 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Impact of Children Raised Outside of Intact Marriages on Children’s Risk for Criminal and Delinquent Behaviors, Research Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Research Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Abstract
This research papers looks at the various studies and research done to analyze the relation of juvenile delinquency due the failures of intact marriages. Marriage is viewed as strong institution and the lack of has shown to contribute to the criminal behavior of children from the broken homes. There are many factors that can contribute to juvenile delinquency. Of the most popular factor has been the role the family plays in juvenile behavior. It is obvious that a child’s family can have a significant impact on the child’s level of delinquency. The goal of this paper is to tie the two interdisciplinary fields of Sociology and Psychology in order to give support to the main ideas that children raised outside of intact marriages has an increased risk for crime and delinquency. This research paper uses the research methods of literary studies, articles, qualitative, and quantitative data to provide relevant analysis. This research will provide useful and valuable information that will contribute to the growing study on familial and juvenile behavior.
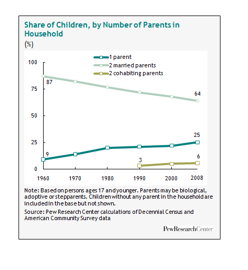
In Pew Research Social & Demographic Trends shows that Changes in marital patterns have had a major impact on the lives of children in this country. According to that research, marriage is no longer considered a prerequisite for parenthood. Over the past 50 years, the share of children born to unmarried mothers has risen dramatically—increasing eightfold from 5% in 1960 to 41% in 2008.This trend has contributed to the decrease in the share of children under age 18 living with two married parents – to 64% in 2008 from 87% in 1960.4
There are distinctive socio-economic, generational and racial patterns in the trends away from marriage and toward single parenthood and other emerging family forms.
“Marriage rates are now more strongly linked to education than they have been in the past” (The decline of marriage and rise of new family Released November 18, 2010). With college graduates (64%) much more likely to be married than those who have never attended college (48%).
In the current research on the effects of divorce on children by Constance Ahrons, Ph.D. he The divorced couples he first interviewed in 1979 had over two hundred children, now ranging in age from twenty-one to forty-seven, and finding them two decades later proved a challenge Ahrons said.
These grown-up children of divorce knew about my original interviews with their parents and stepparents and wanted to be heard about how they felt about their parents’ divorces, how it impacted their lives and how they felt about living in the new families created by divorce.
“What I heard from them is that not only did they survive their parents’ divorces but the vast majority thrived, despite the stress and upheaval that are common in the early stages of parental divorce. The majority told us that they felt that their families were normal and their relationships with each of their parents had actually improved. As adults—most in intimate relationships themselves, some married, others were cohabiting, still others looking for mates—most felt their parents’ divorce was a good decision and that both they and their parents were better off because of it”. (http://www.responsibledivorce.com/) others spoke of warm relationships with their stepparents and shared happy stories of joyful celebrations that included both their biological and stepparents.
Nevertheless, In the Ezinearticles.com by Peter West the crime rates among children from single parents has decreased. Peter said that a case in point would be the fact that most high profile crimes, like school shootings, involve kids from two parent households. “While the case can be made that many crimes are committed by children from single homes, studies indicate that there has been a decline in youth crime even though single parenthood still exists” (Ezine articles). FBI crime statistics even indicate that violent juvenile crime stats are at their lowest point in twenty years. It cannot be ignored that major crime rates among children occur across all demographics.This is especially true when it comes to school shooters, who tend to come from two parent homes.
Overall, in the family facts.org article, adolescents living in intact families are less likely to engage in delinquency than their peers living in non-intact families. Compared to peers in intact families, adolescents in single-parent families and stepfamilies were more likely to engage in delinquency. This relationship appeared to be operating through differences in family processes—parental involvement, supervision, monitoring, and parent child closeness—between intact and non-intact families.1
In today’s society, marriage is not as popular as it once was. Couples today are waiting for marriage, and getting married at older ages than 30 years ago. Marriage is significant social institution that is in a state of fragility. Parents play a vital role in the conditioning, learning, and grooming of their children’s behavior, morals, and personality. The purpose of this research is to analyze if children raised outside of intact marriages has an increased risk for crime and delinquency. Presented through a sociology and psychology perspective in order to gain a better understanding of the topic. Growing up outside an intact marriage increases the likelihood that children will themselves divorce, become unwed parents, or begin a life of criminal behavior. Along with various studies and literary research this research will try to back the thesis while helping to further the topic for future research.
Functionalism articulates the notion that people cultivate a foundation of paradigms from their first years of life. Depending on their social, historical and environmental context they adopt various core beliefs. These remain with them throughout their lives as their primary belief system. These core beliefs are re-enforced as people adopt habitual behavioral responses, they continue the same idiosyncrasies unless they cease to prove effective. The knowledge that people gained is limited only to that of which is similar to one’s subjective reality. This is a factor in the realm of the society where rules are bred from structure; they provide the staple to achieve the greater good. “Parenting practices during childhood and early adolescence are often cited as critical factors in shaping social and behavioral outcomes in children.(Schroder, Giordano, Cernkovich, 2010) Parents take an active role from birth in influencing behaviors, the differences of right and wrong, and what not to do. At an early age children see both parental figures in the house that both give discipline, direction, and influence social and personal development. At ages when children are readily able to understand and process images they picture of their parent’s on the outside of an intact it is viewed as a negative connotation. In the matter of parent’s divorcing or the choice to have children out of wedlock, the father is usually the one to be absents. “
In McCord’s, research she pinpoints the much research done to link the cause of juvenile delinquency, and many studies pointed that most juveniles came from a broken home. Studies have been conducted since the 1920’s drawing a relationship between broken homes and juveniles. McCord details as the years continued more studies taken into account the racial and socioeconomic backgrounds of juveniles and the absences of usually the male figure. The nuclear family being a two parent household is essential in showing equal roles of the parents in exerting control, while dividing the role of enforcer, disciplinarian, and teacher.
In cases where the one of the paternal parents remarry, a stepparent is present. In Martin Daly and Margo Wilson study they explore the roles of abuse and neglect in households were one of the natural parents is not present. “Preschoolers living with one natural and one stepparent were 40 times more likely to become child abuse cases than were like-aged children living with two natural parents.”(Daly, Wilson, 1985) However this information is at best outdated and requires a bigger sample and updated information. The main points from the study however suggest that abuse and most importantly neglect when the nuclear family is disrupted can lead to problems in school aged children. The effects of abuse and neglect in children stem from the possibility of the parents being abused victims themselves, alcohol present, coming from a non-nuclear family, or pure neglect. Differences are seen in McCord’s study between children who are loved or neglected and abused. “Those children reared in loving homes were most likely to have self-confident mothers and least likely to have aggressive parents.” “Apparently the antisocial impact from parental abuse, neglect and rejection is largely reflected in juvenile delinquency.” (McCord, 1983) As the functionalist theory asserts the shared values and common symbols among the familial ties are what propels an individual or society. “Paternal alcoholism and crime as well as parental aggressiveness appear to increase the probability that child abuse and neglect will be damaging to future development.” (McCord, 1983)
Cognitive behavioral theory takes into account the childhood origins of distorted thinking. It assumes that a reorganization of one’s self-statements will result in a corresponding reorganization of one’s behavior. When parents’ divorce it can leave a lasting impact on the children left to deal with the split. In some instances, behavioral changes are seen as well as changes in academia, and social interactions with others. “That is out-of-wedlock births increase within a community, the rate of high school graduation decreases.”(Mackey, Immerman, 2000) In terms of divorce, “contact between non-custodial fathers and their children is generally low and is consistently lessened over time.” (Mackey, Immerman, 2000) According to family systems theory, when the married couple has conflict and cannot solve it in a constructive way, they are likely to involve their children in the conflict to release some anxiety and tension between them (Wang & Crane, 2001). Children behaviors are influenced by the lack of nurture or love given from their parents, when one parent is absent it increases the risks of abuse and neglect in the household. As children age, the paternal bonds will loosen or strengthen depending on the foundation established as children. Growing up outside an intact marriage increases the likelihood that children will themselves divorce or become unwed parents. (Wingfield, n.d)
The overall view from a sociology perspective is that the “costs of not maintaining on-going nuclear families include threats to the reproductive health of the community, increased levels of violent behavior, increased levels of infant morbidity and mortality, and increased levels of high school drop-outs. All of these dynamics–either directly or indirectly–tend to decrease the overall public health within a community.”(Mackey, Immerman, 2000) The absence of the father in a nuclear family is not of the greater good. However the cognitive behavioral theory suggests the behavioral changes influenced by a change in the nuclear family will breed changes with a lasting impact. This impact will either be see in education, social situations, or later on in life when they begin a family. What is best to note is that in both perspectives and the literary research, children raised outside the intact of marriage do have a higher chance crime, abuse, but, not in all cases. Much more research needs to be done for further analysis of juvenile behavior and the nuclear family. The gaps in current research conducted are mostly out of date for cases where abuse is present in step-parent too children family dynamics. The nuclear family is declining in America, however, the number of co-habitation households have increased and are more common. Where the father is still present, but the parents are not married has not been studied to the extent of married and divorced couples. Other research studies should be conducted on children of non-traditional households such as gay, lesbian, and transgendered. Do these nontraditional nuclear families show the same statistics as heterosexual families? Methods to test out these theories are generally the same as previous research, surveys, in-person, interviews, school records, criminal records of juveniles, and observations of different family dynamics.
Bibliography
Daly. M & Wilson M.I (1985). Child abuse and other risks of not living with both parents Ethology and Sociobiology 6: 197-210
Mackey, Wade C. PhD & Ronald S. Immerman MD (2007). Fatherlessness by Divorce Contrasted to Fatherlessness by Non-Marital Births, Journal of Divorce & Remarriage, 47:1-2, 111-134
McCord J. (1982). A longitudinal View of the relationship between paternal absence and crime: Abnormal Offenders, Delinquency, and the Criminal Justice System 7 113-128.
R Agnew, T Breina J.P..Wright, F.T Cullen (2002). Strain, personality traits, and delinquency: Extending General Strain Theory Criminology 40 pp.43-72.
Umberson, D. (1992). Relationships between adult children and their parents: Psychological consequences for both generations. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 54, 664?674.
Wane, Crane (n.d) Depression in Children: Causes and Interventions. Retrieved from http://www.personalityresearch.org/papers/sokolova.html
William H. Jeynes PhD (1999): The effects of Children of Divorce Living with Neither Parent on the Academic Achievement of Those Children, Journal of Divorce & Remarriage, 30:3-4, 103-120
Sources
http://responsibledivorce.com/
http://ezinearticles.com/?Crime-Rates-Among-Children—Is-Single-Parenting-the- Cause?&id=3034904
http://familyfacts.org/briefs/26/marriage-and-family-as-deterrents-from-delinquency-violence-and-crime
Stephen Demuth and Susan L. Brown, “Family Structure, Family Processes, and adolescent Delinquency: The Significance of Parental Absence of Research in Crime and Delinquency 41, No. 1 (February 2004): 58-81

Stuck with your Research Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

