 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Study Two Methods, Results, and Discussion, Research Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Research Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Participants
Two hundred and five participants took part in the study. The subjects were (n=153) male and (n=52 female) college students who were offered an opportunity between extra points or credit in exchange for their participation. The participants took part in the study during the class a class session of research methods. Four to five students participated in each session, and the researcher informed them that they would be taking part in the study. To assess the effectiveness of the self-manipulation was conducted using a 2×2 ANOVA on the items that were identified to evaluate how the respondents felt. The exclusion criteria for the study included expressing manipulation of the failure to take part in the study by not completing the questionnaire. The participants identified themselves as Latino, or South American (n=5), African American (n=3), Asian American (n=50), Arab American (n=6), Caucasian (n=143), and the remaining were either bi or multi-racial. Half of the participants were freshmen, a quarter were sophomores, fifth were juniors, and the rest comprised of 5th seniors or graduates.
Materials and Procedure
A 6 item questionnaire was used to develop the impression the study was measuring an aspect of mortality. The tool was designed to assess the differences in how people experience gratitude in their daily life. Further, the participants were required to rate items on a 7-point Likert scale arranged from 1-7, that strongly disagrees to agree strongly). The one-factor scale had the acceptable internal reliability that was mainly related to the peer ratings of gratitude. The worldview defense was measured using evaluative questions about the essays. The essays included an optimistic essay and pessimistic essays. Before, taking part in the study, the participants were required to sign a consent form and to agree or disagree to take part in the study.
Results
In the current study, the predictor variables include the mortality salience scores versus dental pain and school variables. The hypothesis depended on the likelihood that there exist different categories of individuals who would show a tendency of susceptible to mortality salience. As a result, the initial steps of the analysis involved classifying the participants based on their levels of humanism as well as normativism. The participants who scored the highest or the lowest quartiles of the scores in humanism and normativism were categorized as a high humanist or high and low normative. The participants who remained in the middle quartiles were not labeled. During the experiment, after categorization of those who took part in the study, the ANOVA and the t-tests were explained in further detail. The analyses were conducted to determine whether self-esteem, negative mood, and identity had implications on mortality salience and the elicitation of death thoughts. The predictor variables that were used comprised or mortality salience and versus dental pain and school. The variables were recorded in the initial step of the regression equation to test the major implications, and the interaction term was recorded. When considered together, the regression analysis suggested that the main variable of the participant’s self-esteem and negative mood never had any effects on the relationship between the elicitation between mortality salience and death thoughts. Further, the analyses also suggested that there was no relationship between self-esteem and negative mood and the worldview defense.
Manipulation Check
From the results, to determine whether mortality salience manipulation worked as anticipated, t-tests were carried out. This was done by comparing the variables that were elicited on each of the worldview defense measures. There were no significant differences obtained. As such, it demonstrated that no manipulation worked. There were no differences that were observed suggesting that the manipulation never worked. Further, no differences were observed in the overall sample of the participants. The hypothesis suggested that the mortality salience had different effects which mainly depended on the type and strength of the worldview. Apparently, there was lack of a resolution to reveal the interactive effects.
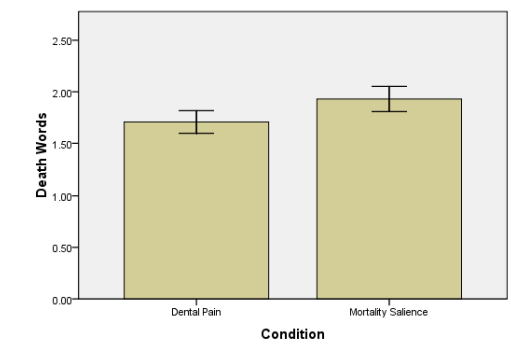
Figure 1: Mean (+- SEM) death words completed by the participants
The figure above demonstrates that there is no variation between variables on how strong the participants defended worldview.
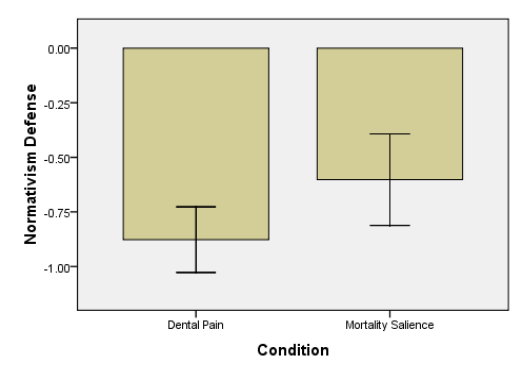
Fig 2: Normativism defense in mortality salience and dental pan conditions by participants
It would be appropriate to understand the conditions of death thought the accessibility of the group given the death words rated as 1 and the group given the neutral words rated as zero, to test whether completion of death thought accessibility measure and the effects on worldview. The scale was mainly used as a predictor of mortality versus death pain x 2 death words versus neutral stems ANOVA with three worldviews defense scores, which was considered as the best criterion variable. It was observed that there were no main effects that demonstrated death thought accessibility measure. Further, t never had any effects on worldview either the mortality salience or control condition.
