 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Economics Commentary on Macroeconomics, Essay Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Introduction
The economic crisis in the Eurozone raised the specter of long-term economic stagnation and even the collapse of the currency. Many explanations have been offered for the economic crisis in Europe: the profligate policies of the peripheral states that led other more fiscally responsible states to bail them out; an inadequate supervision structure of the European governance body gave France and Germany an early pass that may have contributed to the moral hazard of the other states. Another explanation, however, seldom heard at the beginning of the economic crisis is also gaining currency: The European economic crisis is a function of German economic policy. This argument, at least at first glance, seems highly counterintuitive: Germany is the ideal picture of fiscal rectitude in the European Union- the country had the highest economic growth rate of all European countries after the crisis; the country was one of the only in the continent to run a fiscal and current account surplus; finally, the reason for Germany’s growth was the envy of the European Union: a sleek, industrial exporting machine that exported goods. \
There is a lot of truth to this purported narrative. Germany, as an economic model, has a lot to recommend to it, including a robust “apprenticeship” training system and a sound educational system. There is, however, a problem with this basic narrative: As part of the currency union, Germany is essentially connected to all other countries in the Eurozone- particularly through trade. Some countries will be more competitive and run a trade surplus; some countries will be less competitive and run a trade deficit.
Germany, as one of the more competitive countries in the Eurozone, arguably had the most room to expand demand and help boost other countries’ economy both before and after the economic downturn. Germany, however, essentially maintained a policy of wage austerity that suppressed domestic consumption, limited imports, and created substantive competitive advantage for the German economy.
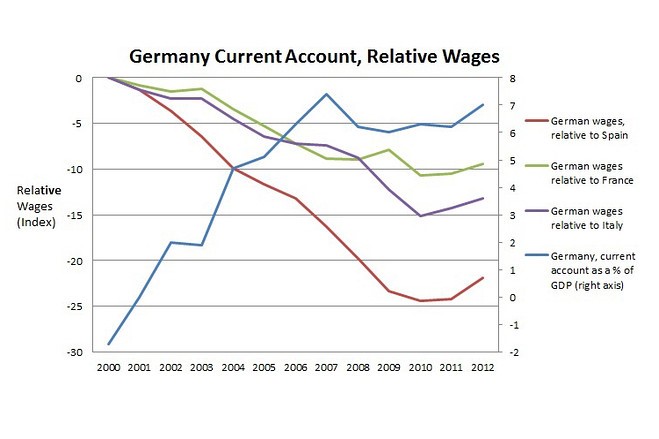
Table 1: Germany Current Account- Relative Wages
There are many ways to look at this potential issue. One is to look at the German economic growth identity in isolation- Germany with a low consumption rate and limited government support was trying to drive growth through exports. Another is to look at the connection with neighbors in a currency zone in which although one country can run a deficit or surplus, the trade zone in total must run neither. This is the logic behind table 1 which shows how Germany used wage policy as a means to run a current account surplus, even in spite of countries in the same region running a current account deficit. Indeed, looking at the graph shows that German wages versus other “deficit” countries in the Eurozone was much lower: German wages were roughly 75% of the wages in Spain; German wages were roughly 85% of the wages in Italy; German wages were roughly 90% of the wages in France. These wages were arguably the source of Germany’s competitive advantage over the long-run: that is, rather than helping other countries through promoting internal demand, the German government adopted an austere policy of wage control.
The policy of wage control had two main results: 1) the wage controls kept Germany’s goods at a lower price than others in the Eurozone- this meant that goods were more competitive vis-à-vis potential countries in the Eurozone; 2) the wage controls limited internal demand in the country for other countries goods’- and this, perhaps, is the biggest indictment of Germany’s policy: it was unable to help build domestic demand for imports that could have helped other countries’ economic growth during a time period of economic downturn.
Overall, it is not likely correct to say: Germany’s economic policy, particularly its wage policy, was a “cause” of the economic downturn in Europe. Countries that ran a fiscal deficit and did not undertake robust structural reform should not be left off the hook; in the end, however, as part of an economic union the countries of Europe’s fate were ultimately intertwined. Germany’s wage policy may have saved it the need to import more goods; however, the country was still forced to shell out for bailing out countries in the Eurozone. Thus, Germany’s story should be seen as a complementary story to the existing one- not one to replace it.
Works Sited
Foroohar, R. How Germany Can Save the Euro. Available at:
http://content.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,2149122,00.html#ixzz2lDjmaRm8

Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Tags:

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

