 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Adding Microprocessors to Rubber Mixing Equipment: Oil Well Cable Company Inc, Case Study Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Case Study
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Executive Summary
The operation manager, Norm St. Laurent, for Oilwell Cable Company recommended an idea to the general manager, Bill Russell, that adding microprocessors to the rubbing mixing equipment would save manual adjustments on the machines, as well as increase improvements and reduce costs. In addition, the change would not replace employees. The problem that Norm St. Laurent was debating was the need to submit the idea and discuss the idea with the production team before implementing the new change. The company uses a “Team Management Process”, which allows for more responsibility of an individual employee, such as creating their own work schedule, as well as the team being part of the decision making process for changes.
The disadvantage to the Team Management process system is the amount of time that would require the team to discuss the new idea and implement the new idea. The operation manager had already reviewed the microprocessing process and analyzed the outcome to indicate that the addition of the microprocessors would in fact reduce costs and cut production time by 1 percent and reduce scrap rate by a half percent. It seems this process would benefit the company according to the operation manager. The operation manager needs to set forth a plan of action to make the decision at the executive level and implement the new procedure, without consulting the team.
Statement of the Problem
The original manager, Gino Strappoli, of the Oilwell Cable Company, formally known as Chord Cable Company, was to structure the company to include everyone having some sort of decision responsibility, even the employees in the production department. His decision to structure the company in this direction was based on the fact that the company was a continuous manufacturing process, which included quick decision making. Gino left the company and was replaced by Bill Russel, who continued to include the team in the decisions. Norm St. Laurent then replaced Bill Russell. Norm St. Laurent realized that company could operate at the same level with involving only the executives. The company’s management was put forth with a decision, as to if they should continue to use the Team Management process, or let the management itself make more decisions without the teams involvement. The employees have responded in the past indicating that they did appreciate the involvement from the management; however, on certain parts of the business, they did not want the responsibility, along with the amount of time and energy it took. Therefore, the production manager was faced with the decision of whether he should move forward with implementing the microproccessing procedure and make the decision at the executive level, or if he should include the production team as the company has done in the past.
Causes of the Problem
As indicated in the Statement of the Problem, the production manager was faced with the decision of whether or not he should move forward without consulting the production team of the company before implementing the microprocessor procedure into the production procedure. The company has been working with the strategy of a “Team Management” process; however, the current production manager, Norm St. Laurent, was aware that the company could progress without including the “Team Management” and making the decisions through “Executive Management”. In addition, Norm found two disadvantages of the Team Management style, time and energy required for employees to make decisions. Norm, therefore was stepping up and managing the company based on objectives. “Management by Objectives”, involves analyzing different aspects of the company and ensuring that the objectives are being conducted. (The Times 100) In the past, the company was run by a consultative manager, who consults others, such as employees to find out their views before making the decision. (The Times 100)
The type of management style chosen should depend on the given situation, the type of company, the time needed for the decision to be made, and the perspective reaction of the employees to the change for the given situation. For instance, there was a case study conducted for the Fortune 500 retailer responsible for a popular web site that merged with another company. The two companies began to experience different challenges that decreased the cost and productivity. It was found that there was competition within the team members which caused the lack of the company to move forward. The solution was to create a structure where the team’s members could help each other and build team success. (5.12 Solutions Consulting Group) In this case, the type of management style was chosen based on the situation and company, as well as their employee’s needs. In regard to the OilWell Cable Company, the situation is implementing a new process without consulting the team. The production manager feels that there is a possibility that the team may not respond well without being consulted, as it had happened previously with a minor change to production. However, the production manager has found the facts and knows that the change will increase productivity. In addition, the production manager is aware that the does not want to be a part of every decision making process at the business level.
The production manager needs to implement a strategic management plan. A strategic management plan would include the stakeholders, which in this case could be referred to as the employees. Stakeholders are individuals who have a part in the success of the company. It has been found that managers would not be successful if they only emphasized on one stakeholder. For instance, if the company was only interested in gaining profits, the employees may feel resentment and customer service decreases; however, in cases where stakeholders take multiple stakeholders into account, the organization satisfies all needs and the company progresses. (Dess, 2005)
Decision Criteria and Alternative Solutions
The production manager’s analysis of data concerning the implementation of the microprocessor found that the production time would be decrease 1 % and the scrap rate would reduce to 0.5%. In addition, it would reduce the need for manual adjustments on the field and most importantly, not reduce the number of employees. The production manager is also aware that the employees have noted the amount of time and energy that was needed in being a par to f the decision making process. For instance, when the team was given the task of putting together a layoff list, it took three days for them to develop a list, which increased for their normal meeting of once a week a 1.5 hours. Furthermore, the team had indicated that they were okay with not every decision being placed on them and had also indicated that there was some difficulty in facing management on decisions. In addition to the time, the cost of the meetings and decision making puts production back and increases the cost. Furthermore, the production manager already has made the decision. He understands this is the best move; therefore, the acceptability of the production manager to the input of the team members is low.
There are a couple possible alternatives to make all stakeholders in this decision feel comfortable. One alternative should be a formal meeting for the team with lunch provided. Since the team is used to giving their input on the decision making, the production manager should hold a formal meeting describing the events with his decision, as well as the benefits for the decision, for the company and employees. In addition, the production manager should focus on the benefits of the employees with the new change, such as a decrease in manual repairs and no change in employee status. Providing lunch would just show the company appreciation to for their understanding.
Another alternative would be to involve the employees, as conducted in the past. The benefit to this situation is that the employees are used to this process; however, the disadvantage is that the management team is still relying on employee time and energy, as well as not being able to make their own executive decisions. In addition, if the employees do not agree with the new process, ultimately, the management team needs to make the final decision and therefore, the time, money, and energy spent on convincing the team would be wasteful.
Recommended Solution, Implementation, and Justification
The recommended plan is for the project manager, Norm St. Laurent, to begin implementing the process without consulting the team. The first timely event would be to schedule a meeting with Bill Russell, the general manager, indicating his plan of action. The second step would be to put together the plan of implementation and then include the team members in a lunch meeting over viewing the new change. Including the team members in the overview with resolve the issue of the members not feeling included in the decision. The project
Manager should incorporate a Strategic Management Model (as seen in Figure 1) describing the course of action and the implementation of the new plan. The employees having a visualization of the plan will be more receptive to the idea. In addition, there should be a contingency plan in order in case there is difficulty with the decision and the employees. The production manager should provide a comment box for anyone who has concerns and ensure that the management overviews and tries to deal with employees who are dissatisfied.
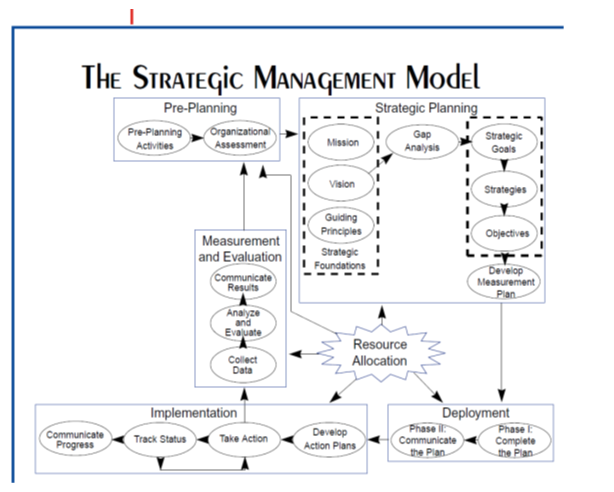
Figure 1. Strategic Management Model. (Wells)
References
5.12 Solutions Consulting Group. (2012). Fortune 500 Retail/Product Company. Retrieved on
May 10, 2013 from: http://www.512solutions.com/about-us/case-studies/management-team-building-case-study
Dess, G., Lumpkin, G.T., Taylor, M.L. (2005). Strategic Management. 2 ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
The Times 100. (2013). Methods of Management. Retrieved on May 10, 2013 from: http://businesscasestudies.co.uk/business-theory/people/methods-of-management.html
Wells, D. L. Strategic Management for Senior Leaders: A Handbook for Implementation.
Department of the Navy Total Quality Leadership Office. Retrieved on May 10, 2013 from: http://govinfo.library.unt.edu/npr/initiati/mfr/managebk.pdf.

Stuck with your Case Study?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Tags:

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

