All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Articulations & Body Movements, Micro Anatomy & Organization of Skeletal, Lab Report Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Lab Report
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Introduction
During this week of lab activities, the main goals were to continue the examination of the skeletal system, focusing on articulations, or joints, and also to examine the microscopic and gross anatomy of the muscular system. This week was also a hands on approach when examining joint movement, types, and functions. In the examination of microscopic musculature, we viewed slides of skeletal muscles (longitudinal and cross section) under the microscope, but did a physical examination when viewing gross musculature. My belief is that these laboratory exercises will be enlightening, astounding, and exciting. I am sure using our bodies to further our understanding of the material will be an aid to help us remember more about the material.
Procedures
In order to learn more about articulations and body movement, microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscles, and the gross anatomy of skeletal muscles, the lab had several activities to perform. Joints and body movement activity one required us to examine a skull, a skeleton, and an anatomical chart for fibrous joint examples. . Joints and body movement activity two required us to use a skeleton and an anatomical chart of joint types to identify cartilaginous joints. Joints and body movement activity three required that we examine a beef bone to identify structural features of a diarthrotic joint. Joints and body movement activity five required us to read the material on types of joints and to use our bodies to manipulate each joint type on ourselves.
Microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscles activity one mandated that we examine the 3-D model of a skeletal muscle cell and then compare it to a skeletal muscle cell that we examined under the microscopic. Microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscles activity two used the microscope to examine the structure of a skeletal muscle, making note of all the parts.
Gross anatomy of the musculature system activity one required that we identify the head and neck muscles using the display torso, an anatomical chart, and also our bodies. Gross anatomy of the musculature system activity two required that we view the pictures of muscles in the lab manual, use the torso and chart to identify the muscles of the trunk.
Materials
Joints and body movement materials included articulated skeleton, skull, Diarthrotic beef joint, disposable gloves, water balloons, clamps, anatomical chart of joint types, and x-ray images of normal and arthritic joints.
Microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscles materials included three dimensional model of skeletal muscle cells, three dimensional model of skeletal muscle showing neuromuscular joint, prepared slides of skeletal muscles, and prepared slides of skeletal muscles showing neuromuscular junctions.
Gross anatomy of the muscular system materials included human torso model or large anatomical chart showing human musculature, tubes of face paint, one inch wide artist bristle brushes, and the video tape-Human Musculature.
Methods
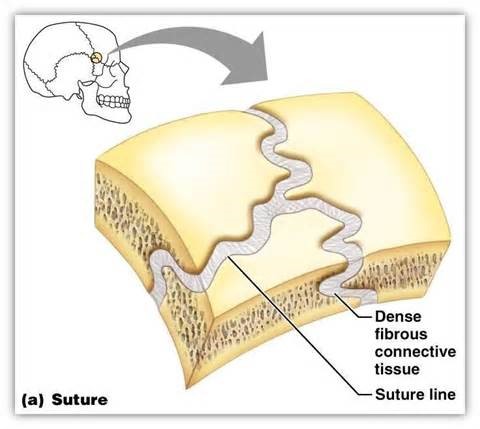
Joints and body movement activity one, first step was to examine the skull from the display. Secondly, notice that the skull plates were separated by ossified fibrous connective tissue joints. Next step was to use the chart and torso to identify other examples of fibrous joints. Joints and body movement activity two, only step was to use the chart and skeleton to identify cartilaginous joints. Joints and body movement activity three, step one was to put on gloves. Step two was to examine the general structures of a diarthrotic beef bone. Joints and body movement activity five, first step was to read the material on joint types. Secondly, manipulate each type of joint identified on myself and the articulated skeleton.
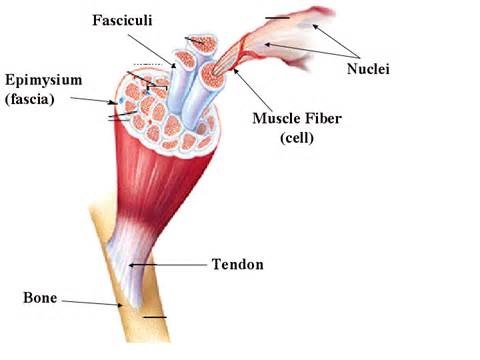
Microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscles activity one, first step was to examine the 3-D model of the skeletal muscle cell, paying attention to shape, size, and parts. The second step was to examine a skeletal muscle cell under the microscope. The final step was to compare the results of the first two steps. Microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscles activity two, only step was to examine a section of a skeletal muscle under the microscope, identifying the parts.
Gross anatomy of the muscular system activity one, first step read the information in the tables about head and neck muscles. Then, use the display torso or the chart to identify the muscles. Lastly, identify the muscles on myself. Gross anatomy of the muscular system activity two, step one was to read the information about trunk muscles shown in the tables in the lab manual. The second step was to identify the muscles in the pictures. Third, identify the muscle on the charts and the display torso.
Results
The results of activity one from joints and body movement included the identification of fibrous joints of the skull. Activity two from joints and body movement results ended an identification of cartilaginous joints in the body. The results of joints and body movement activity three was identification of a diarthrotic bone joint. Activity five joints and body movement results were identification of each joint type located on my body.
Skull Joint
The results of activity one from microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscles was gaining insight about how the structures of a microscopic skeletal cell actually looked as compared to how the 3 D-model showed it to look. The results from activity two of microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscles was to gain knowledge about the structures of a skeletal muscle specimen.
Skeletal Muscle Cell
The results of activity one from gross anatomy of the muscular system was identification of the muscles of the head and neck. The results of activity two from the gross anatomy of the muscular system was identification of muscles of the trunk and their location within the body.
Conclusion
This week of laboratory activities focused on examining the joints of the skeleton and their assistance in movement of the body. This was also very hands on lab where we used our bodies to aid us in identification of joints and skeletal muscles. We also used the microscope to examine a section of a skeletal muscle. I concluded from these activities that the joints are specially designed to assist body movements. Skeletal muscles are designed to be able to both contract and expand, working with joints to move the body.

Stuck with your Lab Report?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Tags:

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee