 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Organizational Benefits to Enterprise Systems, Business Plan Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Business Plan
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Introduction
The foregoing essay examines Project Integration Management (PIM) from an enterprise system (ES) perspective. ES are “large-scale, real-time, integrated application-software packages that use the computational, data storage, and data transmission power of modern information technology to support processes, information flows, reporting, and business analytics within and between complex organizations.” [1] In Seddon and Calvert’s hypothetical research study of ES, testing of ES systems implementation in organizations was analyzed based on short and long-term effects: 1) Short-term factors indicate that once a system is live, benefits flow from those improvements after functional fit and override of organizational inertia has been established; whereas 2) the long-term model advances those benefits with integration, process optimization, improved access to information, and on-going enhancement of ES based improvement projects. The case defines enterprise systems referenced in all large organization-wide packaged applications; including enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), data warehousing, and software platforms on which those systems database applications are built (i.e. SAP). The data collection was derived from one hundred twenty-six customer presentations at SAP 2003 and 2005 Sapphire conferences in the United States. Results to the preliminary study of ES integration in this format indicate that all six (6) factors mentioned in the two temporal scoping simulations were found to be significant to integration outcomes determined by participating senior management on behalf of organizations responsive to the study.
Article Synopsis
The complexity of enterprise systems network design and execution of processes poses challenge to companies interested in employing SAP and related ES into legacy IT networks. Nevertheless, global investment in ES is extensive, and had already reached upwards to $36 billion in the United States by 2004. Despite cost and assimilation difficulties, software corporations such as SAP and Sapphire have done exceptional business on large systems consolidation projects with large conglomerate entities such as Disney Corporation which spent a reported $400 million on integration.
Costly up front expenditures coupled with dense risk in applications failures during the process of ES implementation points to the depth of response required by project managers and administrators working together on systems integration of this size, as impact on daily capitalization may accumulate very rapidly. Variance in organizational benefits from enterprise systems is also a crucial factor in disseminating information on the capacity of an organization pre-ES, during implementation, and from point of training to full use of ES function.
The Seddon and Calvert study is important in that analyses of multi-project ES implementation offer new information about the variables in organizational benefits from ES (OBES), and those projects may include incremental strategies for coordinated development of the system over time with different functionality according to consecutive timeframe, and including varied geographic locations. The objective of the study was to test model ES toward construction of a two-part organizational benefit model for ES, OBES. A two-part model was required because most organizations find that they need to conduct additional projects after the initial implementation (e.g., systems upgrade) as illustrated in Figure 1.
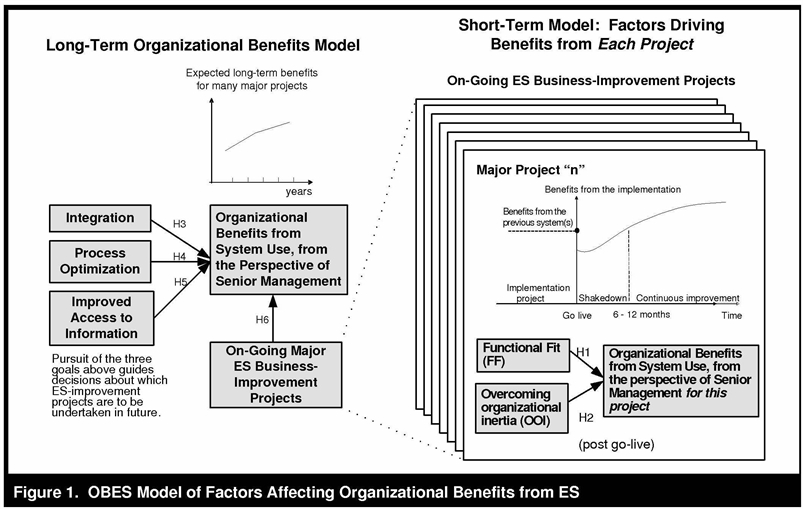
Source: Seddon, P.B. and Calvert, C. A Multi-Project Model of Key Factors Affecting Organizational Benefits from Enterprise Systems. MIS Quarterly, Jun 2010, Vol. 34 Issue 2, p305-A11.
The two-part model is requisite since most ES implementation projects have varying success. The OBES model separates the project-related factors on the right from the long term drivers on the left. The right side of the model shows illustrates the hypothesis that functional fit and overcoming organizational inertia defined the key OBES in implementation projects in the first few years after go live. The long term factors present on the left side of the model illustrate the second half of the study’s hypothesis that integration, process optimization, and improved access to information, along with on-going ES improvement projects and explain variance in OBES for the duration of the system life. Ranked prioritization of goals such is established according to timing of implementation, as the system integrates, optimizes, and improves networked access to information as real-time processes are translated into artificial intelligence; making workday activities smoother. Representation of three theoretical concepts illustrated as systems options for integrated project implementation are shown in Figure 2.
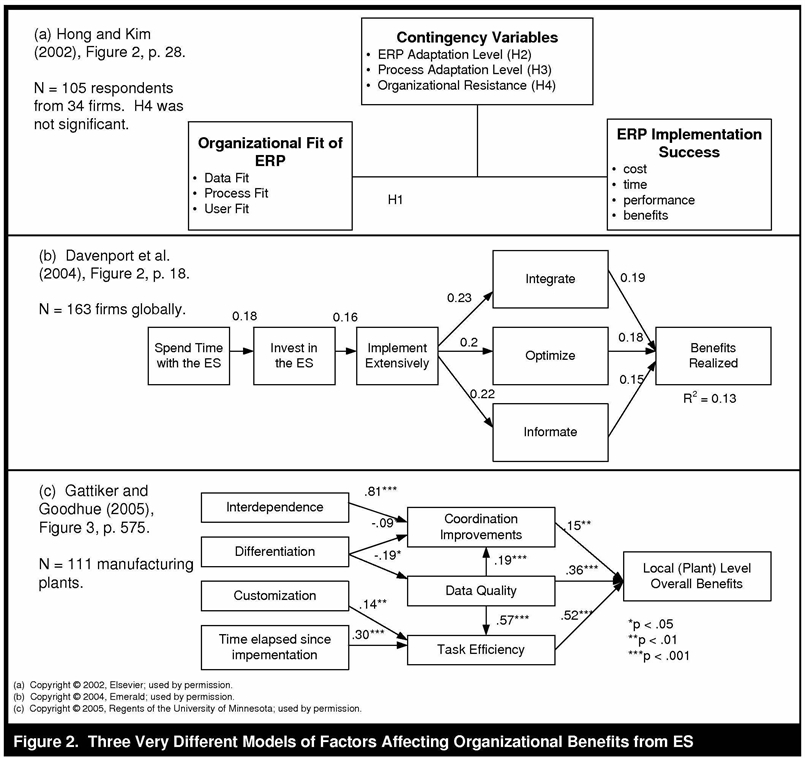
Source: Seddon, P.B. and Calvert, C. A Multi-Project Model of Key Factors Affecting Organizational Benefits from Enterprise Systems. MIS Quarterly, Jun 2010, Vol. 34 Issue 2, p305-A11.
Results from ES project integration denoted in Figure 2 outline improvements to organizational channels toward “better management decision making; improved financial management; faster, more accurate transactions; cost reduction; improved inventory and asset management; ease of expansion/growth and increased flexibility; and cycle-time reduction.”[2] According to the study the cited theorists in the study do not include cost of implementation and administration of organizational ES within OBES theories. Cost amortization is assumed in planning, as the idea is that once ES is complete the organization and particularly management will benefit from the integration of information and process optimization, offsetting initial fiscal expenditures.
Consideration of ES design is largely based on analysis of ‘functional fit’ to the existing processes, and individual activities within an organization. As Seddon and Calvert note, the saliency of functional fit as the first of six (6) hypotheses is so critical to integration that tools like data-flow diagrams, event driven process chains, and business process execution language (i.e. OASIS 2007) have been developed to meet functional capabilities in IT systems. A great degree of function fit has been achieved in the past decade with standardized software packaging of operational systems and related logistics relationships (i.e. manufacturer to distribution). Configuration of software program codes are now typically industry specific, and widely available for immediate exploitation by businesses operating within a particular sector. Visual process composition tools have advanced the universality of functional fit even beyond industry requirements, in everything from dashboards to retail operations inventory (ROI) systems.
The second key benefit driver to the study looks at the impact of OBES in overcoming organizational inertia by way of new assimilation of cutting-edge tools and applications. Fresh inputs into the workday process seemed to increase motivation to utilize the system as opportunities for training were made available. Integration is the third hypothesis to OBES, and is the distinguishing feature acknowledged in ES planning. Integration leads to benefit by four pathways: 1) simplification of data for human interface; 2) end-to-end visibility in real-time integration initiates process optimization; 3) reducing of decision time due to heightened access to valuable information; and 4) front end user interfaces promote motivation, in that they are easier to learn.
Process optimization (PO) generated data as the fourth benefit driver in OBES as ES is used to increase process improvements. Six-Sigma theorists argue that process improvement is a core competency to sustainable organizations, as noted in industry indexes on the topic where the IT industry ranks PO as the first priority. Business improvement projects serve as the primary mechanism for this development. Resultant improved access to information substantiates the fifth benefit driver hypothesized in the research, and the combined effect of process optimization on information flows in business analysis illustrated in Figure 3.
