 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Ten to Zero, Research Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Research Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Ten to Zero: Discontinuation of NASA’s Space Shuttle Program in the Aeronautics Industry
During the past year America has been watching and waiting for NASA’s final launch of the space shuttle program with U.S. Shuttle Endeavor. In March 2010, after 130 space shuttle missions, only four remained prior to scheduled retirement of the fleet (NASA 2010). Nowhere perhaps, has the countdown to the final chapter of the Mission been more esteemed than the American aeronautics industry that contributed the intelligence and technological deployment to the rockets and their capabilities. On May 27, 2010 the last set of space shuttle rocket segments arrived at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida from Alliant Techsystems (ATK) factory based in Utah (Moskowitz). The manufacturing company has built and processed solid rocket boosters for NASA’s propulsion of space shuttles to orbit since the commencement of the program approximately 30 years ago. The last SRBs are rescue components for Atlantis, and will be assembled this summer for mount on the STS-135 rescue rocket. The boosters were redesigned by the manufacturer after the 1986 shuttle Challenger disaster, “when an O-ring on the right SRB failed to seal, causing the loss of the vehicle and its seven-member crew” (Moskowitz).
In the United States, NASA provides all oversight on the Space Transportation System (STS), encompassing ‘intergovernmental agency requirements and international and joint projects, and the launch and space flight requirements for civilian and commercial use’ (NASA). NASA shuttle systems are comprised of four elements: 1) an orbiter spacecraft; 2) dual Solid Rocket Boosters (SRB); 3) an external fuel tank for oxidizer; 4) and three Space Shuttle main engines. Reuse of the tank and boosters is a critical. The shuttle is launched in an upright position by thrust of the engines and the two SRB. In an approximately a two minute time interval, the two boosters are spent and are separated from the external tank. Once spent, they fall into the ocean at predetermined points and are recovered for reuse.
After about eight minutes firing of the engines shuts down, and the craft is injected into orbit. At this time, the external tank is then separated from the orbiter, and is sent into a ballistic trajectory in a designated, yet remote area of the ocean, and is not intended for recuperation. The engine system is constituted of thirty eight primary Reaction Control System (RCS) engines and six vernier RCS engines. RCS are used for maneuvering leverage. Reaction control system release of the engines is done in sequential separation from the orbiter. Initiation of the Orbital Maneuvering System (OMS) engines fires the orbiter into orbit. OMS are used to increase velocity on the orbiter’s maneuvers. Two OMS execute the orbiter into orbit, while only one thrust sequence is utilized for deorbit. Velocity is attained at approximately 25, 405 feet per second (17,322 statute miles per hour). Deorbit requires a decrease of velocity at about 300 fps (205 mph) for reentry.In the initial entry sequence, the RCS engines control the attitude (i.e. pitch, roll and yaw) of the orbiter, as aerodynamic pressure builds toward activation of the primary reaction control system engine inhibitors. High temperatures induced by entry, are mitigated by a reusable thermal protection system over the entire orbiter. Once unpowered, the orbiter glides to Earth and lands with aviation instrumentation with nominal touchdown at 186 to 196 knots of speed (i.e. 213 to 213 to 225 miles per hour.
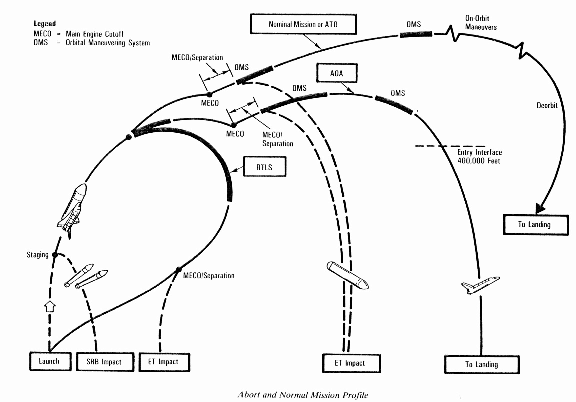
Source: “NASA-STD-8719.7, Chapter 7: Other Hazard Analysis Methodologies.” NASA, January, 1998. Web 3 July 2010.
In David Harland’s Space Systems Failures: Disasters and Rescues of Satellites, he discusses the types of priority risk within space engineering, and reviews the most failures most consistently tested within satellite and space probe launch Citing redundancies, common failures include complications in the: propulsion system; attitude control system (i.e. Gyros); electrical system – component, communications, electromagnetic interference or instrument; environmental failures – electrostatic discharge, impact, space, solar and radiation; structural failures – mechanism or thermal; and on the ground – construction, hazardous environment or testing; operator or software errors. Although some degree of failure is random, says Harland, where there is little in terms of ‘empirical support’ so too there is likelihood of failure.
Fault tree analysis (FTA) are also employed by NASA, and is an analytical technique that enables targeted issues in the state of the system as specified (usually a state that is critical from a safety standpoint) to be found and analyzed ‘in the context of its environment and operation to find all credible ways in which the undesired event can occur.’ FTA offer’ a model representation for the interpretation of a limited set of parallel and sequential combinations in faults that may result in convergence during a predefined event.
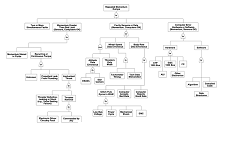
Source: Harland, D.M. and Lorenz, R., Space Systems Failures: Disasters and Rescues of Satellites, Rockets and Space Probes. Dordrecht: Springer, 2005.
Fault tree of possible causes of the repeated momentum dumps by the NEAR spacecraft after it aborted its burn. Certain events result from AND-ing or OR-ing other events (Failure Report).
Often referred to as a ‘gate-way’ analysis, FTA do not serve as models of all possible system failures or all possible causes of system failure. A FTA is not an exhaustive classification of faults, and is tailored to its top event and corresponds to some particular system failure mode; thus incorporating only faults that contribute to a designated top event. Preliminary risk planning ‘against development time and cost’ is best supported by utilization of a metric for assessment. Planned schedule duration as seen in the ‘Complexity Index’ for researched assessment of factors such as spacecraft power, pointing accuracy and type of propulsion by The Aerospace Corporation of El Segundo, California.
Conclusion
Aeronautics and aerospace corporations have of course been forced to reinterpret strategic planning in light of the termination of the U.S. NASA Space Shuttle Mission. The ground for some buoyancy between the national space program and the industry had already preceded this projection earlier in the decade. At present, legislative financial allocation to NASA missions typically exceeds the agency’s requests. Introduction of the Zero Gravity, Zero Tax Bill to the United States Congress July of 2001 set the stage for legislative policy on space-oriented enterprises with the amendment of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to provide tax incentives for investing in companies involved in space-related activities. The provision allows for income investment credits to fund new enterprises in this area, and augmentation of those incentives for established company’s already engaged in space related activities. Other aspects of the Act resulted in capital gains exclusions and 10 year tax exclusion on gross income. Zero-G Zero-T ‘is intended to create an enterprise zone in orbit’ (Rohrbacher 2002). For suppliers to National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the Act incited renewed interest in partnership with the Agency’s $15 billion budget. Once the province of the few due to the high cost of risk within space – and especially launch with its complex, multi-scale risk assessment, and disaster mitigation planning, logistics and material expense – space-based companies were presented with a range of profitable rather money-losing contract incentives.
Works Cited
“A Countdown of Countdowns: The Space Shuttle’s Finale.” NASA, 12 May 2010. Web 3 July 2010.
Harland, D.M. and Lorenz, R., Space Systems Failures: Disasters and Rescues of Satellites, Rockets and Space Probes. Dordrecht: Springer, 2005.
Moskowitz, Clara. “Last Space Shuttle Rocket Boosters Delivered to NASA.” Space.com. Space.com., 28 May, 2010. Web 3 July 2010.
“NASA-STD-8719.7, Chapter 7: Other Hazard Analysis Methodologies.” NASA, January, 1998. Web 3 July 2010.
Rep. Rohrabacher. “H.R. 2504 Zero Gravity, Zero Tax Act of 2001 (Introduced in the House), 107th United States Congress, 1st Session, H. R. 2504.” Space Ref.com. Space Reference, 16 July 2001. Web 3 July 2010.
“Risk Management.” The Aerospace Corporation. Web 3 July 2010.

Stuck with your Research Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

