Mergers in Saudi Arabian Banging Sector, Essay Example
Abstract
Mergers have become a common phenomenon in Saudi Arabia. They involve two or more firms getting into a contract to unite their operations, assets, markets, or capital to form a new single firm operating as a single entity. Most of the mergers happening in Saudi Arabia in the recent past were motivated by various reasons. These include goals to expand into new markets, regain lost market share, wade off competition from other established players, or consolidate their assets, resources and capital to form a more competitive entity. A recent merger in Saudi Arabia approved by the Saudi General Authority for Competition (GAC) on January 27, 2021, was the merger between the Samba financial group and the National Commercial bank of Saudi Arabia, forming the Saudi National Bank. The two entities consolidated their assets into $239 billion, making the new entity the 3rd largest bank in the GCC in terms of the asset base. The merger was identified as part Vision’s 2030 strategy on financial growth geared towards establishing stable and profitable financial institutions within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia that would span significant economic growth throughout the region.
Introduction
A merger is described as the voluntary union of two businesses on broadly equal relations into one newly lawful entity (Abdelrahim, 2018). The companies that decide to merge are almost identical in size, clients, and operations measurement relationships. Therefore, due to such reason, the word merger equals occasionally becoming most used within most markets in Saudi Arabia (Al-Jarrah, Al-Abdulqader, & Hammoudeh, 2021). Mergers identified as most generally done to regain marketplace share, reducing costs of working, expansion into new territories, uniting common products, growing incomes, and increasing profits, all where one benefit the business’ stockholders (Martínez-García, Basco, & Gómez-Ansón, 2021). However, after a merger, new business shares become distributed to both original industries’ prevailing on key stockholders (Jones, Alderete, Kim, & Goran, 2019). As the biggest lender by assets, Saudi Arabia’s National Commercial Bank decided to merge with its competitor Samba Financial Group for $ 20 billion within the current largest merger in the banking industry. NCB would repay SAR28.55 ($7.60) for every Samba share, based on a report released last year, valuing it around SAR56.4 billion. For every share in Samba, NCB would create a new share worth 0.740. Generally, at the lowest point of 0.729 ratios, the financial banks set when all signed first framework contract in early June. The offer is considered at $3.5 for each cent in Samba, during the October 10 closing costs of SAR28.10 and around 23% high than level shares transacted at early talks measured within highly made concepts in public (Guo, Yang, & Wang, 2021).
The Key Concepts affecting the industry are considered high competition and lack of funds; the mergers have led to an alliance with a vengeance. Mergers and attainments are usually done to enlarge a corporation’s reach, increase into new sections, regain market share, and lessen business competitiveness. In trade business, mergers and attainments are key dealings on businesses’ key ownership, where most corporate administrations engage. The leading biggest banks control 69% of all properties and are projected to control 86% of bank assets in other years, largely via mergers (Al-Jarrah, Al-Abdulqader, & Hammoudeh, 2021). The Saudi alliance likewise agrees with a longer-awaited tendency of mergers and acquisitions in the banking sectorwithin Europe, whereby lenders analyze constraints, where have started taking over competing firms (Martínez-García, Basco, & Gómez-Ansón, 2021). Merging two leading national banks considered Crown Leader Mohammed’s main constituent in “Vision 2030” enterprise to spread where Saudi economy focused on oil through generating local victors in businesses like finance. The Saudi’s kingdom’s self-governing prosperity fund, the Public Venture Fund, emphasized crown leader chairmanship (Jones, Alderete, Kim, & Goran, 2019).
Literature Review
Merger and Acquisition
The review purposes of understanding the key idea of merger and attainment in detail (Al-Jarrah, Al-Abdulqader, & Hammoudeh, 2021). The merger and acquisition would comprise theoretical contextual foundations of an earlier study on the key subject. Merger and Acquisitions would comprise data from different study paper, books, and study in understanding the meaning and application of research in banking sector being identified as key benefits built on subordinate Data (Martínez-García, Basco, & Gómez-Ansón, 2021). The section would comprise numerous features impacting merger and attainment decision, achievement and failure within a business (Jones, Alderete, Kim, Goran, 2019).
The focus would remain as key emphasis assessing the earlier findings on the study and understanding future study necessities. Currently, mergers and attainment were rising within the market in 2015. A 48% rise within mergers worldwide after the downfall from 2008/2009; over 95% of the contract had a high value than $ 4 billion (Azman-Saini, & Law, 2020). The increase in union deals remained more than 6% in the worldwide marketplace, performing well with a 60% increase in merger and attainments (Martínez-García, Basco, & Gómez-Ansón, 2021). The 2014 overall value of mergers within the marketplace is considered as about US$870. 1billion.The study’s purposes of recognizing the necessity for merger and attainment within the banking sector were the specific emphasis on the Saudi Arabian Market’s effect on key marketing strategy (Al-Jarrah, Al-Abdulqader, & Hammoudeh, 2021).
