Project Definition Report, Coursework Example
Preface
The purpose of this document is to establish the project definition and define the deliverables, tasks, work to be performed and the approach regarding tools and methodology to accomplish the project. The project organization will be mapped out through a hierarchical chart as well as a responsibility matrix to ensure everyone from the project champions to the customer know their roles and responsibilities throughout the project. As will any project the triple constraint dilemma regarding time, resources and cost will be analyzed. The ultimate result of this document is to provide the project scope, requirements related to success of the project and baseline the acceptance criteria needed to verify a successful project. Within this document you will find the following:
- What the Project encompasses
- Benefits/Schedule/Cost Analysis
- Information on whether or not to accept the project
- How the project fulfills strategic intents of the business
- How the project aligns with the portfolio management strategy
- Priority and Impact of the Project
- Resource Needs regarding effort, capital and operating funding
- Commitment needed from the organization
Management Summary
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is an approach to alleviate unnecessary business processes by reducing the amount of source and legacy systems into a wing-to-wing operating model which allows multi-directional data and information flow that is not available within the current configurations. The span of impact is enterprise wide encompassing finance/accounting, manufacturing, sales, service, customer relationship management, supplier management, and human resources.
The process of implementing ERP will fall into multiple phases and require input, effort and dedication from each function acting as a single unit to be successful. Initially experts in each section will be required to document and discuss current processes, create To-Be processes and illuminate potential areas of risk. As the process moves forward, design, test and implementation will take place within each module provided ultimately leading to a roll out of functionality in staged and progressive iterations. The objective is to have as little impact to the business as possible and create an inclusive community within the business and project.
Currently three suppliers offering the Enterprise Resource Planning modules are competing through an electronic auction based upon the company’s requirements and baseline specifications for business function. These companies are Cloud Computing Systems, Acquisition Computing Skills and Cradle to Grave Solutions. Each offer benefits on their ability to perform ERP functions and how they will meet their requirements and future needs.
Background
The company is a global multi-national corporation which produces not only consumer related goods but also financial and technical services. Through acquisition, internal company growth, technological advancements and lack of communication between operating units the current business system configuration is not optimal. The goals of the company are to provide top notch products and services to the customer with the highest quality and the quickest time to market in the industry. Currently the company has many disparate systems in which communication is lacking between them. The operational objective metrics based upon the strategic intent of the company are:
- Time to Market
- New Product Introduction to the consumer
- Project Lifecycle for internal customers
- Six Sigma Principles
- Quality
- Financial Services Quality
- Product Quality
- Six Sigma Principles
- Line of Sight to Shareholder Wealth
- Operating Profit/Cash Flow
- Portfolio Management/Optimization
- Product Management
- Supply Chain Optimization
Time to Market
For ERP focusing on optimization and utilizing the tools necessary to get the job done are imperative to success. In order to be competitive in an ever changing market, products must be available for the consumer to purchase. Time to market focuses primarily on the manufacturing side of the company. The financial management portion of the company’s overall strategic portfolio has optimized its stance regarding market trends due to leadership’s push to lean forward and take a proactive approach to customer demands. The manufacturing segment has multiple moving parts and the entire supply chain is impacted by every make, model or engineering change that occurs with the product. With current disparate systems communication between engineers and suppliers or finance and invoicing take days to accomplish tasks. The goal is to implement a product that allows each function to work in the same workspace allowing real-time access to work queues, messages, notifications or other action items. Each section of the new product introduction will be reworked and revamped to streamline the process and reduce as much non-value add actions as possible. The implementation of ERP not only will improve the functionality of the systems but allows the subject matter experts time to step back and redesign their processes to optimize and configure their work efforts. The project lifecycle will also undergo a facelift allowing unnecessary approvals and project review stages to be eliminated due to the increased insight my peers, leadership and stakeholders. Project reviews will be available on demand by the requestor and not only data but information will be available regarding schedule, cost, deliverables and documentation for all projects required to report in the system. Integrating project management enhancements will remove the roadblocks presented in the traditional business operating model and allow the free flow of information on demand when business decisions are being made. This also allows leadership to manage not only projects at the operating level but make informed decisions on the portfolio of the business.
