Cloud Computing and Management Implications, Capstone Project Example
Abstract
The objective of this study is to examine the future of business applications through cloud computing and the implications for management. This work will focus on businesses in Ghana and answer the question of how cloud computing will affect businesses in Ghana, particularly in the banking and telecommunication sector. This work will also address how this technology will affect traditional IT companies and employment and answer the question of what challenges exist to cloud computing in Ghana and how these challenges might be overcome. Also addressed is the question of who it is that stands to benefit the most. This work will examine any laws that could serve to hinder cloud computing in Ghana and answer how individuals in Ghana would react to security issues that are associated with cloud computing. Finally, this work will examine how cloud computing might affect economic growth in Ghana.
The Future of Business Applications Using Cloud Computing and Management Implications: A Case of Businesses in Ghana
Objective
The objective of this study is to examine the future of business applications through cloud computing and the implications for management. This work will focus on businesses in Ghana and answer the question of how cloud computing will affect businesses in Ghana, particularly in the banking and telecommunication sector. This work will also address how this technology will affect traditional IT companies and employment and answer the question of what challenges exist to cloud computing in Ghana and how these challenges might be overcome. Also addressed is the question of who it is that stands to benefit the most. This work will examine any laws that could serve to hinder cloud computing in Ghana and answer how individuals in Ghana would react to security issues that are associated with cloud computing. Finally, this work will examine how cloud computing might affect economic growth in Ghana.
Examination of ‘Cloud Computing’
Cloud computing is reported to enable agility and to offer benefits that are both “real and powerful”. (Golden, 2010) Agility is reported to be “…tied to the rapid provisioning of computer resources. Cloud environments can usually provide new compute instances or storage in minutes, a far cry from the very common weeks (or months, in some organizations) the same provisioning process can take in typical IT shops.” (Golden, 2010) Agility can then be defined as the “power of moving quickly and easily, nimbleness.” (Golden, 2010)
Golden states that if cloud computing “comes to be seen as an internal IT optimization with little effect on how quickly compute capability rolls out into mainline business processes, the potential exists for IT to never receive the business unit support it requires to fund the shift to cloud computing. It may be that cloud computing will end up like virtualization, which in many organizations is stuck at 20 percent or 30 percent penetration, unable to garner the funding necessary to support wider implementation. If the move to cloud computing is presented as “helps our programmers program faster,” necessary funding will probably never materialize.” (2010) Golden relates that more value can be offered to customers through “the ability to surround a physical product or service with supporting applications” and as well this provides the vendor with a competitive advantage. In addition, “knowing how to take advantage of cloud computing to speed delivery of complementary applications into the marketplace is crucial to win in the future. Failing to optimize the application delivery supply chain will hamper companies as they battle it out in the marketplace.” (Golden, 2010)
Vikas Aggarwal (nd) states in the work entitled “How to Effectively & Efficiently Monitor Your Cloud Computing Infrastructure” software applications “…and the underlying computing infrastructure are essential enablers of business processes in today’s technology-dependent enterprise environment. Almost every single business activity – from taking an order from a customer to delivering purchased products – depends directly on the effective performance of the Information Technology (IT).”
According to Aggarwal there have been various tools and approaches used by organizations in monitoring their networks and ensuring “…optimum performance of their enterprise IT infrastructure. It is clear though that traditional network management tools have been stretched to the limit, given the widespread adoption of multi-tier applications, distributed computing, and Internet technologies in recent years. The arrival of cloud computing, the latest evolution in IT, creates a new set of challenges that require innovative monitoring tools to help businesses leverage its cost and efficiency benefits, while mitigating the risks of underperforming infrastructure.” (nd)
Cloud computing includes the use of “virtualization, grid architectures, and software as a service application delivery, both inside and outside the boundaries of the enterprise network. This computing approach or ‘technology’ promises significant cost savings and business agility compared with traditional methods of computing. In a cloud environment, a business application, for example, may leverage a combination of in-house vanilla virtual machines, pre-built storefront virtual machines from an external cloud vendor (e.g. Yahoo), and an external application service (e.g. NetSuite).” (Aggarwal, nd)
In addition, various elements of networking and linking compose the infrastructure required to “…ensure the effective functioning of the overall application. This type of complicated environment requires a new approach to network management and monitoring.” (Aggarwal, nd) The focus of management of traditional network management and monitoring systems have had as their focus the measurement and monitoring of “technical metrics and trends of individual elements and components in the infrastructure.” (Aggarwal, nd)
While IT operations are enabled by the systems in identification of challenges of a technical nature there are still gaps in determination of the business impact of specific challenges. The example stated is that should a router and an external application both fail simultaneously “legacy monitoring systems offer no way for the Network Operations Center (NOC) operator to determine which of these is more critical or which business services have been impacted by these failures. When an isolated issue occurs in the complex Web of new technologies – one that may impact one or more user-facing tasks in a business process – the current monitoring approaches are incapable of determining its impact on the business.” (Aggarwal, nd)
Network management is required to make a move from IT infrastructure monitoring to business service availability and performance monitoring and must “go beyond just looking at the performance of individual nodes or components to include a holistic service-oriented view.” (Aggarwal, nd) In order to ensure more reliability of processes and systems in the virtual computing environment it is reported that Business Service Management systems can assist enterprises in connecting processes of business with operations of IT in achieving a perspective that is more holistic. (Aggarwal, nd, paraphrased)
Survey Results on Cloud Computing
Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky write in the work “Navigating the Cloud” that cloud computing enables users to “…procure their IT services on a flexible basis according to their needs, putting companies in an ideal position to meet the dynamic demands of their markets. This enables IT to be flexible and react quickly to accommodate the needs of the business world, which results in cost savings and a more effective use of available capacity.” (2011) There are risks and challenges associated with this and this is reported in a study that sought to make identification of the primary challenges that cloud computing providers face. A study was conducted in which a number of German-based cloud providers were surveyed and it is reported that the study results “illustrate how cloud providers are meeting the current demands of the market.
The survey also provides an overview of the risks and challenges that cloud providers are facing and shows what they need to do to make the use of cloud services successful and profitable for their customers.” (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011) Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky state that it is worthwhile to note, “while this survey was conducted exclusively in Germany, the challenges and opportunities are pertinent to cloud providers around the world.” (2011) There are reported to be three specific factors that were highlighted in the survey: (1) Information security needs to be guaranteed; (2) Data protection ensured and compliance achieved; and (3) Finding solutions for these issues represents a significant challenge for the providers and is an important factor in achieving customer satisfaction. (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011)
Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky (2011) state that cloud computing “…enables companies to procure their IT resources over the internet—on a flexible basis, cost-efficiently, almost limitlessly, and effectively with payment based on consumption. This means that companies no longer need to keep a certain amount of computer capacity or data storage space free, or constantly run applications. This leads to a reduction of necessary capacity, investments and costs for companies, and, most importantly, allows them to structure their specialist departments in new ways.”
The questions that need to be asked by users include those as follows:
- For which purposes, processes or applications would it make sense to use cloud services?
- Does the company know of all the potential risks of the services?
- How should the cloud provider be managed and monitored (sourcing governance)?
- Which conditions need to be met in order to integrate the cloud services into existing IT?
- Which criteria are decisive in choosing the ideal cloud provider? (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky. 2011)
Providers need to consider the following core issues:
- Which user compliance and security requirements should providers fulfill?
- How can data protection be guaranteed when data is stored abroad or in different countries?
- How should data migration, archiving and the return of data to the client be arranged?
Which contractual implications do our approach and business model entail? (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011)
The survey conducted asked how developed is the cloud strategy of your customers and what the general impression were. The following chart shows the responses given by survey participants.
Figure 1
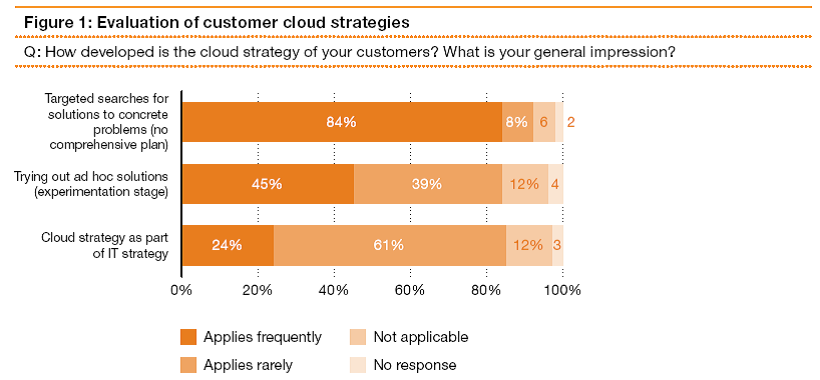
Source: (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011)
Significant factors that affected the satisfaction of customers were found to include those stated in the following chart labeled Figure 2.
Figure 2
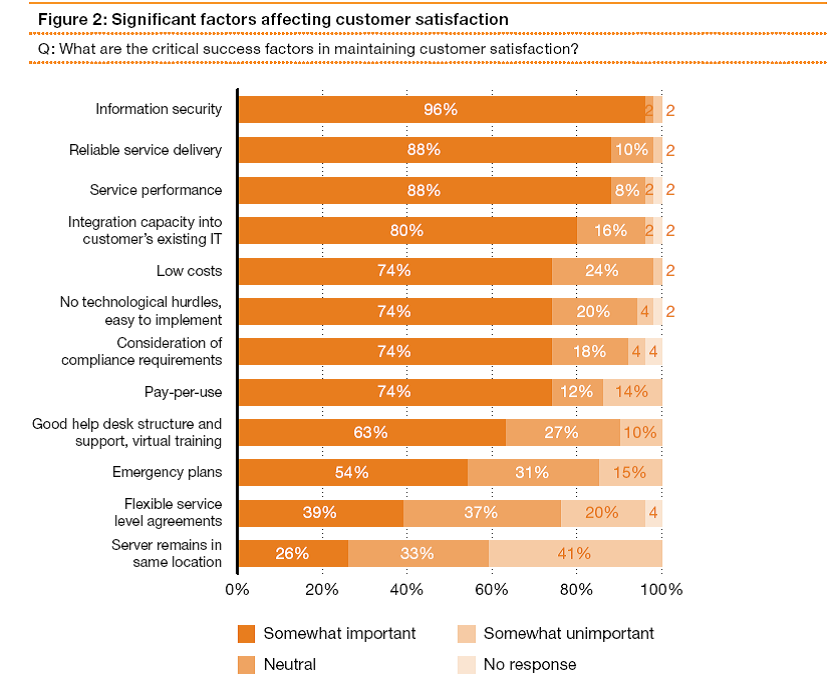
Source: (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011)
Challenges in the cloud computing market were found to include the following stated challenges:
- Data protection and compliance requirements;
- Standardization of internal processes;
- Individual services level agreements;
- Information security;
- Customer satisfaction;
- Definition of Cloud;
- Recruitment of qualified employees;
- Identification of appropriate sub-contractors; and
- Departing from the licensing model. (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011)
One important finding in the survey in terms of the business environment of cloud computing and the location in which the company or companies is situated is the findings that 33% of the cloud computing companies surveyed used outside contractors to ensure that customers were completely satisfied and to ensure service provision. (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011, paraphrased)
When the cloud computing companies were questioned as to what actions they had taken to guarantee the protection of customer information the companies replied as follows:
- Detailed risk-analysis;
- Certification of information security;
- Security penetration test;
- Adapting security concepts; and
- User audits (by third external party). (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011, paraphrased)
The survey revealed that 84% of respondents believe that “the combination and integration of different cloud services will become increasingly important.” (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011) 78% believed that in the years to come that cloud computing would serve to “radically change IT. Internet-based work will become the norm.” (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011)
Cloud computing is reported by 76% of respondents to have the capacity to “greatly change the relationship between customer and provider and pose new challenges for vendor management.” (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011) Cloud computing customers were found to be employed in the industries listed in the following chart labeled Figure 3 in this study.