The study requires to assess the banking segment situation in Saudi Arabian Marketplace and earlier trends of merger and attainment within the banking business, its Accomplishment. Bloomberg News initially stated the merger deliberations (Jones, Alderete, Kim, & Goran, 2019). The new financial bank would have entire properties for over $220 billion, making the Gulf section’s third-bigger lender (Azman-Saini, & Law, 2020). The unit’s $48 billion marketplace capitalization almost matches Qatar Nationwide Financial Bank, where is also mentioned within the largest lender in the middle east with around $269 billion of assets. On the other side, United States banks have vanished by a merger at a level of 1.80 for each working day between 1979 and current states (Martínez-García, Basco, & Gómez-Ansón, 2021). During the two known periods, around 8,250 unaided financial mergers and 1,159 aided mergers of distraught banks have happened. Generally, the ownership of approximately $2.6 trillion of banking properties has transformed via mergers, especially during an actual period with over half the United States (Al-Jarrah, Al-Abdulqader, & Hammoudeh, 2021).
Hypothesis
The financial health of any company can be determined by common indicators. These indicators include net income, the total assets, the total liabilities, the profits after tax, the company’s level of indebtedness, and the shareholders equity. All these indicators can be determined by measuring and analyzing the company’s ROE and ROA. Other indicators such as the Debt-to-Equity ratio (D/E) and the Deposit to Equit7y ratio will also be considered. As such, the following hypotheses have been postulated.
H1; that cash levels positive impacts the ROA of the merging firms
H2; that cash levels positive impact the ROE of the merging firms
H3; the merger and acquisition of the 2 firms in question will have a significant and positive impact on the bank’s financial performance.
Methodology
Research design
This research aims to determine the relationship between the dependent and independent variables before and after the merger and attainment to establish its effect (Khotbi, 2018). As such the research will be aimed at examining both banks profitability, growth, liquidity, leverage, working capital debt to equity ratio and deposits to equity ratios before and after the merger. The study will audit different mergers and acquisitions that have taken place in Saudi Arabia’s banking sector (Khotbi, 2018). Data from both firms will be examined from two years before the merger to the current situation. Data from other mergers in the baking sectors in other countries such as the United States, Eurozone and Asia will also be collected and analyzed, to determine whether the mergers had any effects on the financial performance of the companies and firms involved and whether those effects were positive or negative.
Qualitative methods of research will also be applied in this research. These include questionnaires, personal interviews and financial data analysis. The interview will target several individuals in Saudi Arabia’s banking industry (Al Qudaiby Basmah & MR Rahatullah Khan, 2014). High ranking officials from the Samba financial group and the National Commercial Bank of Saudi Arabia. would be identified, and face to face interviews scheduled with them. The interview will be conducted by the same person, or group of people to allow easy comparison of the answers provided by the respondents (Al Qudaiby Basmah & MR Rahatullah Khan, 2014). For the analysis of the data, data will be gathered from the internet and analyzed to give conclusive results.
Variables
A wide range of dependent and independent variables will be selected and used in this study. The independent variables will be the basic financial health indicators of a firm such as the level of liquidity and the net income. The dependent variables in this study will be the basic financial ratios that will be affected, as a direct result of changing the independent variables. These ratios include; the ROE, the ROA, the average dividents Per Share, EPS, the Profits after Tax, PAT, the Debt-to-Equity ratios, D/E and the Deposits to Equity ratios, DP/E.
Methods of data analysis.
The data collected from the interviews and the internet will be analyzed to spot any differences in the profitability before and after the merger. The data obtained from the interviews will also be interpreted. It is important to note that the interviews with the NCB and Samba’s top-ranking officers we conducted in strict confidentiality and the names and positions of those individuals interviewed will not be mentioned in this report. Only general findings from the analyzed interviews will be stated in the findings section of this report.
All the data obtained will be analyzed using a T-test to compare the average values of the profitability ratios before and after the mergers. Simple descriptive analysis such as mean, standard deviations, the maximum and minimums will be performed on the collected data. The correlation between the different data will also be calculated to enable the determination of regression. The data will be presented on graphs and tables.
Findings.
The analyzed data was compared so as determine whether there is any significant change between the data from pre-and post-merger. Data for each variable in question before the merger as compared to the data after the merger, to determine whether the merger had any positive change in the overall companies’ performance. Findings from the data analyzed indicated that the merged company’s ability to generate returns was impaired in the first few months due to new risks that resulted from the merger. These risks included delays in obtaining the required regulatory approvals and environmental and social issues from ongoing projects. The findings from the interview indicate that NCB and Samba financial group have both been involved in mergers before. Samba’s most significant acquisition was that of Cairo bank in the year 1999 (Al Qudaiby Basmah & MR Rahatullah Khan, 2014) NCB has been involved in four mergers previously, the most significant being the acquisition of a Turkish bank (Al Qudaiby Basmah & MR Rahatullah Khan, 2014). The interviews also revealed the strategic motivations of the both banks toward the merger (Al Qudaiby Basmah & MR Rahatullah Khan, 2014). These motivations can be summarized into three major categories; increasing the market share, moving into new geographical areas and creating new lines of business. Different ways of creating financial advantages were also discussed during the interviews.
The return on average capital was calculated from the collected data by dividing the net income by the average equity for both firms, before and after the merger (Kaplan, 2005). Findings show that the ROE for both banks grew to 9.7% from 9.5% (Park, 2020). findings show that after the merger, Samba group shareholders owned 32.6% of the total capital and NCB’s shareholders owned 67.4% of the capital. This, however, had little effects on the average return on capital gains by the shareholders from both sides. The combined capital, however, was greatly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 (Park, 2020). The pandemic has affected by combined banks operating results, liquid and financial condition. As a consequence, it would be impossible to draw any meaningful conclusions from return on capital data that was obtained from the combined banks, due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Table 1 shows the net changes in the basic financial indicators for NCB, before and after the merger.
While testing for the third hypothesis, the finding shows that the firms operating income and profitability were reduced during the first month of the merger as a result of the combined bank’s credit-related contingent liabilities and other financial commitments that lead to losses. The cost to income rations, however, remained constant at 32%. The overall income for both banks increased. Total operating income increased from 4.4 billion SARS to 4.9 billion,
Conclusion
From the data analyzed and evidence provided, it is clear that all three hypotheses were confirmed (Al Qudaiby Basmah & MR Rahmatullah Khan, 2014). The merger also has an overall positive impact on the performance of both banks and is validated by financial data before the merger that was compared to the data after the merger. The increased cash flows also have a net overall positive change in the return on capital and the return on equity financial ratios. The average earnings per share in the two banks increased 0.11%, (Press Release NCB and Samba Enter Binding Agreement Creating a New Saudi Banking Champion, n.d.) when compared to the earnings per share in the year preceding the merger. The net profits after tax also increased.
The findings were consistent with (Al-Jarrah, Al-Abdulqader, & Hammoudeh, 2021), findings, who found that that merger that Saudi Arabia’s marketing strategies are mostly geared toward mergers and attainments of companies and firms in us. The NCB bank and the Samba financial group created financial advantages for both banks by increasing the risk capacities of both banks, which resulted in reduced corporate risk. Both firms also experienced economies of scale (Khan, 2013). The economies of scale in the finances are realized by a reduction in the cost of issuing debts and a reduction in the costs of the transaction. The combined bank also enjoys increased market power and market share and reduced operational efficiencies.
The merger and attainment of the Samba financial group and NCB have not come without its challenges. The COVID-19 global pandemic is a major factor while studying the financial impacts of the merger on both bank’s financial performance. The combined bank has caused liability strain on its assets and as a consequence, its ability to generate returns was greatly impeded. To date, this merger is the largest and most significant in the history of banking.
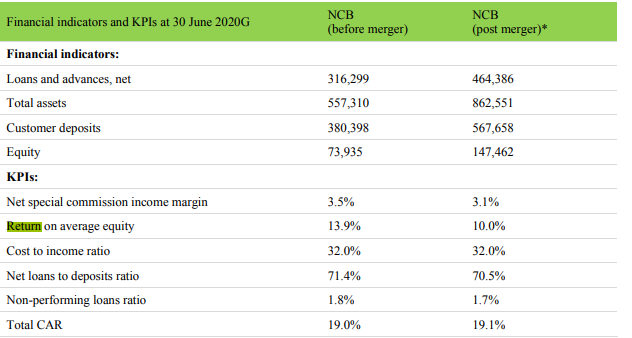
Table 1: basic financial indicators for NCB bank before and after the merger.
Source: https://www.alahli.com/en-us/Pages/RB-NCB-Home-New.aspx
?References
Al Qudaiby Basmah, & MR Rahatullah Khan. (2014). Financial synergy in mergers and acquisitions. Evidence from Saudi Arabia. ResearchGate; Insitututo Estudios Bursatiles. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275225228_Financial_synergy_in_mergers_and_acquisitions_Evidence_from_Saudi_Arabia
?Press Release NCB and Samba Enter Binding Agreement Creating a New Saudi Banking Champion. (n.d.). https://www.samba.com/en/system/designitems/pdf/NCBandSamba-en.pdf
?Qudaiby, B. A., & Khan, M. R. (2013). Financial Synergy in Mergers and Acquisitions in Saudi Arabia. Finance: Challenges of the Future, 15.
Kaplan, S. N., & Schoar, A. (2005). Private equity performance: Returns, persistence, and capital flows. The journal of finance, 60(4), 1791-1823.
PARK, Y. E., & JAVED, Y. (2020). Insights Discovery through Hidden Sentiment in Big Data: Evidence from Saudi Arabia’s Financial Sector. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business, 7(6), 457-464.
AlAhli NCB Home. (2019). Alahli.com. https://www.alahli.com/en-us/Pages/RB-NCB-Home-New.aspx

Time is precious
don’t waste it!

Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee