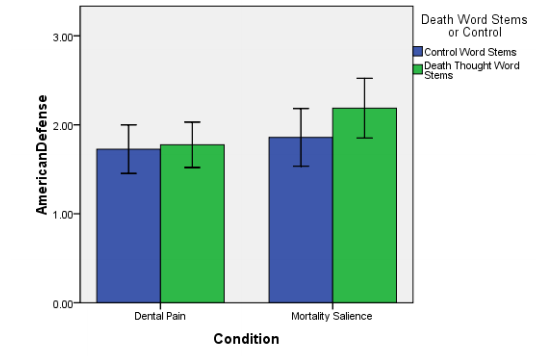
Figure 3: Effect of mortality salient on word system
The figure shows a mean score for dental pain and word systems, dental pain and thought systems, and mortality salience and controls word systems. The figure also shows death thought word stems, mortality salience, and control word systems. Mortality salience and death thought word stems. It is evident completing the test measure did not affect the normative worldview in the experimental conditions.
Discussion
The study examined the generalizability of Terror Management Theory and the mechanisms through which individual differences operate through the process. Whether an individual’s worldview implied mortality salience on the traditional or cultural worldview, it may determine the strength or moderate between proximal defenses and death thoughts. From the result, the manipulation checks indicated that there was no difference, particularly on the number of death words of word view defense measures; hence suggesting that the analyses were carried out on the total of all those who took part in the study. Some hypotheses predicted that mortality salience effects depend on the strength of the worldview held.
There was also a hypothesized interaction effect between mortality salience and humanism that defended the position in the salient mortality condition when compared to the dental pain condition. On the contrary, non-humanist never defended humanism differently given the nature of the experimental condition. Despite the fact that the normative defended normativism, the mortality salience never increased the defense of the normative worldview, especially for the normative. However, contrary to what was expected, the humanists and the normative never showed any difference in their defense concerning the worldviews. Among the formative, mortality salience never had any implication on the differential rating of the essays. On the same note, mortality salience never led to the defense of the worldview for the humanist. Although this provides support to the prediction that mortality salience would not result into the defense of the worldview for the humanists, it never fitted into the prediction that mortality salience would not lead to the defense of the worldview for humanists. Also, t never fitted to the prediction that the strength of mortality salience effect would differ from the perspectives of the humanists and the normative. The humanists and the normative never deferred on the accessible death-thoughts regardless of the of the experimental treatment.
Interpretation of Results
Manipulation Check: As noted, manipulation never appeared to work. Given the analysis of all those who took part in the study, a number of the hypotheses stated that based on the different worldviews would moderate the defense of worldview. It would not necessarily be observed in the analysis, which includes all the participants. Furthermore, the manipulation never worked. Some studies noted that self-esteem reduced the need for a worldview. Therefore, it can be suggested that by providing answers to the items on the self-esteem scale, this made individuals who took part in the study to be cognizant of their self-esteem, which mainly decreased the need to provide a defense to the worldviews. For this reason, one would argue that the participants with higher self-esteem provided a defense to their world-views compared to the participants with lower self-esteem especially after self-esteem was found. No relationship existed between self-esteem and the total number of deaths-thoughts that were made available.
Some studies do not support the importance of implicit self-esteem. However, this was never evaluated or manipulated in the current study. Thus, the evidence of the analysis when compared with the current literature demonstrates that the measures of self-esteem were not the main cause of the lack of overall mortality salience effects. Based on Hypothesis, it was predicted that mortality salience increased the defense of humanist worldview. In essence, this position is congruent with terror management theory and the past and is also culture-specific. The findings of the experimental study suggest that terror management theory may be generalized to be able to provide a defense to the worldviews together with the defense of more specific and cultural worldviews.
Mortality salience never increased the defense of the normative worldviews considering the second hypothesis. Despite the fact that the normative never defended normativism, the defense of the position never depended on the experimental condition. Therefore, there are potential responses that could fail the normative, and which could demonstrate a typical mortality salience. There could be the social desirability of bias. For instance, the wording of the essay could not be congruent with the messages that are taught in institutions of higher learning. Although the essays never accurately represented the views of other people, they would either support or be against the normative worldview. Perhaps, the essays could provide an expression of a normative person more practically without necessarily being against the messages that are sent to the institutions of higher learning. The other potential reason that the mortality salient never induced the defense of the normative worldview could be attributed to the fact that the normative never responded to the mortality salience in the same manner that the humanists did. From the findings, it would be possible that the normative is mainly affected by mortality salience in the same way in which the other group of the humanists is affected.

Stuck with your Research Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