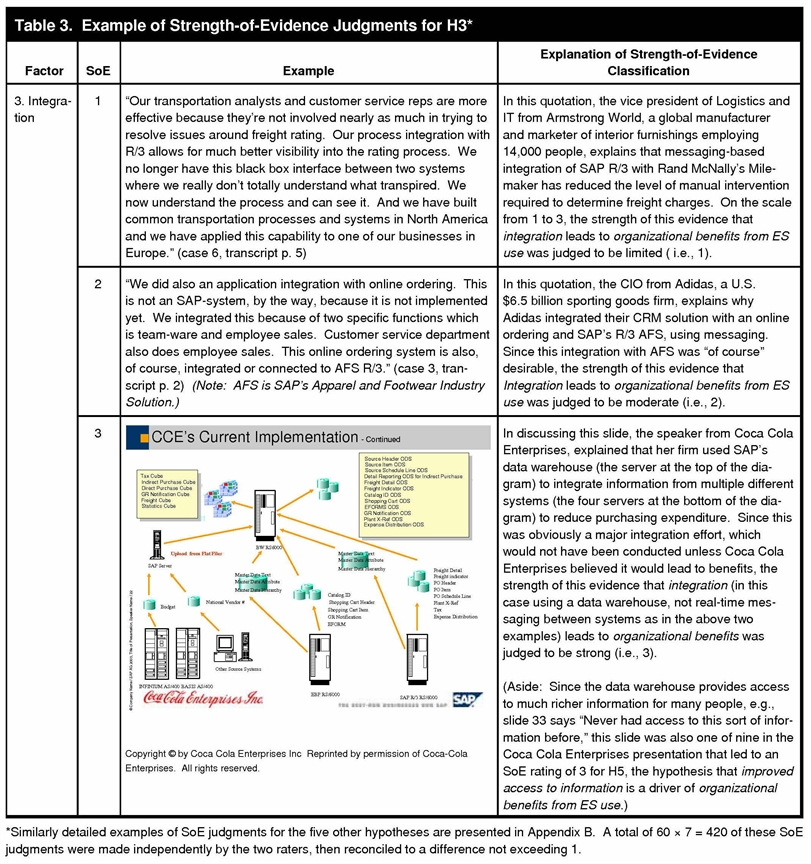
Source: Seddon, P.B. and Calvert, C. A Multi-Project Model of Key Factors Affecting Organizational Benefits from Enterprise Systems. MIS Quarterly, Jun 2010, Vol. 34 Issue 2, p305-A11.
Future benefits constitute much of the impetus within long term strategic planning of ES and the OBES model accounts for this perspective in everything from investment in innovative enterprise-wide business intelligence solutions, including embedded analytics in transactional applications, to maturation of ES systems as a central vehicle for management strategy as data evolved from integrated reporting contributes to well informed decision making.
Conclusion
The analysis of enterprise systems (ES) by Seddon and Calvert in the aforementioned research study touches upon the impact of project integration management on the total operations picture within corporations. The Project Management Institute’s (PMI) PMBOK® Guide offers project managers in the IT field much in terms of thinking about the potential of project management tools to large, multi-scale capacity building business strategies dependent upon ES systems integration implementation.
While most project integration management theory is dedicated to analysis and recommendations toward inter-organization integration projects, the influence of intra-organizational executive management in the IT sphere, and especially Chief Information Officers (CIO) and other related operations and IT staff within lead organizations creates an environment where the internal party to the contract is drawn into the external environment with ES project managers and systems engineers are, to find IT solutions of accountability within their own institutions.[3] Directly involved in the scientific praxis of organizational management, CIOs are a significant factor in the precision and success of systems outcomes, in that they are the primary responsible party for how those systems will be maintained. Although the concept of ‘oversight’ as systemic procedure seems out dated in the face of object oriented applications, how well this human benefit in OBES ensures that ES information is managed will affect future improvements.
Works Cited
A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) – Third Edition, Paperback. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute, 2004.
Davis, B. J. Prepare: seeking systemic solutions for technological crisis management. Knowledge and Process Management, 12(2), 2005: 123-131.
The imperative to be customer-centric IT leaders. CIO.com, 2010.
Seddon, P.B. and Calvert, C. A Multi-Project Model of Key Factors Affecting Organizational Benefits from Enterprise Systems. MIS Quarterly, 34(2), June 2010: 305-A11.
[1] Seddon, P.B. and Calvert, C. A Multi-Project Model of Key Factors Affecting Organizational Benefits from Enterprise Systems. MIS Quarterly, Jun 2010, Vol. 34 Issue 2, p305-A11.
[2] Ibid 1
[3] Cio.com.

Stuck with your Business Plan?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Tags:

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