To first understand what portfolio management provides to a corporation it is necessary to understand what the purpose and functions include. Portfolio management is a function within project management to analyze each project based upon economic measures, strategic leadership guidance or regulation compliance. Each project will have certain factors impacting the overall portfolio in which such factors are cost, consumption of resources, proposed timeframes, expected results and their corollary or contradictory nature among other projects in the business’ portfolio. Portfolio management is a mix of art and science where costs economic impacts can be calculated quantitatively but the skill of measuring qualitative data impacts the overall project blend. The goal of the portfolio manager is to create the optimal project mixture to create the maximum shareholder wealth with the minimal risk necessary. Portfolio management goes from an arduous scientific and artist form to a tool to help leadership make informed decisions for the future of the business
Quality
With an optimized process to get product to market it would be all-for-not if the product delivered was of poor quality. First focus of quality will be on the financial services segment of the business. Quality is of utmost importance when it comes to financial services but measuring quality is somewhat of an art form. The main objective is to provide line of sight for the customer to their investments. The goal is to provide real time insight with the ability to make changes, increase or decrease funding, report out on investments, calculate ROI and view historical data and how it compares to multiple other factors such as market trends, S&P etc. The investor utilizing the financial investment modules will have direct insight at any given time to the information regarding their investments. This varies slightly from today’s model that requires financial closeouts and end of month/quarter/year postings prior to availability. Although all information will still be available once the month, quarter or year closes the improved access for on-demand functionality will also be present.
Quality for manufacturing is greatly more tangible than financial services but also just as challenging if not more challenging to control. The requirements for quality are based on the lean management and six sigma methodology encompassing product design, supply chain management, and continual service/project improvement. This being said it is necessary to have the tools and insight into the entire supply chain so that each section can be measured, monitored and enhanced. In the current systems available insight and visibility are not accessible so unnecessary time is spent tracking down potential areas for improvement instead of knowing where improvements could be made. This allows the limited resources of time and funding to be applied in a more effective and efficient manner. The basis for the quality function is based upon defects per million which leads to the 6 sigma methodology. All projects for improvement will follow the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control) methodology while still maintaining flexibility if new or improvement methods are needed. For the manufacturing section when new product lines are built they will be based upon DFSS (Designed for Six Sigma). Having quality controls and processes for improvement will allow wing-to-wing opportunities for improvement which allows greater return on investment when optimizing and alleviating the problems.
Purpose, Scope and Objectives
Purpose:
The purpose is to implement a wing-to-wing enterprise wide Enterprise Resource Planning program allowing all systems and employees to act as one team with one purpose.
Scope:
The Scope of ERP includes all functionality in all aspects of the business. Each function will roll out on different schedules falling under the ultimate program of ERP. The overall ERP program will have a project for each module as well as an integration of those modules into the entire ERP system.
Objectives:
Growth-A system that provides growth opportunities and is scalable with business needs. This system will provide
Return on Investment- The return on investment for this program is estimated at 18% over the course of five (5) years. This return on investment includes the estimated ROI for each section and module and does not include the cost avoidance or productivity increases.
Line of Sight to Data/Information for Key Performance Metric- On-demand reports, metrics and key performance indicators
Work Structure
The work break down structure will be based upon work packages. A work package would consist of the project manager, subject matter experts, vendor, programmer and center of excellence. A work break down structure for the ERP project is:
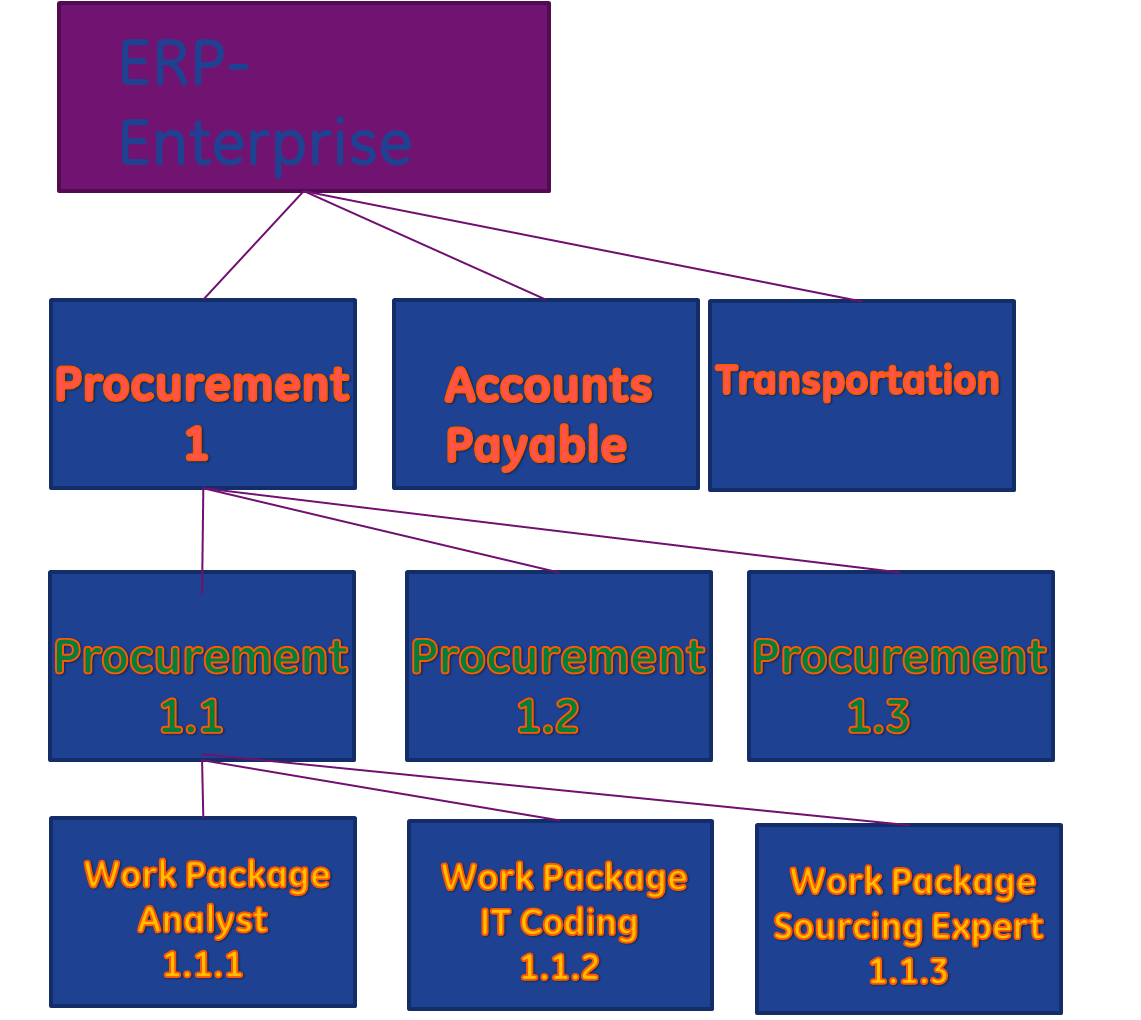
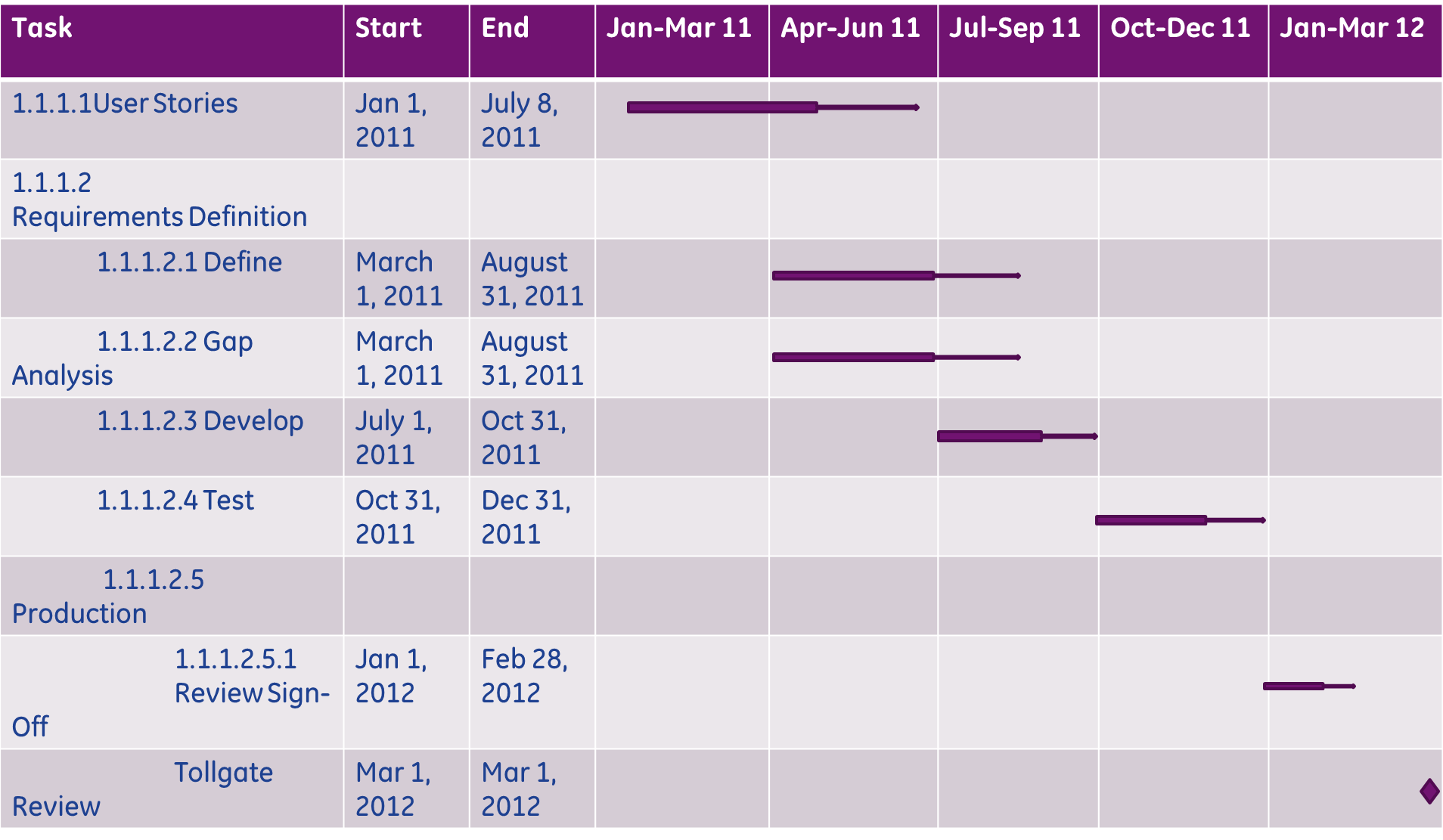
Gantt charts will be utilized to visually depict the work to be completed, the timing, and what will be accomplished. A further breakdown of each task will be accomplished to show eight (8) hour increments and who is performing the work. Each person will be assigned two week assignments based upon their percentage of availability to the ERP program. This is key when garnering support from leadership because a total of eighty (80) hours of work per two (2) week sprint is optimal from each team member.
Project Organization
The project organization will include a hierarchy of leadership starting at the Project Sponsor.
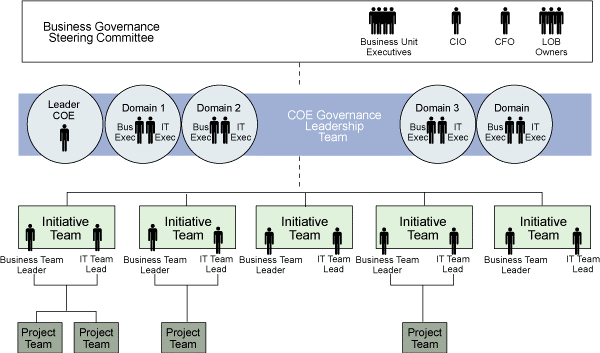
The project team reports up the hierarchy ultimately ending at the project sponsor or project champion. The initiative team will be discussed later in the project definition paper but the project organizational chart show the proper reporting structure. To determine the roles and responsibilities of each member a RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) chart will be utilized so that every member is aware of their position and responsibility.
Project Management System
The project management method used for the ERP program is between the traditional waterfall project management methodology and the agile project management methodology. The graphs represent the typical methods in which the company goes through the toll-gates as wells as a graphical depiction of a “Total Project” look. Each method has the inherent positive and negative aspects regarding successful project management and each have their place in the ERP process. The business as a whole must adjust and redefine the typical Project Management methodology based upon the PMBOK (Project Management Book of Knowledge) while maintaining the tested values of the methodology.
The waterfall method follows the basic principle of Requirements, Design, Implementation, Validation and Maintenance. This allows movement from one phase to the next only when all of the requirements are met in the prior phase. The waterfall method spends a great deal of time gathering requirements and locks in the scope of the project from the very beginning. Agile project management on the other had revolved around iterations or sprints broken down into very specific measures of time which are typically two (2) week intervals. This method allows for a project to deliver to the business without fully knowing 100% of the program/projects requirements from the beginning. This method is very useful in the software development lifecycle and allows the project team to maintain flexibility on overall project delivery and cost but firm on time and sprint deliverables.
The inherent nature of the potential changes increase the risk of the project failing. To mitigate this risk it is necessary to implement the appropriate tools necessary to accomplish the job. Considering the lack of initial project definition in terms of requirements and the amount of time provided by leadership to implement the first phase of the project the methodology in which to conduct the project is essential for a successful outcome.
The agile project management methodology will be utilized in this project because of the inherent uncertainty of each sections initial requirements as well as the need to maintain an “agile” and flexible nature when accomplishing business needs. Below are examples of both methods and a description of what is needed at each review.
Each toll-gate is defined below:
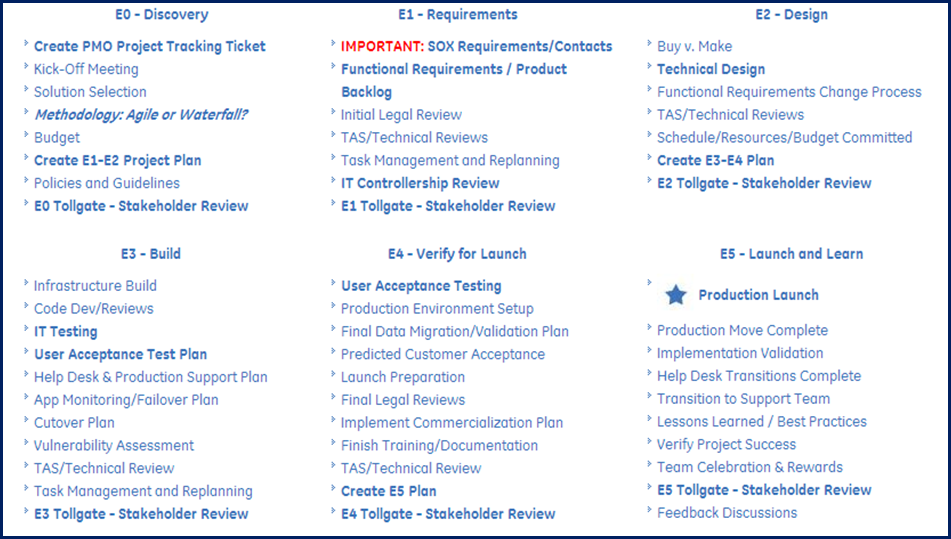
As the visuals depict the agile method will deliver small increments of usable modules that will facilitate the acceptance and usability by the employees and stakeholders. The project management methodology will still maintain control criteria through the project tollgates as outlined but the sprint working sessions and stand up meetings will allow information to flow between teams easily.
The overall project will be broken down into functional project leaders and IT project leaders. They will also have integration with each function, security, the vendor and each area’s Center of Excellence where the subject matter experts will reside.
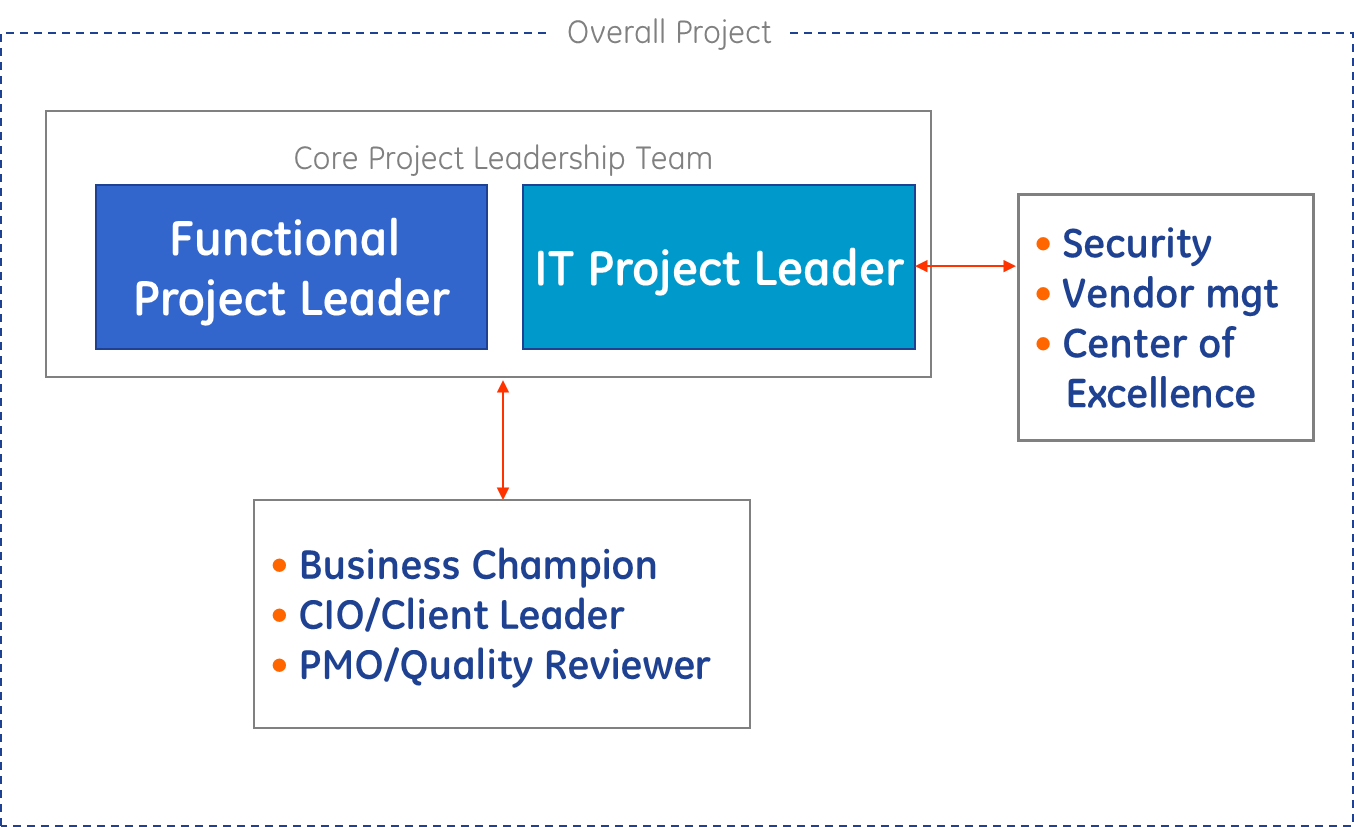
The project is broken down by Functional project leader and IT project leader. Each of these people has an indirect reporting responsibility to the ERP project leader to provide updates, roadblocks, progress and implementation updates. The functional leader is the representative for the operating unit and is the subject matter expert for that respective operating unit. It is his or her responsibility to provide the ERP leadership team with business needs, wants, as-is and to-be processes as well as insight into the business process for that function. An example of this would be a financial manager’s monthly closeout reconciliation. The current process involves manually adjusting the journal entries according to specific rules and logic that each line item must pass prior to uploading the data into the ledger. The to-be process would be to have the logic built into a user interface that would ensure each line item passed the logic provided by the SME.
The IT functional leader would manage the IT resources needed for hardware implementation, software implementation and upgrades as well as sourced IT support needed for programing and coding of functionality into the system. They would also provide current IT resources’ ability and tools available for the project and provide updates on current projects and projected change management plans according to business best practices afforded by senior leadership.
The center of excellence is a parlance and conglomeration between in-house and sourced professionals utilized to implement the ERP process. This includes but not limited to the ERP functional teams, sourced professional consultant, business writers, business analysts, program and project managers and other leadership resources available. Their roles are to provide input and guidance as well as provide the ability to remove roadblocks, provide way-ahead scenarios/answers and answer questions in the difficult project implementation
The roles of each section such as the IT PMO, security and the IT project leaders are defined below.

A re-organization will also need to occur in regard to the arrangement of team members. To facilitate the knowledge transfer and removing barriers to communication team representatives that will maintain a presence for the entirety of the project will be collocated with their project teams. The project manager, subject matter experts, logistics support and other members of the team will share open environment workspaces to enhance collaboration. Schedules will be posted with removable post-it notes defining key deliverables and their associated responsible party. Each section will be updated daily during the standing Scrum session and a report out on what was accomplished, what is going to be worked on and barriers to progress will be reported by each member. The Scrum master will address each issue and assign resources, priority or assignment if necessary.
The key to the project success is visibility by each team member. Each person will have a visual of the project time line, scope, budget and resources as well as direct contact with each key participant on the team to reduce the cycle time to resolution of key issue impacting the project. Key dependencies and impacts will be readily available to all team members to ensure all bases of the project are covered and the points of contact are informed when decisions are made. Problems and roadblocks will need to be raised as soon as possible to mitigate the impact the issues have on the overall project.
A project timeline describes the over-arching program with each section containing its own project timeline. This timeline was built with input from the various team and is tentative in nature only and shows the visual depiction of how the breakout could occur. Each module can be moved or extended depending on the needs of the business and available resources to perform the function.
Risk and Assumptions
Risks
- Large project impacting every aspect of the corporation
- Potential work stoppage and line closure if not strategically planned and tactically implemented
- Failure to redesign business process
- Implement due diligence when designing business processes
- Do not over analyze the process/100% optimization is not the goal
- Set the stage for future process improvement
- Management Acceptance and Support
- Management must support the changes
- Management/Leadership must be the best proponents of the system
- Software Design/Technology
- Scalable to business needs
- Adaptability
- Integration cross-functionally
- Technological based decisions should be made on existing capability not future state
- User involvement and training
- End Users must be committed and involved with the development and progress
- End Users must be fully training
Assumptions
- Leadership will lead the change
- Promote acceptance throughout the corporation
- Provide user/employee buy in by making them part of the change and not just an impacted recipient
- Ensure scalability of tool
- Technical feasibility test on all technology based tools
- Utilize tested functionality and not untested methods
- Accountability among all parties: Internal and External
Project Budgets
The below budget is based upon initial estimates from industry standards, initial quotes and market research. The research was based up purchasing minimal hardware configurations and allowing the leasing of storage based upon the technological advances with cloud technology. Considering the company is mitigating their risk of utilizing a “cloud based” technology as a risk mitigation plan several off-site servers are utilized as a back to create redundant back-up of key financial, client, employee and business information.
Within this cost/benefit analysis it is necessary to employ several consultants to design, consult and implement the project utilizing the resources. The company is also leveraging in-house talent to facilitate our knowledge transfer, training and expertise necessary to be successful. The goal is to utilize as little as possible outside entities but also knowing that in order to create a successful implementation program that it will be necessary to increase the knowledge base of our talent pool.
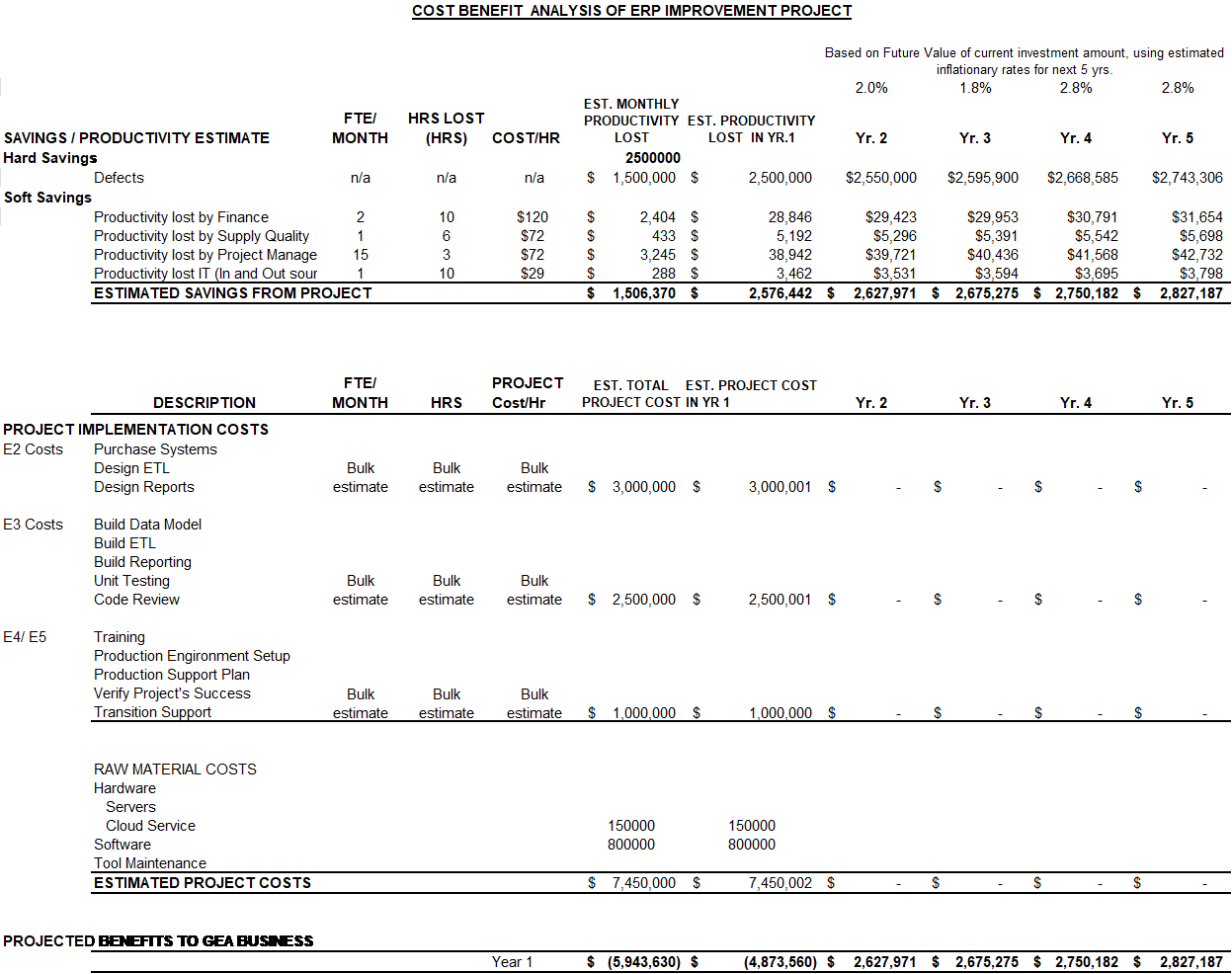
The cost benefit analysis below shows the relationship between the amount of investment needed and the amount of tangible and intangible return on investment that the company will enjoy once the project is complete. The costs are broken down by project timeline and tollgate (E1, E2, E3 etc.) if costs are associated with that phase of the project. The soft savings are broken down initially by the function that will enjoy the benefits with the initial implementation. Since this project will implement the ERP functionality utilizing Agile project management methodology only certain functions will go-live with their portion of ERP in the initial roll out phase hence why not all operating units are listed with corresponding benefits and costs. The functions initially rolled out are Finance, Supply Quality (Sourcing), Project Management, and Information Technology. Throughout the project hardware and software costs will be incurred buy through process management improvement hardware will be leverage utilizing the virtualization of the servers and maximizing resource management but that is another project requiring separate but equal integration and implementation.
These initial forecasts are in the preliminary stage due to the fact that the ERP system supplier has yet to be selected and the stakeholders will be part of the selection process. These initial estimates have a potential accuracy of +/- 50% due to the inherent risk of cutting edge technology, scope of the project and market trend success in this type of implementation.
Project Justifications
As in most projects the more credible the project regarding return on investment, solving compliance issues, reducing effort or benefiting the company in other tangible and intangible ways the better off the project will be regarding stakeholder buy-in and support. The best projects regarding support and push from leadership are those projects that identify specific problems with measurable results. Monetary values are always an easy way to describe to leadership the value of a project. Monetary value comes from cost savings, freeing up budget constraints, reducing headcount or completing a process more efficiently and enjoying the cost avoidance of a prior labor intensive process. With the implementation of an enterprise resource planning system benefits come in many different forms. There are the cost savings of a more efficient process in which each system has the ability to communicate with one another but there are also areas for improvement and cost savings because building a new foundation utilizing the DFSS (Designed for Six Sigma) process allows future process improvements and monetary savings.
Another important part of the justification is showing the qualitative improvements. This includes training opportunities for employees so that they can do their job more proficiently or allowing enhanced business opportunities by creating a system that puts change control in the hands of the men and women on the front lines experiencing the everyday issues faced. In regard to ERP implementation the project has both quantitative and qualitative benefits within the project.
ERP measurements can be hard to measure because ERP as a whole is a systematic approach to project/process implementation. The power behind ERP can be symbolized like that of the human brain. The brain is powerful and we know that but we cannot quite measure how powerful or efficient it is. We understand that the brain controls our movement, thoughts, memory, breathing, cell reproduction, heart beat and sensory functions. ERP is like that of the human brain. It is the central function that interprets different departments or functions across the business functions. It manages data while deciphering inputs and outputs into manageable and understandable methods. The first portion of project justification falls onto the shoulders of the cost/benefit analysis.
The project will continue to be profitable even past the five year timeline defined in the cost/benefit analysis. The basis for the project allows the establishment of a wing-to-wing methodology and implementation for continual improvement and scalability to meet current and future business demands. The initial investment will be returned with a payback of less than three (3) years after year one (1) completion. This is for the first phase and does not include all of the potential cost avoidance and rework. Basing solely on hard numbers and the payback rate of approximately three (3) years this is beating industry standards and allows our initial investment to be fully optimized. The estimations provided have a rough order of magnitude in the +or- 50% due to the risk but the benefits realized will greatly negate the impact of cost increases.
Through the implementation of ERP there will be benefits in multiple sections of the process. The areas initially impacted by the process renovation include supply chain planning, service management, customer relationship management (CRM), and financial management. Leadership needs data so that they can receive information leading to informed business decisions. Without the information they need when they need it leadership cannot guide and influence the business in a fashion that would benefit the shareholder’s wealth in a positive fashion. For supply chain planning, obtaining information from each section is difficult within itself let alone combining different sections and coming to a conclusion based on information that is not cleansed, formatted or in a global world market even in the same language. The problem here is that garbage in equals garbage out and with an ERP system the composite data is streamlined, cleansed and standardized among the systems so that the data can roll up to senior leadership as well as drilled down to the lowest denominator to perform root cause analysis or segment a data point for further investigation.
In regard to data integrity and its importance to financial information, ERP is more than a remedy for Accounts Receivable (AR) and Accounts Payable (AP). ERP is a cradle to grave approach to financial management. It shows one version of the truth in accounting. Each department can view the same data and have the same information provided no matter where they are located or what time of the month they are viewing the data. This is vastly important when senior leadership needs an answer and instead of manually grinding the numbers to something that is recognizable the data is available in a dashboard display with all data provided in the same timeline and at the same point. All data is congruent and available for each section of the business and operating unit.
References
Highsmith, J. A., & Highsmith, J. (2010). Agile project management, creating innovative products. Addison-Wesley Professional.
Magal, S. R., & Word, J. (2011). Integrated business processes with erp systems. RRD/Jefferson City: Wiley.
Monk, E., & Wagner, B. (2009). Concepts in enterprise resource planning. (3 ed.). Boston, MA: Course Technology Cengage Learning.
Prencipe, A., Davies, A., & Hobday, M. (2007). The business of systems integration. Oxford University Press, USA.
Project Management Institute. (2008). A guide to the project management body of knowledge. Project Management Inst.

Time is precious
don’t waste it!

Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee






