 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Rock Cycle, Research Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Research Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Introduction
Sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic processes describe the fundamental concept known as the rock cycle. Equilibrium conditioning predisposes the three types of rocks to tectonic forces that lead to the altering or destruction. The rock cycle is mainly determined by two major factors; namely plate tectonics and cycle of water. Essential to this research, the plate tectonics process is further subdivided into spreading forces and subduction zones.
Figure 1: The Rock Cycle Rock Labels
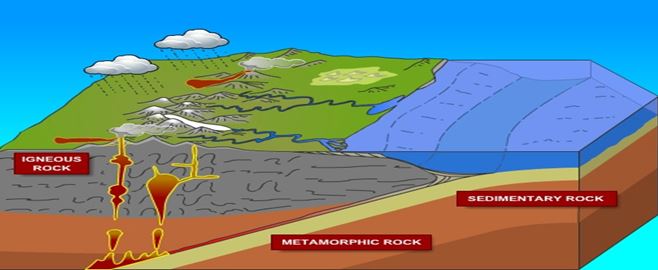
Source: http://www.geolsoc.org.uk/gsl/education/rockcycle/page3445.html
Sedimentary Rock
Classification of sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary rocks are also referred to as secondary due to the concurrent accumulation of broken pieces of pre-existent rocks. Sedimentary rocks also form on land and Sand on beaches and in deserts turns into rock. They can be found in the crust of earth and in Appalachians of the Eastern United States. It is made up of layers of small particles that are pressed and cemented tightly together.
During the formation of sedimentary rocks, various rock segments cover dead animals and plants as they gradually change into rock. Initially, weather forces will lead to the breakage of rocks into small pieces that are carried away by wind or water.
Figure 2: Conglomerate

A conglomerate consists of individual clasts that been joined together. The texture of the conglomerate consists of at least 15 percent of sand sized grains. This type of rock has the form of a matrix eventually forming the metaconglomerate. Location of the conglomerate ranges from deepwater, shallow and fluvial marine environments and can be found in Connecticut Valley. Conglomerate colours ranges, but there seems to be a uniform colour of a whitish grey.
Figure 3: Sandstone

The sandstone sedimentary rock is composed of debris formed by weathering. The debris is made of sand-sized particles with a 2 millimetre diameter. Colours of the sandstone are not specific but main colours include red, grey, pink brown and black. The sandstone is located in beaches, deserts, deltas and flood plains.
Figure 4: Mudstone

Having a diameter of less than 0.05mm, the mudstone is composed of minute clay particles rarely visible with the naked eye. The colour ranges from black, white and grey mixtures. Since mudstones are tiny particles, they are mostly located in deep seas, lakes and areas with flat tides.
Figure 5: Limestone and Chalk

Source: http://www.geolsoc.org.uk/gsl/education/resources/rockcycle/page3458.html
Limestone is mainly composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Accumulating shells and coral debris form the limestone. Limestone forms in warm, shallow and clear marine waters. The chalk is a limestone that is soft, but with an extremely fine texture. The colour of chalk is white or grey formed from microscopic organisms. They can be found in south-eastern Alaska.
Metamorphic Rock
Metamorphic rocks are classified in two main divisions. Metamorphic rocks can be foliated and non-foliated. The foliated rock consists of divergent kinds of minerals while the non-foliated rock is of a single composition with a few minerals like calcite and quartz. The colour is green-schist and blue-schist. Geologists will often refer to metamorphic rocks as igneous or sedimentary rocks that may have undergone modification features in terms of size, shape and arrangement of present minerals in rocks. The figures below show the types of metamorphic rocks.
Figure 6: Slate

This is an extremely fine-grained rock consisting of minute mica flakes classified under foliated rock. It is normally grey in colour and forms in areas with high density and temperature. Slate is the result of low grade regional metamorphism of shale or volcanic ash. It is an excellent rock for roofing and floor tiles.
Figure 7: Gneiss

Gneiss rarely develops as isolated structures. Instead they commonly occur as a group of structural highs with a variety of sizes and geometric arrangements in map view. The gneiss is pink or grey in colour while the texture is coarse grained. The rock mainly forms in areas with high density and pressure.
Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks can be classified under volcanic and plutonic rocks. The texture is like Crystallization and hardening of the molten crustal rock will lead to the formation of the igneous rock. The quartz and feldspar minerals are generally light colours, whereas the ferromangensian minerals are dark generally green or black. Therefore, colour of the rock varies depending on the percentage of these light and dark colour minerals. Their location is deep within the earth’s crust, the existent magma will harden in the form of fire ball rocks due to the extremely high temperatures deep within the earth (Shelly 149).
Figure 10: Basalt

The basalt normally forms on the ocean floor or in areas with extensive lave flows. The texture is fine grained, or compact, such as leutice and oxide of iron. The colour of this rock is dark greyish black or brownish greyhey are composed of joints, or blocks of the same angular shapes, resting one upon another.
Figure 11: Gabbro

“The gabbros are the most frequent plutonic rocks originating from the dark basic magma type. They consist of 50-70% plagioclase with a black grey, dark brown or grey white coloration. Depending on the grain size, the appearance can vary from mottled to a uniform deep black colour. Texture is granular, seldom porphyritic” (Mason 78). They are into the quartz mica diorite of the Spanish Peak area, the two masses not being separated on the map by a sharp line.
Work Cited
Mason, Roger. Petrology of the Metamorphic Rocks. Phoenix: Springer, 1990. Print.
Shelly, David. Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks under the Microscope: Classification, Textures, Microstructures and Mineral Preferred-Orientations, Volume 20. Phoenix: Springer, 1993, Print.

Stuck with your Research Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Tags:

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

