Political Events and Their Impact on the Air Transport Industry, Essay Example
Part 1
Macro environmental factors are the external factors that affect the management of a particular industry. Understanding these factors is vital in analysis for the decision making of a particular industry. They belong outside the organization and have an impact on the strategies that will be developed by the management during decision making to satisfy customer needs. In this case, the industry of discussion is the airline industry. The outside factors, categorized as macro, are political and economic.
Macro Environmental Factors
Political Factors
The changes or the norms of a large political environment contribute to the type of strategy developed by a particular industry. For a multinational industry, political factors have a significant impact because different governments portray varied political influence. Examples of political factors include government policies and regulations, political stability of a particular country, activities of corruption, taxation rules, labor laws, trade governance, and whether the political system of a specific place is closed or rigid.
Economic Factors
The indicators of a striving economy are economic factors. These factors often change from time to time. They include the economy’s growth, the variation in exchange rates and interest rates, the value of income of a given population, and employment.
Analysis Using The STEEPLE Framework
Macro Environment of Interest
For British Airways, the political factors being considered macro-environmental factors will be a particular region’s political stability.
Ongoing and Emerging Changes
Political rivalry is heating up in different countries, leading to changes in the leadership systems, constitutional reviews, amendment of trade laws, and increased taxation on foreign commodities (Airportprofiles, 2019). There are civil wars in different countries; thus, trading in these regions is difficult due to insecurity.
Trends and Patterns
Political instability is mainly caused by the disagreement between the opposition and the government. These countries are not welcoming foreign trade at the moment and have limited accessibility. There is increased demand but no supply.
Future Direction of Environmental Changes
Prolonged instability may lead to a shift in the market regions due to insecurity to favor trade, constant reforms in the constitution will affect general policies, and the industry will have a hard time adopting the continuous changes.
Implications
Clashes in different markets cannot support trade; hence there is limited profit from these regions. If this continues, the business may collapse due to dependence on the areas for maximum profit. The strategies should be changing the trading regions and finding new markets. The charges for flights are also likely to hike.
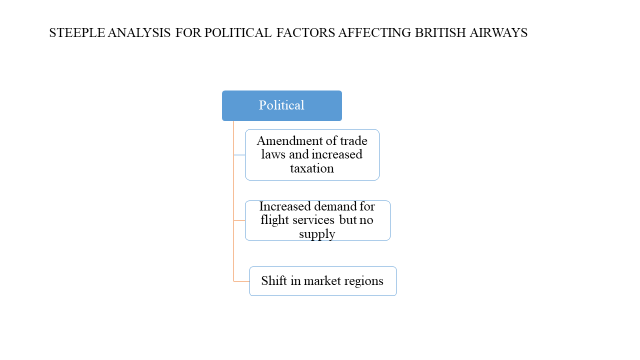
Figure 1: STEEPLE analysis for macro-environmental factors affecting British Airways
Discussion
The above image represents the STEEPLE analysis for the macro-environment factor affecting British Airways. It is a political factor with ongoing and emerging changes as an amendment of trade laws and increased taxation. This is because the political instability in certain regions has led to several changes in governance. The consequence of these changes is increased demand for flight services, but the company cannot access those regions.In the future, the company will have to find new market regions to maintain its profitability.
Part 2
Airline Industry
The airline industry provides a wide range of services and products to its consumers. Among them include passenger flights, cargo transportation to and from different parts of the world, transportation of jet fuel, fleet and asset utilization, and airline alliances (Revfine, 2020). The competition of the airline industry is both national and global. This is because of the emergence of several airline services in different countries and different regions as well. For example, the British Airline in the UK faces competition from other airlines in the UK that charge lower prices for passenger flights and cargo, such as Ryanair and EasyJet. Globally, British Airlines is facing competition from other airlines such as Air France and Emirates. The airline industry has evolved over time, mostly due to market fluctuation. Several companies are lowering prices, while the products and services in the industry are constantly similar. There are shortlisted options for new capacities in the UK that include building major runways while maximizing the possibility of new players entering the market.
The air transport has 162 firms, ROE 15.32%, ROCE 6.78%, ROS 9.34%, AUR 0.72
Numbers equivalent of firms = 1/H index
162= 1/H index
162 H index = 1
H index = 1÷ 162
H index = 0.0062
The airline industry exhibits perfect competition due to a large number of firms within. The range of H index is 0.0062, which is less than 2 with good information flow, lack of entry or exit barriers, and it is unlikely for product differentiation. The concentration level calculated by the United States Department of Justice also shows that unconcentrated levels have a H index of less than 0.15. The European Commission applies the H index in mergers such that when the post-merger concentration H index is below 0.1, then the industry is not obliged to further checks.
In perfect competition, an industry with several firms provides a uniform variety of products and services to the consumers. The prices, products, and competitors in the market are usually present at any time. It also permits other firms to enter the industry because the system is not so rigid with complexity. However, a company within the industry may not attain the maxim profit to survive. A large number of firms in this industry may lead to price wars since the competitors will consequently reduce their prices to cover their costs. The continuous decrease in price leads to less profit, making some companies exit the industry. In this case, the airline industry includes several airline companies whose customers are aware of their commodities.
Most of the companies have reduced the charges for cargo and passenger flights. Besides, the customers are also free to choose which company suits them best. In the industry life cycle, the first stage is the introduction stage. This is characterized by very few competitors and a few firms. The industry then begins to attract more firms and mergers. The competitors exit the industry, and the profit here is maximum. This marks the growth phase, which is the second stage. The third stage is the maturity stage, whereby the weakest competitors tend to leave while the existing firms fight for market shares. The last phase is the decline phase, where too many exist are observed. The airline industry may have such a life cycle due to its competitive nature.
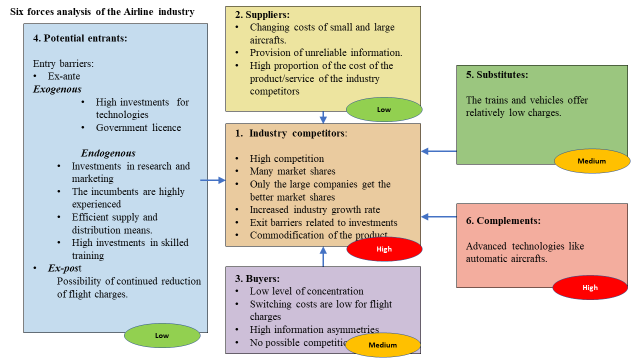
Figure 2: Six forces analysis for competition
Discussion
From the six forces analysis, the highest forces are from the complements and the competitors. Advanced technologies and competitors’ advantages are likely to pose a competitive threat for British Airways because the market shares are distributed to large companies, and there is an increased growth rate for several companies. Advanced technologies from other companies within the industry make them have increased efficiency for customer travel and less manual work during piloting. Buyers and substitutes are medium competition forces because air transport is the fastest means of transport, covering long distances. Also, there is low competition in buying market shares. The lowest forces are potential entries and suppliers. This is because they are similar in all companies within the industry.
Competition
The airline industry is characterized by hyper-competition in which each company makes fast moves to gain a competitive advantage over others. The customers of airline industries are always expecting more and comparing the products and services. For example, in the UK, one may choose whether to board British airways or Ryanair by comparing the prices. The industry is also associated with high technology, computer devices, and other electronics provided to the customers, and radar makes this industry very competitive. There are also limited barriers to access the industries in different geographical regions. For example, the Emirates that initially belongs to the Middle East has its services in the United States and Africa, offering similar services to those it provides in the Middle East.
The financial resources of these airline industries are big and have considerable players in it. The competition in these industries is sustained by the large corporations and allies with numerous ways of accessing resources to sustain competition in times of price war, thus preventing the industry from collapsing. A hyper-competition challenges oligopolistic competition because the firms in a hypercompetitive target vast markets and incorporate the use of high technology at the same time. The airline industry can also be classified as a “lean and hungry industry” based on its entry barriers. Entering this industry is not difficult, but the incumbents tend to push out the new firms so as to retain their markets and reduce competition.
The exit barriers prevent the competitors from leaving the industry. For example, the airline industry has many companies that have investments and assets. Among the assets are the various airplanes that belong to the companies. The emotional attachment also serves as a good barrier for the exit. A company that has been serving for an extended period in the industry may not easily leave the industry. For example, British Airways started serving customers in 1974 and covers 183 destinations. Legal factors also limit the exit of the companies. For example, when the government is investigating the malpractice of a given airline company, it is recommended that the company operations proceed unless otherwise.
Part 3
Resources and Capabilities
The strategies adopted by a given company are crucial in facilitating its competitive advantage. The company may invest its resources to enhance service delivery speed and sustain production in the competitive market. This makes the organization reliable and capable of retaining customers compared to others. The airline industry has tangible and intangible resources. Capabilities include standard operating procedures and routines. Substantial resources include land, buildings, capital, equipment, and supplies (Mahoney, J. 2016, 7). Intangible resources include copyright, trademark, trade secrets, culture, knowledge, brand equity, patents, and reputation. An organization’s capital is determined by the amount it generates for income and whether there are borrowing tendencies.
The size and location determine other tangible assets. For example, an airline industry with several airplanes as its resources must look at the passenger or cargo capacity and the distribution of such airplanes in different parts of the world. The intangible resources must comply with the technology reputation of the industry. For example, patenting a business is a legal issue and makes the business brand authentic and original without copying or losing the business name. A good brand also gives the industry a good reputation for producing quality brands without copyright issues. In human resources, employee training is essential. This increases competency among workers through the acquisition of adequate skills from the training process. Employee training increases the productivity of the organization.
The indicators of a reputation are brand equity and the price of a given product. The value of the tangible and intangible resources is used to determine a particular industry’s competitive advantage. For example, if the tangible resources are valued to be $1 billion, and the intangible resources are valued to be $10 billion, then the competitive advantage is likely to come from the intangible resources. Resources heterogeneity shows the differences in the resources of companies within the industry. For example, Southwest Airlines has high employee productivity and informal organization whereby the pilots assist in loading cargo. The company also has resource immobility in which the resources are sticky and do not move quickly. The advantage of this immobility has enabled Southwest Airlines to have superior performance over the years and protect the model, which cannot be replicated by the competitors.
Other resources that can be used by the airline industry include the production of new models using technology, opening a facility like a hotel to support the historical models of the Airline and the heritage, starting up a museum for exhibition (Bolognese, 2018), and collections of the airline models and facilitating sporting activities. The VRIO framework is used to assess the airline industry’s resources and capabilities; in this case, British Airways.
The Capabilities of British Airways
- It wins flight simulators.
- It provides a training ground for its employees in BA training school.
- Takes passengers to different routes
- Provides safety training for the cabin
- The flight attendants can attend to 12 customers, and 64 passengers can travel in the BA subsidiary.
Resources of British Airways
- Capital: the company owns more than 245 aircraft, traveling to take passengers to more than 550 airline routes and destinations. This makes it more competitive over EasyJet.
- Human Capital: these are valuable assets. The employees have their own knowledge and skills that they use to run the company (British Airways, 2016).
- Financial Resources: these include various investments in codeshares, subsidiaries, and franchise associates. They have a partnership with American Airlines.
- Technologies: the company has a database that includes the details of all customers worldwide. This enables it to link with all its customers globally.
- Reputation: The British Airline is known for its long survival in the airline industry. This builds its reputation in the market as a good brand.
Appraising The Resources and Capabilities Using The VRIO Framework
Appraising the Capabilities
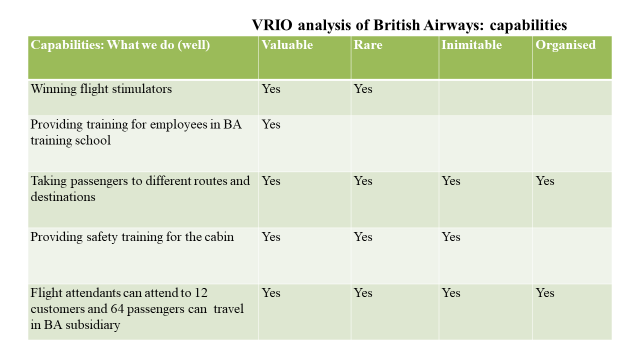
Figure 3: Appraising the capabilities of British Airways
Discussion
Capabilities include the activities which the company does best to satisfy the needs of its customers. The strongest capability of British Airways is taking passengers to different routes. This enables the company to travel while taking their customers to various destinations. This makes the British Airline highly competitive and gives it a branding as well. Each flight attendant’s ability to attend to 12 customers and the accommodation of 64 passengers in the BA subsidiary is also another high capability for competitive advantage. Another strong capability is the provision of safety training for the cabin. The least of the abilities is providing training for employees (British Airline, 2020). This is the lowest because several airlines do the same. After all, employee training is a requirement.
Appraising the Resources
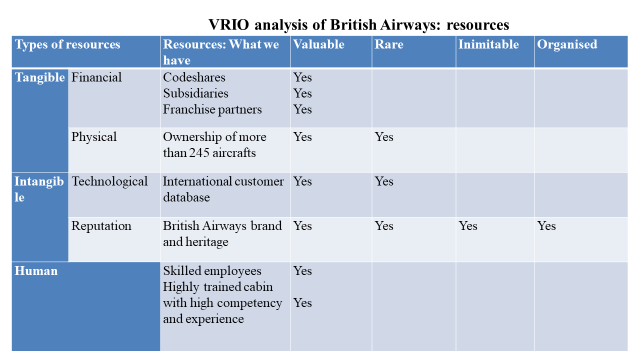
Figure 4: Appraising the resources of British Airways
Discussion
The resources include tangible, intangible, and human resources. From the resources, the most valuable resource is the brand and its heritage. This distinguishes British Airways from any other brand. The company has a good reputation in the market due to its longevity in providing its services to customers for an extended period and traveling to different destinations worldwide. The reputation as an intangible resource can be used to determine the competitive advantage in this case. The least of the resources are human resources. This does not qualify as an excellent factor to foster competitive advantage because several airlines also have higher knowledgeable and highly trained personnel. The financial and tangible resources for this company do not exhibit an excellent competitive advantage. For instance, several airline companies have aircraft and various investments.
The financial resources are also a characteristic of several airline companies. This is the backbone of their survival in the competitive market. The Airline industry is inflated with several companies that source their finances from local and international corporations, shares, and subsidiaries. For example, British Airways has a partnership with American Airways (British Airways, 2016). This enables the smooth operation of both airlines in both Europe and the United States. Technology is also a vital component of intangible resources. To fit in the modern world, the company needs to use a comprehensive means of communicating with its customers globally. British Airways has a database that manages the customers as one. Through this, it is possible to monitor the customers’ activities and maintain good customer management relationships.
Developing Capabilities
The airline industry is a very competitive industry that offers similar products and services to its customers. However, modifications in the stiff competition are experienced from time to time. Therefore, it is meaningful for the industry to continually develop capabilities to maintain its market position and protect its brand. Capabilities are expected to change naturally with a gradual pattern that can be termed a capability life cycle. The life cycle helps in understanding the developmental stages. In an organization, the capabilities may rise exponentially then halt at the maturity stage. This is because the capabilities cannot grow further until other developmental strategies are put in place. For example, when the industry begins to operate in the airline industry, there is a range of prices for different flights. As the industry continues to transport people and goods, several companies lower their prices such that the amount of profit obtained is minimal. It then reaches a stage where no additional capabilities in reducing the costs to attract customers can attract more customers, and the companies are forced to employ new strategies.
Capability Life Cycle Branches
The capabilities may not necessarily stop at the maturity stage. The factors that influence the trajectory pattern of the capabilities that determine the industry’s fate depend on the management of that particular industry. The capability life cycle may have several branches, including:
Retirement: this inhibits or benefits the future capabilities of the industry. For example, the early retirement of employees due to health status may lead to reduced employee productivity.
Retrenchment: this leads to the removal of certain capabilities for a long period. For example, the Airline industry’s use required highly skilled Information Technologists, which led to the retrenchment of manual operators of typewriter machines.
Replication: this involves the transfer of capabilities to other regions. For example, if the Middle East bans British Airways from the region, British Airways may be operating mostly in Africa, where it has not been banned.
The company may also renew, redeploy recombine capabilities to enhance the capabilities’ trajectory to maintain a competitive position in the industry.
Part 4
The skills I have learned in this course are the internal and external analysis of a particular industry. In the internal analysis, the resources and capabilities of the industry contribute to its competitive advantage. The resources include the tangibles and the intangibles, while the capabilities include the activities involved during service delivery. The analysis of these resources can be done using VRIO analysis to determine which of the capabilities or resources best suits a given company’s competitive advantage component in an industry. For example, when looking at a particular capability, like the airline industry’s ability to travel to several routes, it is compared to other airline services based on the categories. When traveling to other destinations is of value, organized, rare, and cannot be imitated by other companies, this capability is a major strength for the competitive advantage. Internal analytical skills are essential because they help understand the necessity of competition in the industry and determine which companies have the highest potential to survive in an industry.
External analytical skills are essential in analyzing the macro-environmental factors that influence a particular company. When making the analysis, one of the approaches that can be used is the STEEPLE approach, which analyses the external environmental factor based on the ongoing changes, the trends and the patterns involved, the future changes, and the implications. For example, when analyzing the political factors likely to influence an organization like a fuel industry, the political environment changes may be constitutional amendments affecting trade laws. The trend can be increased prices of fuel due to limited supply. The future changes may include higher fuel or inflation costs in the fuel industry to meet the high demands in the unstable regions, and the impact may be increased competition.
References
Airportprofiles, 2019. Political Events and Their Impact On the Air Transport Industry in 2019. https://www.airportprofiles.com/blog/political-events-and-their-impact-on-the-air-transport-industry-in-2019
Bolognese, S., 2018. Automobili Lamborghini Achieves Another Record Year: 3815Cars Delivered to Customers in 2017. Volkswagen Aktiengesellschafthttps://www.volkswagenag.com/en/news/2018/01/Lamborghini_sales_17.html#
British Airways, 2016. Annual Report and Account Year ended 31 December 2016 [Online]http://phx.corporate-ir.net/External.File?item=UGFyZW50SUQ9NjYzMTQyfENoaWxkSUQ9MzcwNDI0fFR5cGU9MQ==&t=1.
British Airways, 2019. British Airways Factsheet [Online]https://mediacentre.britishairways.com/factsheets/details/86/Factsheets-3/33
British Airways, 2020. About BA https://mediacentre.britishairways.com/
Mahoney, J., 2016. Internal Analysis: Resources, Capabilities, and Activities. Southwest Airlines. University of Illinois. pp 7-34 https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.business.illinois.edu/josephm/BADM544_Spring%25202016/PPT/BA544Chap004.ppt&ved=2ahUKEwjzue6ow-3tAhWMlxQKHd6SDPAQFjABegQICxAB&usg=AOvVaw1rwaufXMomN_9saswrCrnG
Revfine, 2020. Airline Industry: All You Need to Know About the Airline Sector.https://www.revfine.com/airline-industry/

Time is precious
don’t waste it!

Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee






