow is reported to have stated that the component of his theory that is most important is that which “supplements…’Freudian pessimism’ and ‘neo-behaviorist relativism’ with positive and empirically grounded theories of human behavior, motivation and development. The other approaches had ignored the highest achievements of humankind by focusing on problems and illnesses, studying mainly crippled people and desperate rats. Maslow’s positive theories of human behavior and motivation were pragmatic as well as hopeful, realistic optimism about human beings capacity to develop is necessary to address social problems and improve the human condition.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008)
There are “phenomenological differences between people and other, which complicates any attempt to decipher the meaning of the human experience through studies of other species…” however, Maslow is reported to have “always maintained a sense of connection to the biological aspects of the human experience.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008) Maslow’s theory is reported to be “grounded in the human experience. This fundamental belief in the value of anthropocentric research methods for developing a theory of human motivation was echoed in Maslow’s writings about the hierarchy of needs.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008)
The assertion of Maslow was that the human being is “a whole, integrated organism but social science research and theory has attempted to simplify the study of human beings by reducing them to a collection of separable and identifiable drives. Maslow cautioned against strategies modeling higher human needs on physiological drives.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008) Maslow noted that the behavior of humans is “not often singularly motivated…” and that there are multiple factors that serve to motivate the human being.
Maslow stated the assumption that each individual “will self-actualize in an endemic and idiosyncratic way that fits with his or her personality, circumstances, culture, and other factors.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008) In other words, “a musician must make music, an artist must paint, a poet must write, if he is to be ultimately at peace with himself.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008) Maslow wrote in his journal that “every baby and potentially every person, should be regarded as capable of self-actualization and of creativeness.” (Maslow, 1979, p., 1200)
It is related in the work of Reid-Cunningham (2008) that Maslow’s observational and experiential knowledge greatly added to his works. For example, the difference in temperament of his two daughters is related to have “served to confirm that human beings do not enter the world as a blank slate to be shaped entirely by the environment, there are intrinsic and unique qualities of individuals that must inform any comprehensive theory of human nature.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008)
Maslow’s entire life played out confirming the tenants that he set out in his hierarchy of needs and demonstrating the progression of Maslow’s intellect, increase of self-esteem and ultimately his self-actualization evidenced by his accomplishments in this field of study and practice. Reid-Cunningham (2008) reports “in contrast to his high self-esteem in adulthood, Maslow experienced extremely low self-esteem as a child and adolescent.” In fact, it was observed by Maslow (1924) that “a description of the possible reactions to the loss of self-esteem could be expanded almost infinitely because of the breadth of responses that feelings of worthlessness, inadequacy, and inferiority produce. Threats and damage to self-esteem may be considered threats to self actualization because thwarting basic needs hinders the prepotency of higher-level goals.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008)
Reid-Cunningham writes that Maslow “exemplifies the process of self-actualization: his satisfaction of the basic needs opened up the desire to achieve his highest potential, which he pursued relentlessly until his death in 1970. Self-actualization needs occupy the position of the highest relative prepotency in Maslow’s model, and they include cognitive, aesthetic, and potential fulfilling motivations for behavior.” (2008) Peak experiences were very interesting to Maslow and he associated these with “extremely good inner health and self-actualizing tendencies.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008) Peak experiences were described by Maslow through use of “20 common features, including temporary disorientation, feelings of wonder and awe, great happiness and a ‘complete momentary loss of fear and defense before the grandeur of the universe.” (Reid-Cunningham, 2008) Peak experiences could, according to Maslow “leave profound and transformative effects in their wake.”
It is stated in the work of Tomasulo (2001) that Maslow’s theory “may have had earlier roots in the ‘powerhouse of the Universe’ and Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is compared to the Seven Chakras as shown in the following table labeled Figure 2 in this study.
Maslow’s research methodology has been on the receiving end of a great deal of criticism and specifically due to the small sample size, lack of empirical methods and the use of vague terms (i.e. peak experiences). Maslow’s hierarchy is reported to be “among other things a taxonomy or classification of human needs. Taxonomy per se is more logical than an empirical device.” (Dick, 2001) The result is that is “makes more sense to talk about its logical consistency than it does to test it empirically.” (Dick, 2001) It is stated to be more appropriate to make use of conceptual testing means when testing taxonomy effectiveness and specifically stated is “A successful taxonomy is one which successfully encompasses the classes of events which it addresses. Its classes have minimal conceptual overlap.” (Dick, 2001) The more comprehensive in nature the taxonomy in combination with the less categorical overlap the more sound the taxonomy is likely to be. (Dick, 2001, paraphrased)
Summary and Conclusion
This work has reviewed the Hierarchy of Maslow and his theory relating to human needs and self-actualization. As well, the ontological, axiological and epistemological assumptions of Maslow’s theory have been examined as well as the contributions of Maslow to the field of psychology and the limitations of the research methodology utilized by Maslow. Maslow deeply and progressed psychology’s understanding of human behavior and self-actualization.
References
Bob Dick (2001) Maslow revis(it)ed: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs examined and reformulated. A discussion paper. Retrieved from: http://uqconnect.net/~zzbdick/dlitt/DLitt_P02masrev.pdf
Huitt, W. (2007). Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Educational Psychology Interactive. Valdosta, GA: Valdosta State University. Retrieved [date] from, http://www.edpsycinteractive.org/topics/regsys/maslow.html
Humanism (2011) Learning-Theories. Retrieved from: http://www.learning-theories.com/humanism.html
Reid-Cunningham, Allison Ruby (2008) Maslow’s Theory of Motivation and Hierarchy of Human Needs: A Critical Analysis. 3 Dec 2008. Human Needs. Scribd. Retrieved from: http://www.scribd.com/doc/8703989/Maslows-Hierarchy-of-Needs-A-Critical-Analysis
Tomasulo, Daniel (2011) Maslow Revisited: The Hierarchy of Chakras. Psych Central. World of Psychology. 2001. Retrieved from: http://psychcentral.com/blog/archives/2011/02/06/maslow-revisited-the-hierarchy-of-chakras/

Stuck with your Term Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Tags:

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