Figure 3
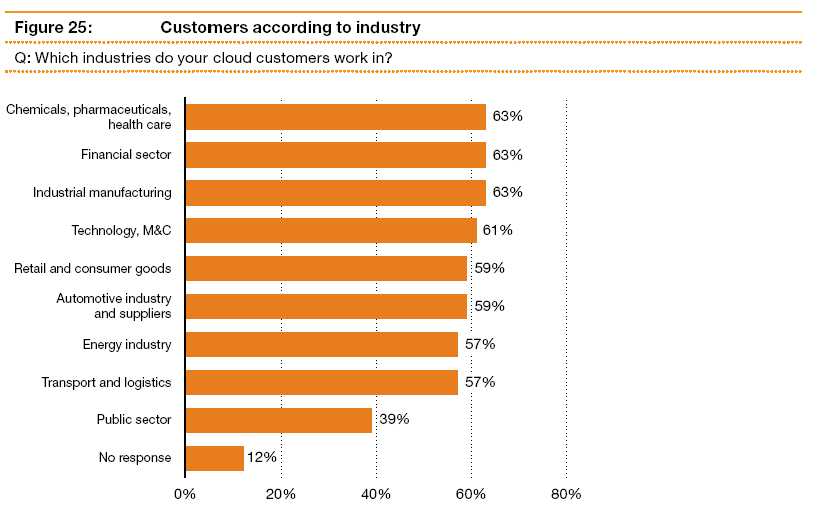
Source: (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011)
The type of cloud computing services offered by those surveyed are reported to have included those as follows:
- software as a service – 83%
- infrastructure as a service – 53%
- Advisory services for cloud computing – 51%
- Platform as a service – 39%
- Business process as a service – 27%
- Other cloud services – 21% (Kampfer, Vehlow and Golkowsky, 2011)
Ghana’s Business Environment and Cloud Computing
The work entitled “The Cloud and Africa – Indicators for Growth of Cloud Computing” states that cloud computing and its recent emergence “as a paradigm for economic development opens opportunities for African countries seeking to engage world markets despite lacking the traditional infrastructure used to facilitate trade.” (The African File, 2011) More countries are reported to be pursuing policies that serve to open the country to penetration of mobile, internet and broadband services. Reported is that on the African continent “only mobile technology has seen significant growth thus far. However, the landing of three broadband submarine fiber-optic cables promise to bring increased connectivity to the region leading to a spurt of broadband penetration. These three key areas of mobile, internet, and broadband will be critical to the spread of the model of cloud computing. With cloud computing, economic growth can be spurred through the cost reduction in hardware and software that businesses and governments must spend to run their information systems technology. The cloud, the common shorthand for this linking of terminals, can allow users to scale services, to reprovision technical services, and keep overhead costs like security and server space at lower levels. It can provide powerful computing systems at a fraction of the cost of traditional infrastructure.” (The African File, 2011)
Beneficiaries of the benefits of cloud computing include small and large companies and governments. Savings to the costs associated with housing and maintenance of IT systems will be realized by large companies as they move these systems offsite “to the remote servers that power the cloud.” (The African File, 2011) Small firms can realize savings on start up costs through conducting assessments of the applications that come ready-made by the provider of cloud computing service. African developers and entrepreneurs can achieve “collaboration and communication…through the cloud to be a part of global development and conversation in ways that traditional communication systems have limited their involvement. A current example is the development of mobile apps. A developer in Rwanda can use web-based applications to create and test an app for the iPhone and then publish their completed work to Apple’s App Store where any iPhone user in the world can purchase the app and download it. This creates economic links that were unimaginable before cloud computing.” (The African File, 2011)
Access to cloud computing contains many advantages for developing countries and these countries should “pursue policies that increase ICT infrastructure and increase availability of cloud computing tools. However, substantial challenges stand in the way of cloud computing in Africa. These go beyond the traditional obstacles seen in the current debate on cloud computing such as data controls, vendor ‘lock-in’, and sovereignty issues. Obstacles in Africa center primarily on infrastructure and government policy. With most development studies on the cloud focused on countries in the BRICS alliance this paper will set out to examine these infrastructure and policy obstacles specifically on the African continent to understand which countries are ‘cloud-ready’.” (The African File, 2011)
The idea of cloud computing is reported as coming into focus when the present needs of information technology are assessed including the associated costs of increasing or addition of capacities that make a requirement of new infrastructure as well as the training time for preparing users and technicians for system maintenance as well as the software licensing that are very expensive and “prohibitively” so for smaller companies. (The African File, 2011) IT’s present capabilities are extended by cloud computing through creation of a pay-per-use, on demand service that can be deployed in real time over the internet. Benefits offered by cloud computing include “the ability to scale and flex” as well as the fact that the cloud is “a multi-tenant facility, allowing more than one user or company to use the same service at one time.” (The African File, 2011)
It is reported that the cloud must “be resilient…there must be data storage options for when there is a loss of electricity and to provide sufficient security to satisfy the needs of businesses and governments to keep information safe and private. The provisioning of services is automated meaning that the user can requisition services as needed without having to go through a lengthy registration and allocation period. This is a key component for African businesses who often deal with some of the longest wait periods to start a business. Lastly, many of the cloud’s services are standardized meaning a certain ease of use for users to collaborate cross-platform in the cloud. When one thinks of inter-African trade and the many obstacles such as tariffs, corruption, and infrastructure that stand as hindrances, the Cloud provides an avenue of clear inter-state relations that can encourage trade rather than inhibit it.” (The African File, 2011)
Jim Furrier of Silicon Angle, states that ‘cloud readiness’ is “determined by the knowledge level of how technology services and solutions will take advantage of expertise and how best to implement this technology. Cloud readiness is an issue addressed in the literature reviewed in this study. It is reported that the state of “cloud readiness is determined by the knowledge level of how technology, services, and solutions will take advantage of expertise and how best to implement this technology. While ‘cloud-ready’ terminology has generally been applied to companies, this term will be used to gauge the ability of states to utilize cloud computing based on the level of ICT penetration that has been gained. The benefits of infrastructure cost reduction, leveled the playing field, the lack of software roll out on hardware which benefits rural and poor users, and finally the ability to scale up as demand increases all speak directly to the needs of African businesses and consumers.” (The African File, 2011) Five categories are stated to show which Sub-Saharan African countries are the most ‘cloud ready’. Those five categories are inclusive of the following:
- ICT;
- infrastructure;
- business;
- investment; and
- socio-economic. (The African File, 2011)
ICT Development represents a high interest area for the International Telecommunications Union, the World Bank and other development agencies, it was inevitable that the functions of cloud computing would be applied towards development.” (The African File, 2011) These functions are stated to be listed as:
- e-health;
- e-education;
- e-health;
- e-commerce;
- e-governance;
- e-environment; and
- telecommuting. (The African File, 2011)
It is stated that these functions are “areas that governments and aid agencies can devote projects and resources to in order to improve a target socio-economic statistic. However, these categories are still in the embryonic stage, just like cloud computing as a whole in Africa, thus their definitions and uses will likely vary in application, but each primary role is outlined below.” (The African File, 2011) The following shows the web and networking technology available in African countries at present.
Figure 4
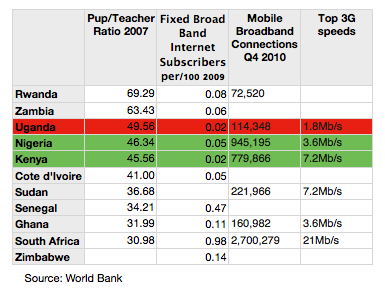
Source: (The African File, 2011)
The report states a determination that countries “with high literacy rates would most benefit from a Cloud that provided health information and infrastructure. By aligning literacy rates with the rates of the three major diseases in developing nations, TB prevalence, deaths due to malaria, and HIV/AIDS infection rates we can see which countries have the demand for e-health services and capacity to implement.” (The African File, 2011) The report concludes by stating that cloud computing “offers many advantages and benefits to emerging and developing nations.” (The African File, 2011)
It is reported that the SME Records Bank Cloud Computing Project in Ghana, was initiated by Hypersoft in cooperation with IBM. This initiative “seeks to roll out Cloud Computing Laboratory/Platform in Ghana (with possible adaptation in all developing nations) that will facilitate proper records management for businesses. “ (Lonlon, 2011) This is stated to include both small and large business and to have special emphasis on “SME’s towards sound growth” including better credit rating and a less risky environment in addition to faster access to financing and so on. The SME Records Bank Project is reported to have been voted as a Green SME and a Climate Friendly Technological Project. (Lonlon, 2011, paraphrased) This initiative reports seeking to accomplish the following:
- Provide a Laptop to every Senior High School and Tertiary Student in Ghana in the form of a Technology Loan pre-financed by Hypersoft for the Government of Ghana and repayable by beneficiaries over a specified and agreed period of time;
- Work with ICT giants such as IBM to modernize the Computer Science curriculum and establish mentorship programs between IBM ICT experts, physicists and scientists and Ghana University Lecturers and Students;
- Establish computer laboratories in all Senior High Schools across Ghana;
- Make Ghana a significant exporter of ICT Brains | i.e. Ghanaian graduates will become the most computer literate group on the African continent. ICT will become a major GDP contributor through the creation of job; and
- The Project Management Offices (PMOs) Roll-Out Program– seeks to roll-out Business Driven PMOs in all public sector agencies (Ministries, Departments and Agencies) to ensure flawless delivery of projects and programs towards accelerated growth at all time. (Lonlon, 2011)
Expected social impacts include the following:
- The SME Records Bank Cloud Computing Project will create over 50,000 Cloud Platform Data Processing Jobs for Ghana’s unemployed graduates. It will better living conditions and reduce unemployment– hence crime. This project will also widen the tax-net for Governments and stabilize revenue generations from the SME Sector.
- The One Laptop Per Student (OLPS) Project hopes to create 2 million ICT-related jobs over the next five years and make Ghana a significant exporter of ICT. The project seeks to build a vibrant ICT workforce for Ghana. Ghana’s youths will become extra creative and focus their attention on innovative solutions. Crime will be reduced.
- The PMO roll-out Program seeks to roll-out the right Project Management processes, build the right PM Skill-sets for Ghana AND implement the Project Delivery Now Culture in our public sector settings to ensure flawless execution of developmental projects and programs at all times; – hence high productivity, professional delivery, better rewards and accelerated growth countrywide. It seeks to properly reform the public sector and accelerate Government agenda. (Lonlon, 2011)
Legal Issues in Cloud Computing
Legal issues associated with cloud computing include such as:
- location (where is the data, what law governs?)
- operational (including service levels and security);
- legislation/regulatory (including privacy issues);
- Third-party contractual limitations on use of cloud;
- Security;
- investigative/litigation (ediscovery); and
- risk allocation/risk mitigation/insurance. (Mills, 2009)
It is reported that contracts will be the primary legal enforcement mechanism in cloud computing. Key contractual issues include the following:
- Privileged user access – who has access to data and their backgrounds
- Regulatory compliance – vendor must be willing to undergo audits and security certifications;
- Data Location – Can the physical location of data be controlled?
- Security – implementation is a technical matter; responsibilities is a legal matter.
- Data segregation – use of encryption to protect data – a sometimes tricky issue;
- Recovery – what happens to data and apps in the event of a disaster? Test procedures should be in place.
- Long-term viability – What happens to data and apps if company goes out of business?
- Investigative support – will vendor investigate illegal or inappropriate activity? What happens in the event of a security breach? (Mills, 2009)
Security Issues include those as follows:
- physical security – physical location of data centers; protection of data centers against disaster and intrusion;
Operational security – what has access to facilities/applications/data? Will you get a private cloud or a service delivered more on a utility model?
Programmatic security – Software controls that limit vendor and other access to data and applications (firewalls; encryption; access and rights management) Encryption accidents can make data usable. (Mills, 2009)
Investigative and Litigation issues include those of:
- Third party access – subpoenas in that one may not know when the vendor receives the subpoena; criminal and national security investigations; search warrants and possible seizures;
- E-discovery – considerations include enforcement of document holds, protection of metadata; and information search and retrieval. There must be a clear understanding of what cloud provider will do in response to legal requests for information.
The biggest issue in intellectual property issues is that of trade secret protection. In the event that third parties have access to trade secret information the legal protection of trade secrets could be destroyed. This issue can be addressed through “appropriate contractual nondisclosure provisions. There is also a stated concern for attorney-client privileged information. (Mills, 2009) Risk allocation and management concerns include the fact that there are presently no benchmarks for service levels and the fact that no cloud vendor is able to offer a 100% guarantee because “the most trusted and reliable vendor can still fail and a decision must be made as to whether replicate data and application availability at multiple sites. Finally, a decision must be made on escrowing data or application code. (Mills, 2009) It is reported that a premium will be charged upon the basis of the “degree of accountability demanded.” (Mills, 2009) It is the customer’s responsibility to make the determination if it is comfortable with the risk of putting service in the cloud. (Mills, 2009) Issues relating to insurance in cloud computing must address specific questions including those as follows:
- Will business interruption insurance provide coverage if your business goes down because of problem at cloud vendor?
- Do CGL or other types of liability coverage handle claims that arise from privacy breaches or other events at the cloud level and finally is the company covered if the cloud vendor is hacked. (Mills, 2009)
Mills work states the following to be inclusive in a checklist of consideration of legal issues related to cloud computing:
- Financial viability of cloud provider: Understand cloud provider’s information security management systems; and Plan for bankruptcy or unexpected termination of the relationship and orderly return of disposal of data/applications. Vendor will want right to dispose of your data if you don’t pay. Contract should include agreement as to desired service level and ability to monitor it. Negotiate restrictions on secondary uses of data and who at the vendor has access to sensitive data. (Mills, 2009)
- Negotiate roles for response to Ediscovery requests: Ensure that you have ability to audit on demand and regulatory and business needs require Companies subject to information security standards such as ISO 27001, must pass to subs same obligation. Make sure that cloud provider policies and processes for data retention and destruction are acceptable. Provide for regular backup and recovery tests. Consider data portability application lock-in concerns. Understand roles and notification responsibilities in event of a breach. (Mills, 2009)
- Data encryption is very good for security, but potentially risky; make sure you understand it. Will you still be able to de-crypt data years later? It is necessary to understand and negotiate where your data will be stored, what law controls and possible restrictions on cross-border transfers.( Mills, 2009)
- Third-party access issues: Consider legal and practical liability for force majeure events. Must be part of disaster recovery and business continuity plan. There is no substitute for careful due diligence. (Mills, 2009)
Summary and Conclusion
Ghana is presently undergoing a transformation in the technological capacities and this includes the area of cloud computing. Those who will benefit from use of cloud computing include both small and large companies as well as government. Savings will be realized in regards to the costs of housing and maintenance of IT systems can be realized by large companies as they move the systems offsite to the remote servers that provide power to the cloud. Security Issues have been found in this study to include the following in the area of cloud computing include those of physical, operational, and programmatic security. (Mills, 2009) Investigative and issues relating to litigation in cloud computing have been found to include third party access and e-discovery. In the area of intellectual property the largest issue has been found in this study to be that of trade secret protection. Ghana is poised to enter into contemporary information technology status however, this initiative will require a great effort at bringing the country up to speed in the area of technology, its applications, access and in preparing individuals through education and training to work with these applications and specifically that of cloud computing which offers great promise to both small and large businesses.
References
(2010) CXO Today. Retreived from: http://www.cxotoday.com/story/comviva-offers-affordable-mobile-communications-to-mtn-ghana-subscribers/
Aggarwal, Vikas (2011) How to Effectively and Efficiently Monitor Your Cloud Computing Infrastructure. Silicon India – CXO Insights. Retrieved from: http://www.siliconindia.com/guestcontributor/guestarticle/290/How_to_Effectively__Efficiently_Monitor_Your_Cloud_Computing_Infrastructure__Vikas_Aggarwal.html
Amenyo, J.T., (2003) A Model of National ICT Policy for Sustainable Development of Ghana. Rhustone Corporation Technical Report RC-2003-ICT-01, (March 2003).
Amenyo, J.T., (2003) A Phrase-structured, Attribute Grammar Representation of a Model of National ICT Policy for Sustainable Development of Ghana. Rhustone Corporation Technical Report RC-2003-ICT-02, (March 2003).
Amenyo, J.T., (2003) TELT (Teaching, Edcuation, Learning & Training) Aspects of Ghana’s National ICT Policy. Rhustone Corporation Technical Report RC-2003-ICT-06, (March 2003).
Amenyo, JT (2003) A Model of a National ICT Backbone Infrastructure for Sustainable Development of Ghana. Rhustone Corporation.
Bezy, Michel (2010) The New Nomads in Cloud Computing in Africa. Next Billion 27 Oct 2010. Retrieved from: http://www.nextbillion.net/blog/the-new-nomads-and-cloud-computing-in-africa
Cloud Computing: The Journey Begins. Dimension Data – Opinion Piece. Retrieved from: http://www.dimensiondata.com/Lists/Downloadable%20Content/CloudComputingTheJourneyBeginsOpinionPiece_129114121386950000.pdf
Cloud Security Alliance (2010) Top Threats to Cloud Computing V 1. Retrieved from: http://www.csa.org/pdf, March 2010.
Cobbinah, J.R., (2003) Enhancing Strategic Competitiveness in Information and Communcation Technology (ICT) – Country Paper: Ghana, (January 2003).
Comviva offers virtual SIM solution to MTN Ghana
CT Project Management Firm in Ghana Wins World Bank infoDev Top 50 Competition (2011) PM World Today, 2011, June. Retrieved from: http://www.pmworldtoday.net/BN/Feb/2011/05/ICTProjectManagementFirminGhanaWinsWorldBankinfoDevTop50Competitio.html
Dzidonu, C., “Comprehensive Strategy for Developing the Information and Knowledge Economy (IKE),” W. African Computing and Telecommunication Conference, Accra, Ghana, (May 25-26, 2000).
Fletcher, Kenneth Kofi (2010) Cloud Security Requirements Analysis and Security Policy Development Using a High-Order Object-Oriented Modeling Technique
Ghanian Government Data Center Almost Complete (2011) Datacenter Dynamics. 18 May 2011.Retrieved from: http://www.datacenterdynamics.com/focus/archive/2011/05/ghanaian-government-data-center-almost-complete
Gold Fields Ghana brings cloud down to earth(2010) Web Industry Solutions. 18 Mar 2010. Retrieved from: http://www.itweb.co.za/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=31404:gold-fields-ghana-brings-cloud-down-to-earth&catid=349
Golden, Bernard (2010) Cloud Computing: Two Kinds of Agility. CIO 16 Jul 2010. Retrieved from: http://www.cio.com/article/599626/Cloud_Computing_Two_Kinds_of_Agility?page=3&taxonomyId=3112
Internet pioneers leave the playground to the next generation: Should we be worried? (2011) Ghana Business and Finance. Retrieved from: http://www.ghanabizmedia.com/ghanabizmedia/january-2011-telecom/189-internet-pioneers-leave-the-playground-to-the-next-generation-should-we-be-worried.html
Internet Solutions Introduces `Cloud’ To The Ghanaian Market (2011) Business World. Retrieved from: http://businessworld.unimartdirect.com/company-news/telecommunications
Kampfer, Georg; Vehlow, Markus; and Golkowsky, Cordula (2011) Cloud Computing: Navigating the Cloud: Strategy, Organization, Processes and Systems. Retrieved from: http://www.pwc.com/en_GX/gx/technology/pdf/Navigatiang_the_Cloud_Final_3-24.pdf
Kizza, Joseph. M. Africa Can Greatly Benefit From Cloud Computing and Data Center Technologies – Part I. International Journal of Computing and ICT Research, Vol. 5, Issue 1, pp. 7-9. http://www.ijcir.org/volume 5-number1/article1.pdf.
Moscaritolo, Angela. Most organizations falling short on cloud security policies. Retrieved from: http://www.scmagazineus.com/most-organizations-falling-short-on-cloudsecurity-policies/article/167415/, April 2010.
National Institute of Standards and Technology.(2009) Cloud computing. Retrieved from: http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/SNS/cloud-computing/index.html, October 2009.
Okpara, Jo; and Wynn, Pamela (2011) http://www.allbusiness.com/management/4508144-1.html
Pina, RA and Rao, B. (2010) The emergence and promise of cloud computing for under-developed societies. Technology Managemnet for Global Economic Growth Proceedings ofPICMET 10. 18-22 July 2010. Retrieved from: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/freeabs_all.jsp?arnumber=5603324
Protecting your brand in the cloud: Transparency and trust through enhanced reporting (2010) PWC December. Retrieved from: http://www.pwc.com/en_US/us/third-party-assurance/assets/TPA-Cloud-brand-protection.pdf
PwC study: Cloud Computing in the Middle Market (2011) PWC. Retrieved from: http://www.pwc.de/en/mittelstand/cloud-computing-im-mittelstand.jhtml
Hanna, “Cloud Computing: Finding the silver lining,” (2009) Retrieved from: slides]http://www.ists.dartmouth.edu/docs/HannaCloudComputingv2.pdf, March2009
Markose, X. F. Liu, and B. McMillin, (2008) “A Systematic Framework for Structured Object-Oriented Security Requirements Analysis in Embedded Systems,” in Magnetism, vol. III, G. T. Rado and H. Suhl, Eds. New York: Academic, 2008, pp. 271–350.
SMEs must embrace technology or risk being marginalized CWG – GhanaWeb. 30 Nov 2010. Retrieved from: http://www.ghanaweb.com/GhanaHomePage/NewsArchive/artikel.php?ID=198492
Software Deployments – Cloud Computing (2011) BizTech Solutions. Retrieved from: http://www.biztechghana.com/bs/web/index2.php?category_ID=1&LlinkID=1&nID=23
Ristenpart, E. Tromer, H. Shacham, and S. Savage (2009) Hey, You, Get Off of My Cloud: Exploring Information Leakage in Third-Party Compute Clouds. Proc. 16th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 2009, pages 199–212.
Technology M&A deals reach $27b in first quarter 2011 (2011) Ghana Business News. Retrieved from: http://www.ghanabusinessnews.com/2011/06/01/technology-ma-deals-reach-27b-in-first-quarter-2011/
Tekpa, Lonlon (2011) Ideas Project: Hypersoft Ghana Limited. 3 May. Retrieved from: http://www.ideasproject.com/ideas/4123
The Cloud and Africa – Indicators for Growth of Cloud Computing (2011) The African File. Retrieved from: http://theafricanfile.com/academics/usc/the-cloud-and-africa-indicators-for-growth-of-cloud-computing/
Trend Micro Unveils its New Partner Program (2011) News Ghana – IT Distri.com 21 Oct 2011. Retrieved from: http://www.itdistri.com/EN/recherche/pays/60/
F. Liu, H. Lin, and L. Dong, (2001) “High-Order Object-Oriented Modeling Technique for Structured Object-Oriented Analysis,” International Journal of Computer and Information Science (IJCIS), 3rd ed., vol. 2. Oxford: Clarendon, 2001, pp.68–73.

Time is precious
don’t waste it!

Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee






