Virtual Society, Research Paper Example
Virtual society is a product of psychological needs for people who generally do not satisfy their social lives in real world.
Introduction
This paper examines the psychological aspects of the virtual society. In this context virtual societies or communities are those that engage in social networking using cyber space or a virtualistic world using a computer as a media for communication. Examples being chat lines, social networking sites like ‘Twitter’ and ‘Linked in’. The concept of virtual being distinct from real or face to face contact in real time. This environment permits the creation of avatars or three dimensional software images used to depict a person and their personality. The paper will explore : (i) The motivation of society to move into a virtual world (ii) The psychological considerations for the need of this environment (iii) The concept of social inadequacy and how the virtual environment addresses the remedial situation (iv) How this concept might evolve in the future and the psychological considerations for same. Does the Virtual Society really meet the needs of socially deprived people or are we dealing with a new form of psychological phenomenon?
Psychological Considerations
Howard Rheingold discussed the virtual community in the online world. He talks about having a network of invisible friends and his young daughter seeing him interact with these on his computer. Equally his talking to them through the computer media ( the virtual world) becomes materialistic when these invisible friends turn up at the door from overseas or different parts of the neighbourhood. Fantasy then becomes reality. Rheingold points out that the advantages of the virtual community allow you to work across space, time and organizational boundaries. He states that this technology changes our personality and the way in which we communicate with people, with the virtual world taking over from the reality of our living world. He moves this claim to a darker side saying that these communities can result in increased attitude polarization amongst individuals, increased prejudice and facilitate sick people to deliberately indulge in their disease. ” The most important critical uncertainty today is how we learn to use digital media and networks effectively, reasonably, credibly, collaboratively, civilly, and humanely. This difference is a matter of literacy–the norms of behaviour as well as the skills of encoding and decoding blogs, wikis, forums, vlogs, microblogs, search engines, text messages, and whatever a local teenager cooks up tomorrow in her basement or dorm room.” (Rheingold, 2010).
Human beings are social anaimals and require social support. This being physical and emotional comforts that are provided to us by our family and friends. We need to know a sense of belonging and that we are part of a community that loves and cares for us. Research studies have denmomstrated that social support is a moderating factor against diseases like clinical depression or hypertension. Such support being rendered by social interaction and participation in a real time environment with other humans. How this all translates to life in a virtual environment is relatively uncharted territory. ” A Google word count (conducted at April 23th, 2007) gives 1 220 000 hits for “virtual community”, while the polar term “virtual society”) lags hopelessly behind with only 108 000 counts. Apart from the psychological need to identify something highly familiar in a new technical environment, there may also more serious epistemological reasons why the community focus was preferred ” . (Geser, 2007).
The recent film Avatar has provided us with a glimpse of how the future might unfold with virtual beings created where we can live a “second life” defined by our rules and conditions in a virtual world. A programmable life is the antitheses of our normal life which is random, unpredicatable and built upon creative thought. ” Second Life has no narrative. It has no soul. It is an unruly chaos without any mythology…without a real story that I can wrap myself around in. With all of its residents…and all that they’ve built…it feels very empty and leaves me feeling cold and detached. While there are no “rules” and the world is largely capable of anything the users wish it to be or do…it is that lack of structure that makes me not care. It simply isn’t enough to buy a piece of virtual land and put something on it. Without story, without mythology, without a living and progressing narrative…without goals and dreams…what’s the point?” (Graham 2007).” (Geser, 2007).
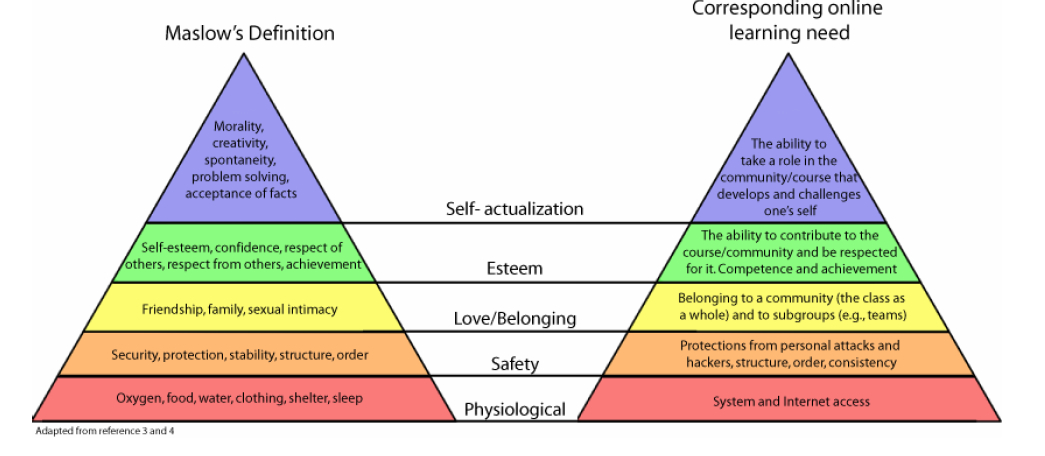
Source: (Furendal & Fredrik Björnskiöld, 2007)
Maslow’s model shows that people need to communicate with one another. The concept of being seen and gaining another persons attention. The model above, as depicted by Furendahl and Bjornskiold, shows that the online or virtual community satisfies the top three of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs i.e. self actualization, esteem and love/belonging. The internet allows you to meet a diverse community of people from all around the world, people who share the same interests, concerns and needs like yourself. This level of interaction further stimulated by use of webcams and audio/visual experiences. The model pointed out that in order to satisfy the top three levels of Maslow’s Hierarchy, then the bottom levels need to be satisfied too. The considers concepts of connectivity and security to the internet. The user needs to feel safe in this environment otherwise they will not use it.
Nick Yee of Stanford University raised some interesting concerns relative to how the concept of the virtual communities are developing ” In the physical world, two people interacting in the same space necessarily share the same reality. On the other hand, in a virtual environment where users view the shared environment from their own computer terminals or virtual reality goggles, their realities need not be congruent. Thus, for example, I may perceive my avatar (a digital representation of myself) to be short while you perceive my avatar to be tall. These non-congruent reality scenarios open up a range of research questions in stereotype threat, behavioural confirmation, and self-perception theory among other psychological theories.” (Yee, 2007).
Concept of Social inadequacy
By joining a virtual community on the internet you are subscribing to a group with common interests, opinions, goals in a virtual state as opposed to physical proximity. Hence relationships can be formed in this environment by describing common interests through text based discussion. The people participating continue the stimulus and thereby the community is self perpetuating, self generating and self regulating. People participating may therefore be said to be both an audience member and performer at the same time. By means of avatars individuals can represent themselves in different format to others. A shy, withdrawn person with poor personality traits may represent himself as a Norse God Thor with his hammer, strong physical body build and ferocious look, thereby dealing with his own social inadequacies in his virtual world. A person who has been stricken with the horrors of war may react by selecting an avatar of a dove representing serenity and peace.
The darker side to this is it creates an environment for predatory beings to gain contact with young children. Child molesters can use the internet to search out young people, gain their trust and confidence in a virtual world and then solicit contact information from them for the real world. Thereby creating a conduit from the virtual or artificial world to the real physical world. Hence the safety net of the virtual world is lifted by the passing of real information to the predator who now has ways of contacting you in the physical world. Despite police monitoring of prime suspect sites it is virtually impossible to police the internet with the millions if not billions of users on the system. This type of activity can also be used to promote drug use, pornography and prostitution. It also facilitates trafficking of people, young people from poor countries like the Philippines offering marriage to older men for the rights to live in more affluent countries like the USA and Canada. This represents a new and different type of immigration control problem for countries in Europe, USA, Canada, Australia etc. It is difficult to restrict freedom of movement whilst trying to restrict the more immoral side of this behaviour.
The other aspect is that of the dehumanization of people as individuals. This new virtual society will result in less personal and social interaction and place us out of touch with the physical reality in which we live. It is a fearful prospect for the future and one which may be the crossroads for mankind and the technology which is supposed to support individual growth. Mass escapism into created virtual worlds will ultimately create a new type of human personality. ” The issue of dehumanization in our society is a another negative aspect. It is essential to our existence that we maintain a humanistic mindset and not become overrun by a technology immersed world. Virtual reality, if as widespread as predicted, could result in a significant decrease in human interaction in the real world. It’s advantageous for building stronger companies and so on; but what will our society turn into if everyone is walking around in goggles and gloves pretending they are somewhere that doesn’t even exist?” (123helpme.com, 2010).
How the concept might evolve
The concept of people spending 1/3rd of their life in virtual societies is tantamount to losing your grip on reality. Living out mass fantasies may also result in increased suicidal tendencies, increased violence in the physical world and breakdown in social relationships. It will also be questionable in terms of your learning experience, learning in simulations is different to real life experiences. ” virtual reality defeats the traditional view that fantasy is unattainable. In a way fantasy and what we cannot obtain is intrinsic to our existence. People may begin to spend more and more time in their preferred “virtual or fantasy world” and less time in reality. One researcher says that if, “people eventually use virtual reality technology for the same amount of time that they spend watching TV and using computers, some users could end up spending more than twenty years inside virtual reality” (Biocca 14). If we begin to lose our hold on distinguishing between fantasy and reality, our entire world will become uncertain.” (123helpme.com, 2010).
We have all experienced one kind of virtual reality over the last 100 years, this is the Telephone. The ability to talk with another person over long distance. This was the audio virtual experience. The onset of Television provided the link of video with the audio experience. As this concept progressed we discovered the power of the IMAX theatre and the sophistication of 3D with films like AVATAR taking us into a new realm of experience. A decade or so earlier we experienced Sensurround that enabled us to feel motion and sound in association with the film. Films like Earthquake and Rollercoaster provided a new experience of placing our senses into a virtual world. The speed of technological progress over the last 100 years has been truly remarkable. It has changed the very society in which we live. The next 50 years look like being equally remarkable and equally somewhat disturbing ” By the end of this decade, we will have full-immersion visual-auditory environments, populated by realistic-looking virtual humans. These technologies are evolving today at an accelerating pace, as reflected in the book Virtual Humans. By the 2030s, virtual reality will be totally realistic and compelling and we will spend most of our time in virtual environments. By the 2040s, even people of biological origin are likely to have the vast majority of their thinking processes taking place in nonbiological substrates. We will all become virtual humans.” (Kurzweil, 2003)
We are really at the dawn of Artificial Intelligence technology and the introduction of this into virtual reality computer systems or simulations. The advent of robotic technology is equally at a very young stage of evolution. The complexity of this science will both benefit and baffle us all as it gets rolled out into every day usage. We are now at the stage of genetic re-engineering and possible cloning of animals and human beings. Essentially a tipping point where mankind may ultimately relinquish control to machines. Films like the Terminator have already projected a potential outcome to this scenario ” Virtual reality and virtual humans will become a profoundly transforming technology by 2030. By then, nanobots (robots the size of human blood cells or smaller, built with key features at the multi-nanometer—billionth of a meter—scale) will provide fully immersive, totally convincing virtual reality in the following way. The nanobots take up positions in close physical proximity to every interneuronal connection coming from all of our senses (e.g., eyes, ears, skin).” The concept of microscopic inspection and the building of minute machinery contrasts starkly with our ability to look out towards the universe and travel to the stars. We are already researching concepts of the ability to create machine engines that potentially can fold space and provide us with the ability to travel across the Universe. Computer simulations will be used as the testing grounds in order to build hypothetical technologically advanced solutions, thereby practicing safe technology.
It is considered that by the time we reach 2030, some 20 years from now, we will start to see the distinction between real and virtual people start to erode. Hence biological people will have enhanced themselves with nanobot technology to combat disease, prolong life, improve learning abilities, increase strength etc. There is also the possibility of communication inplants that will connect us to the virtual world of the internet. ” By 2030, going to a web site will mean entering a full-immersion virtual-reality environment. In addition to encompassing all of the senses, these shared environments could include emotional overlays, since the nanobots will be capable of triggering the neurological correlates of emotions, sexual pleasure, and other derivatives of our sensory experience and mental reactions.” (Kurzweil, 2003)
The integration of machinery into our physical being moves us closer into the concept of the cyborg ( part robotic, part human being) and we are already witnessing elements of this with medical implants, pacemakers, etc. ” Nonbiological intelligence has already secured a foothold in our brains. There are many people walking around whose brains are now a hybrid of biological thinking with computer implants (e.g., a neural implant for Parkinson’s Disease that replaces the function of the biological cells destroyed by that disease). (Kurzweil, 2003)
In Japan they are already creating the virtual city where you create your avatar and enter a virtual reality City for entertainment and online shopping experience. ” Inspired in part by the Music Room type applications, the city is an actual city, inhabited by a multitude of participants, and each with their own purposes. Imagine a virtual city complete with private spaces or domiciles, parks, stores, entertainment centers. As much as a grand social experiment, it also is a far reaching graphical user interface (GUI) for electronic home shopping and entertainment. Precedent for such an application as the city is Habitat, a commercial online service available from Fujitsu in Japan, which features two dimensional applications, and currently has 10,000 subscribers.” (Loeffler, 1992)
Works Cited
123helpme.com. (2010). Essay on Benefits and Dangers of Virtual Reality. 123helpme.com.
Furendal, D., & Fredrik Björnskiöld. (2007). Quality of life:Can online communities satisfy Maslow’s hierarchy of needs? Stockholm: Umea University Sweden.
Geser, H. (2007, 4). A very real Virtual Society. Retrieved 1 27, 2010, from Towards Cybersociety and “Vireal” Social Relations: http://socio.ch/intcom/t_hgeser18.htm
Kurzweil, R. (2003). Virtual Humans. Amacom.
Loeffler, C. E. (1992). Distributed Virtual Reality:. Retrieved 1 22, 2010, from Distributed Virtual Reality:: http://www.w3.org/People/howcome/p/telektronikk-4-93/Loeffler_C_E.html#KREF12
Rheingold, H. (2010). Key Literacies for the 21st Century . Retrieved 1 27, 2010, from Monitor Talent: http://www.monitortalent.com/talent/Howard-Rheingold-Profile.html
Yee, N. (2007, 6 11). Psychological research in virtual worlds . Retrieved 1 27, 2010, from The British Pysychological Society: http://bps-research-digest.blogspot.com/2007/06/psychological-research-in-virtual.html

Time is precious
don’t waste it!

Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee






