 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Environment – Ecology Project, Research Paper Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Research Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

The familiarity of our everyday surroundings often means that we overlook the dynamic structure and diversity of the ecosystems that comprise our environment. Closely examining such an ecosystem makes clear the complexity of these ecological environments, constituted by varied forms of relations between the biotic and the abiotic, which altogether exist in a certain harmony or symbiosis. For example, In the case of the field ecosystem, such complexity is readily apparent. The constitution of the field ecosystem, made up of various animals and plants, all exist together, creating a functional system conducive to the production of life.
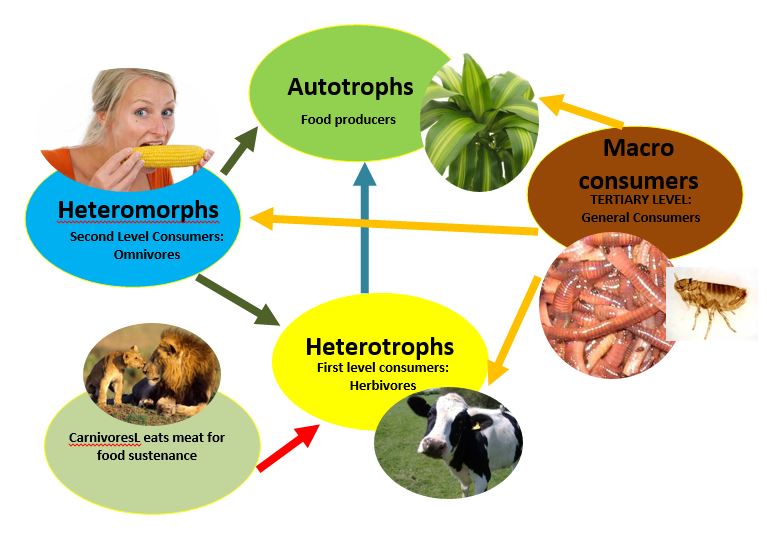
When examining this field ecosystem in terms of scientific terminology, it can be readily divided into trophic levels, which is a key category for distinguishing the various parts of the ecosystem. The trophic level refers to the basic position of the animal within the food chain. Hence, in the case of the field ecosystem, diverse creatures, such as mice and insects occupy different trophic levels according to their role in the system.
In this regard, it is important to distinguish between heterotrophs and autotrophs. Autotrophs are living or biotic creatures, which create organic materials from inorganic substances. Hence, in the context of the field ecosystem, the autotroph or in other words producer, such as blades of grass and other forms of vegetation like algae, may produce their own food supplies, while also providing an indispensable contribution to the ecosystem, by producing the invaluable reserouces such as carbohydrates, which are necessary for the survival of animals, or in other words heterotrophs. Within the context of the field ecosystem, therefore, heterotrophs such as mice and rabbits rely on the production of the autotrophs in order to survive. Mice and rabbits are therefore termed primary consumers, since they directly consume the autotrophs. Furthermore, they designate clear examples of herbivores, who consume only vegetable life for their food sources.
This basic relationship is also further nuanced by the presence of heteromorphs who rely upon other heteromorphs for their food sources, thus indicating another trophic level. These are secondary consumers or carnivores. An examples from our field ecosystem of these secondary consumers are house cats who will enter the field looking for mice. Many times, a secondary consumer will also indicate an omnivore, meaning that they will not only consume heteromorphs, but also automorphy.
Within the consideration of our field ecosystem, the presence of a tertiary consumer and another trophic level is more rare, although it perhaps can be discerned in the form of some species of birds who are able to consume both the first and secondary level consumers. These carnivores would also be known as macro consumers, insofar as they consume a larger part of the ecosystem. Various forms of parasitism are also present in the field ecosystem, such as fleas, which exist in a unilateral relationship with their host, such as field cats.
At the same time, within the field ecosystem crucial work is being performed by the decomposers. This trophic level may include various types of insects, such as, in the case of our ecosystem, worms and flies, who decompose the waste of the other members of the ecosystem. Such a function essentially cleans the environment, preventing the overabundance of dead matter, while also helping provide the autotrophies much needed nutrients: these decomposers, also known as derivers, provide an almost managerial and hygienic role within the field ecosystem.
The delicacy of the balance of the field ecosystem is furthermore defined in terms of three terminological distinctions: that of keystone species, specialist species, and generalist species. The keynote species denotes a member of the ecosystem who, although not on the top of the food chain, is nevertheless crucial for its overall functioning. In the case of the field ecosystem, the house cats that enter the field to eat mice and other first consumers so that, for example, plant life will be allowed to continue to flourish, may be considered a keystone species. The distinction between generalist and specialist species further illustrates the diversity of the field ecosystem. For example, a racoon in the field would be considered a generalist because of his adaptability to numerous food sources, whereas specialists could include the various primary consumers who would be unable to continue to live without the presence of automorphy.
Accordingly, the example of the field ecosystem portrays the complex relations of predation and symbiosis. Symbiosis entails the general relationships between the organisms in the field ecosystem, and essentially how they rely upon each other for their existence. At the same time, the field ecosystem is clearly constituted by predation, as the various trophic levels feed off each other. Yet ultimately symbiosis proves more dominant than predation, since it is only with symbiosis that the ecosystem can continue to thrive: while predation is necessary for the ecosystem, it could be said that in the example of the field ecosystem symbiosis wins out in the end, allowing for the ecosystem to function.
Certainly, human intervention, as a dominant tertiary consumer and heteromorph threatens the symbiotic balance of the ecosystem: the mismanagement of the autotrophs, for example, with lawn care destroys the producers of the ecosystem, which thus negatively affects all the other trophic levels and various consumers, parasites, and heteromorphs. In this sense, symbiosis is always threatened by predation, especially in the human form. The key to maintaining the health of all ecosystems and not only the field ecosystem is to precisely make sure that such predation on one trophic level does not dominate the overall symbiosis of the system.
Food Chain Diagram

Stuck with your Research Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Tags:

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

