 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Two Head Sculptures From Two Different Eras in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston Massachusetts, Research Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Research Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

The two objects chosen to report a formal and contextual analysis were the “Reserve Head of Nofer” and the “Portrait of Augustus”. Both of these pieces of art are displaced at the Museum of Fine Arts in Boston, Massachusetts. The “Reserve Head of Nofer” is located on the 2nd floor in the Old Kingdom Egyptian gallery off rotunda in a glass case. “The Portrait of Augustus Roman” is also located on the 2nd floor in the Roman gallery on a pedestal in the middle of one long wall. This paper analyzes the description of the objects in terms of the material used to construct the art and the identification and explanation of the artwork. In addition, the paper explores the meaning and the function of the pieces of art. Furthermore, the two pieces of artwork are compared and contrasted in regard to their formal components.
The “Reserve Head of Nofer” is an Egyptian sculpture dating back between 2551-2494 B.C. It is 27.1 cm in height and is constructed of limestone. As seen in Figure 1, the sculpture is a portrait-like sculpture of what Nofer may have looked like. The sculpture is represented with a slightly elongated face, high cheekbones, square chin and a large prominent nose. In the sculpture, it is recognized that there are rough cuttings on the edges of the nose, ears and hairline, suggesting the there may have been finer details made of plaster that have been removed or damaged over time. (MFA Online a)
This sculpture, like other pieces of artwork found with Nofer’s image, all have the prominent nose. For instance, the prominent nose is also carved on the relief sculpture found in Nofer’s chapel. This was a limestone relief from the Giza tomb of Nofer dating back to the 4th Dynasty. It was part of the right jam to the entrance of Nofer’s chapel. In addition, the other sculptures found on the doorjamb of Nofer’s chapel and in his tomb shaft not only have the prominent nose, but are three times larger than other art figures found in his tomb and chapel. This suggests that Nofer was a prominent figure during the Dynasty 4. (MFA Online a)
There is no religious or mythological theme to the sculpture, only the depiction of someone of importance during that time. In addition, the only story that can be depicted from this sculpture is that one of signifying strength and power that Nofer had over the people during that time. This sculpture also represents the title that Nofer held, his honor. It has been researched that his titles were referred to as “both real and honorary, overseer of the treasury, overseer of the king’s regalia, overseer of the arsenal, and secretary of all the secrets of the king, estate manager, and royal scribe. (MFA Online a). In addition, it is also good to note that reserve heads of people that were not of importance would not have existed during the Era, or would have not exhibited strong characteristics.
An in-depth look at the face characteristics in the sculpture resemble other characteristics that were found in the royal family, the Cheops. Nofer’s expression on the mouth suggests power and strength. Nofer did not belong to the royal family; however, his mouth shows no irregularity compared to other male heads that exhibit an irritable expression around the mouth. The sculpture of Nofer’s head is said to belong to the school of sculpture initiated by restrained idealism. This was noted after examining the sculptures completed during the following Egyptian reign. (Smith 37)
The “Reserve Head of Nofer” also connects to other pieces of artwork during the Dynasty IV. There is a similar quality to that of the reliefs that were constructed. For instance, the reliefs for both Heminun (another high figure) and Nofer were both from stone chapels during the reign of the Cheops. This was also before the reliefs were replaced with mud-brick offering rooms. The quality of the pieces, however, was both similar in quality and both exhibited the prominent features on the face, such as the prominent nose. This also further justifies the use of the sculptures as a funeral purpose, as both the relief and the reserve heads were found with the deceased. (Smith 37)
The purpose of the “Reserve Head of Nofer” has been argued and theorized by many. It has been indicated that the reserve heads were used to serve as a ritualistic or spiritual object in place of the real head of the dead. Another theory states that the reserve heads were used as molds in order for sculptors to make more sculptures of the deceased. Another interesting point is that all of the reserve heads, including “Reserve Head of Nofer” have damaged ears. The ears have been broken. It is possible that the ears were broken intentionally in order to keep a quiet place for the dead.
The other piece of artwork examined in this paper is the “Portrait of Augustus”. This piece of art is classified as a sculpture as well that was made during the Roman, Imperial Period. More specifically, it is a free-standing portrait bust. The height is 54.4 centimeters (21 7/16 inches). The sculpture is made of diorite; however, possibly basalt. The technique used to sculpt is known as “In-the round”. The style is referred to as Julio Claudian. This sculpture is noted to have had 18th century restorations. The statue was found near Ariccia, which is near the City of Rome in Italy. The “Portrait of Augustus” has many features suggesting that it dated back to the late 30s or 40s A.D.; however, the curling of the hair is more likely to have been from the second century. (MFA Online b).
The tip of the nose in the sculpture has been restored. The edges of the ears are also chipped. The surface of the sculpture is cracked and somewhat worn looking. One individual, R. Delbrueck referred to this artwork as a replica of the bronze bust in the Vatican Library. There has also been some debate whether this was a portrait of Julius Cesar and not the Emperor Augustus. For instance, L.D. Casky, points out in his catalogue of the sculpture that the form of the bust is Julio-Claudian style and that it was most likely in Rome area in antiquity. In addition, he states that the selected material used by the artist was used in order to give the appearance of antiqued bronze and that this type of style gives no firm indication whether the piece was sculpted in Egypt of ancient Rome. He also indicates that the carving in the sculpture is only “okay” and not up to par with the Julio-Claudian quality. He indicates that this type of artwork was usually found in the funerary portraits of people in Rome during the first century A.D. (MFA Online b).
As mentioned previously, the sculpture is made out of diorite. The type of material is not the impressive or expensive type of marble that could have been used. For instance, in the other sculpture portrait of the Emperor Augustus, named “Augustus” and also found at the Museum of Fine Art in Boston, Massachusetts, again we see Augustus’ portrait with curling locks of hair, a soft bone structure in the face and no wrinkles. The only difference is the type of material used. The “Augustus” sculpture used Marble. Marble is one of the most impressive and expensive materials. This was completely opposite of the “Portrait of Augustus”, where only diorite was used. In addition, the “Augustus” piece compares to art work seen in Greek statues constructed of athletes and mythological gods. (MFA Online c). Again, there is a complete difference between these two sculptures. The function of the sculpture is therefore, unknown. Since it is not constructed from the most expensive material and there has been debate on whether or not the sculpture was created by an excellent artist, perhaps this statue was a personal statue not used at the Emperors palace. Although the function of the sculpture is unknown, it is also possible that the diorite that was used to construct the sculpture was used in order to resemble bronze and make the sculpture look more captivating.
The two pieces of artwork analyzed in this paper have both similarities and differences. Although both of the sculptures are of male heads, the similarities and differences range from time period, location, style, and purpose. The “Head Reserve of Nofer” and the “Portrait of Augustus” were both constructed over 2000 years apart in time. The “Head Reserve of Nofer” was sculpted around 2000 years B.C., while the “Portrait of Augustus” was sculpted around 30 A.D. In addition, the two sculptures were constructed in different locations and from different civilizations. The “Head Reserve of Nofer” was found in Giza, Egypt; whereas, the “Portrait of Augustus” was found in a City near Rome, Italy. It is fascinating to see such similar pieces of art from two completely different cultures.
In addition, the style differed in construction. The style of the Egyptians seemed to exemplify strength and authority; whereas, the style of the Romans seemed to exhibit more and an idealistic or god-like quality. This is shown in the differences in the face structures. The “Head Reserve of Nofer” has strong cheekbones and a prominent nose; whereas, the “Portrait of Augustus”, has softer qualities in his face. Even the hair is softer. The “Reserve of Nofer” has this hard short hair; whereas, Augustus has these locks of curls, again showing some idealism.
The main difference between the sculptures is the purpose. Although there is not a clear purpose in either of the sculptures, it has been suggested that the Egyptians used these sculptures for the deceased. It has not been indicated anywhere that the Romans used these types of sculptures for the deceased.
Overall, both of the cultures constructed head sculptures of their high officials. Nofer was not a King or Emperor; however, it was recognized that he was an official during the Dynasty IV. Augustus was the Emperor at the time of this sculpture. It is therefore interesting to compare the two pieces of art that were created 2000 years apart from different cultures and with such striking similarities. This is probably one of the reasons that the curators at the Museum of Fine Arts in Boston Massachusetts placed these two art works near each other, to compare and contrast the head sculptures from two completely different historical civilizations.
Figure1. “Reserve Head of Nofer”
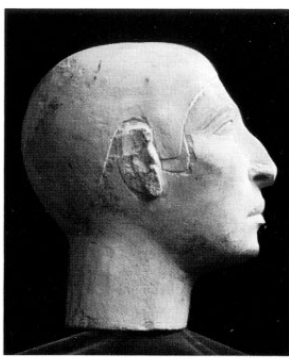
http://educators.mfa.org/objects/detail/178256?classification=Sculpture&page=78
Figure 2. “Portrait of Augustus”

http://www.mfa.org/collections/object/portrait-of-augustus-151324
Works Cited
MFA Online (a). “Reserve Head of Nofer”. 2012. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. Web. http://educators.mfa.org/objects/detail/178256?classification=Sculpture&page=78
MFA Online (b). “Portrait of Augustus”. 2012. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. Web. http://www.mfa.org/collections/object/portrait-of-augustus-151324
MFA Online (c). “Augustus”. 2012. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. Web. http://www.mfa.org/collections/object/151325
Smith, W. Ancient Egypt as represented in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. 6th edition. 1960.
Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, Massachusetts.

Stuck with your Research Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

