Breastfeeding Attitudes of WIC Staff, Article Critique Example
Nursing: Graph/Article Critique – Breast Feeding Attitudes of WIC Staff
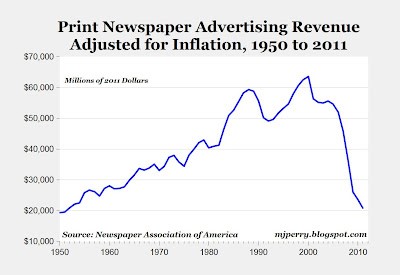
Part 1-Graph Critique
Diagram – Newspaper sales
The Collapse of Print Advertising in 1 Graph
(Derek Thompson, 2012)
This graph is expected to illustrate how a fall in the economy has affected sale of newspapers showing a decline from 1950 through to 2010. The contention is that print newspaper advertisements have fallen by two-thirds from $60 billion in the late-1990s to $20 billion in 2011 (Thompson, 2012)
In explaining the graphic illustration the writer argues that reason for a significant decline in newspaper advertisements was really that businesses were not making because big business were still advertising. It was that business models have changed. Now they have to spend more money in paying employees. This has affected the newspaper industry because it was designed to function with $50 billion to $60 billion emerging from advertising. The staffing structure was built to accommodate a $50 billion industry. As such, the writer continues to contend that layoffs and bankruptcies were undertaken to correct the great deficit in revenue as is being depicted in the graphic illustration (Thompson, 2012).
There was enough information in this text to explain the graph. Data pertaining to an apparent declined was communicated in a very solid tone. The language was very
simple for readers to understand the impact of internet and television on newspaper advertisement. It remained conversational to keep readers focused on the writer’s intention (Thompson, 2012)
This is an uncomplicated line graph showing alterations in a phenomenon. The vertical axis depicted newspaper advertisement revenue and the horizontal line years the writer wanted readers to focus on. Vertical lines appear to be within the factor analysis guidelines, but the horizontal ones depicting years are undefined. One cannot carefully trace where they begin and end.
A deception can be identified when an inference is drawn showing revenue incurred between1950 and 2011. Form the graphical representations they are approximately the same. Thomson communicates to the reader a decline in the new papers advertisement industry, but in my opinion once it is not lower than where it began in 1950 there is no significant fall in revenue as is being argued. Numerical data were draw from representations on the graph depicting this phenomenon to reveal a surge in income between 1990 and 2000. The peaks are shown as $60,000 in 1990 a slight fall within the ten year period and a sudden peak again in 2000 of a little over $60,000.
The color in my opinion is quite appropriate; readable and attractive for an internet audience. Black white and grey even though not catching to the eye is mild enough to demonstrate a degree of seriousness in the information communicated since is not biology of science, but strictly a media representation. Also the blending of colors denotes a mild, but important piece of important. A white background with grey borders; light horizontal lines an black writing is an excellent blend to advertise this data in a news column
Part 11- Article Critique-Breast Feeding Attitudes of WIC Staff
Introduction
This critique explores WIC employees’ perceptions of breast feeding. The study was conducted by a panel of experienced advanced practice nurses in the capacity of advanced nurse practitioners; nutritionists, advanced practice obstetric nurses and community health specialists.
Purpose of study
The purpose of this study was to collect data for designing breast feeding programs at WIC offices. Researchers indicated that the research was expected to retrieve data regarding how WIC staff perceived this intervention. Explanations given offered a concise overview of the project, which in my opinion was simplistic enough for the reader to follow (Reifsnider, et.al, 2003).
In critiquing this aspect of the study it is my conviction that the researchers established the parameters through which they would achieve goals by further explaining it in subsequent paragraphs. This can be considered exquisite research technique. They continued by engaging readers with a brief literature review on breast feeding. Even though this is not the purpose this aspects of a research re-enforced the true purpose of the study by clarifying parameters established in the purpose statement.
Methodology
Methodology is expected to offer guidelines for solving a problem and measuring the purpose. It explores specific variables enclosed in phases, tasks, methods, techniques and tools. From a scientific research perspective methodology can be defined as ‘the analysis of the principles of methods, rules, and postulates employed by a discipline the systematic study of methods that are, can be, or have been applied within a discipline’ (Creswell, 2003).
In this study all these elements mentioned by Creswell were difficult to identify. For example the researchers did not distinctly indicate a particular design. In the methods section they went right ahead telling readers about how the sample was selected. Closely examining the design it could be regarded as a qualitative study employing a focus group instrument.
When using a qualitative method researchers find out why and how decisions are made. They go beyond merely explaining what, where and when. As such, it is likely since these researchers utilized a focus group that this must be a qualitative analysis being consistency with a focus group data collection procedures (Denzin & Lincoln, 2005). Quantitative research methods involve statistics and there are no statistical interpretations in this article.
Advantages of utilizing a focus group approach is that ideas for improvement can be obtained immediately due to concepts expressed by participants. It plays an essential role in identifying strengths and weakness underlying a phenomenon or organizations’ structure. At the same time it provides immediate insights on how changes can influence development of theory and practice (Creswell, 2003).
However, the disadvantage when compared to individual interviews is that they are far less reliable in providing in depth data collection. Participants may be reluctant to openly express their values among other people. It is an expensive process compared to questionnaires and subjectivity can be high due to moderator’s biases (Creswell, 20003).
Based on the foregoing specifics of a focus group, I tis my critique that these researchers used both qualitative method and focus group intervention to their full advantage in this study and the selection was appropriate for the study.
Sampling
Researchers employed a non-probability purposive sampling technique by selecting participants for this study base on their judgment of who will be best suitable from their population. Probability sampling or random sampling has a distinct advantage over nonprobability sampling techniques. The probability of obtaining a specific sample type and size is predictable through scientific calculations (Lucas, 2012)
Nonprobability sampling techniques Lucas (20120 advises, should be applied with caution. It is incapable of generalization purposes to similar populations. For example, in this study researchers wanted to obtain WIC staff perceptions on breast feeding for designing a program across WIC establishments. Clearly, a nonprobability purposive sample is inadequate for this purpose. Generalizations from a nonprobability are subject to personal knowledge of the topic being reviewed. Therefore, while nonprobability sampling is considerably less expensive alternatively they are less reliable (Lucas, 2012).
As it pertains to this study being critiqued researchers gave an incomplete description of the sample. There were no specifics regarding selection criteria expect that they were WIC staff and mothers from 4 clinics. No inclusion or exclusion varibles were mentioned nor the number of staff members who were engaged in the study.
A number of figures for breast feeding women were mentioned who either gave birth or were recipients of services, but no specifics relating whether they were considered part of the sample was given. Also, a description of the sample showed where they were not nurses, but intake clerks and nutrion aids who were involved in the focus group interactions.
Then answers regarding whether the sample could be justified for the population and purpose being reviewed leaves much to be considered. In my opinion more nurses should have been involved in the study as participants and not merely WIC staff. Advanced practice obstetric nurse have the expertise to train and deliver quality service to this population.
Data collection
Data collection involves the process of collecting information for a project using appropriate instruments. There are three stages contained in ta data collection activity; pre collection whereby goals, target data, definitions, methods are agreed upon; then the actual data collection procedures and presentation of findings. The first stage could not be clearly identified in this research study (Creswell, 2003).
Focus group interactions provided data, but explanations of the pre data phase were omitted. 39 women and one man participated in the study. Facilitators for these groups were 92% of WIC staff. Staff was screened for educational background eligibility. According to the researchers these discussions were tape recorded and later analyzed as needed data. Eight questions informed the discussion, but no mention of pretesting was done (Reifsnider, et.al, 2003).
One disadvantage of focus groups is that interactions could be programed to affect a particular outcome, which may not represent a true picture of the issue. However, the data collection procedures just as the sampling methods, has not been not clearly represented in this research study by explaining to the reader the specifics of focus group interations.
There appears to be missing bits of information regarding how many sessions were conducted and what role the 39 women played in the group. Was it an interviewing session or a group discussion? The researchers mentioned that a focus group discussion guide was used to conduct the interviews. This seems contradiction to how a focus group should be conducted. Hence, a bit of confusion was created here for the reader. Discussion should be guided but not organized as an interviewing session (Reifsnider, et.al, 2003).
Data Analysis
In this study the researchers adapted simplified coding methods, which grouped similar data by assigning a convenience code. This helped both the reader and researchers to understand themes which emerged during conclusions and findings. These approaches are consistent with qualitative studies as this one and can be considered an appropriate intervention.
Trustworthiness
Trustworthiness is an important element of research because it determines the degree of subjectivity it contains. Therefore, conformability, credibility, dependability, and transferability ought to be maintained. In this study the researchers did conform to standard research guidelines by soliciting permission to use WIC offices and staff for the project.
Even though credibility in my opinion it was not enough to consider the intervention reliable. This is so because nurses who have the expertise and knowledge about breast feeding were excluded from focus groups. Alternatively, WIC staff formed the focus of this study to plan a program for mothers concerning breast feeding.
Would the perceptions of WIC staff influence whether mothers will breast feed or not? How much influence it would have if it does? The same arguments could be advanced regarding dependability and transferability as well. Questions raised in this study regarding dependability points towards whether policy makers can depend on data retrieved from WIC staff for designing programs, which obviously go beyond nutrion education. Transferability would be limited to the specific populations studied. This is a disadvantage of focus group data collection procedures.
Findings
Themes emerging from the study were ‘benefits of breastfeeding; barriers to breastfeeding; lack of support for breastfeeding; cultural beliefs about breastfeeding, and WIC’s role in breastfeeding promotion’ (Reifsnider et.al, 2003). WIC staff members personal experiences were incorporated in the findings. From this perspective it would confirm the study’s purpose of investigating WIC staff attitudes towards breast feeding.
However, breast feeding women were included while the focus of this research was geared towards WIC staff perceptions of breast feeding. Why was it necessary for 39 women to be included? This aspect of the research was not clearly explained by the researchers. Most of the finds were reveals based on the WIC staff experiences in the focus group discussion (Reifsnider, et.al, 2003)
Conclusion
Implications
My critique pertains towards the conclusions discussed relating that breast feeding among WIC staff was influenced by their cultural beliefs. In my opinion if the results of this study are to the considerations for promoting breast feeding more reliable data is needed. Thes should pertain towards whether mothers accept breast feeding as essential to their child’s nutrion.
Recommendations
Recommendations point towards allowing WIC staff to openly express their tolerance or intolerance to breast feeding and must not be compelled to deliver information inconsistent with their cultural beliefs. However, the focus of this study was supposed to gather data from implementing breast feeding at WIC offices. It would appear that the people intended to benefit formed the exclusion criteria when they should have been included.
Application to Nursing
The application to nursing was quite explicit when researchers emphasized that approaches towards breastfeeding will not be successful unless initiatives are taken to address cultural beliefs among WIC staff and mothers. While this is true breast feeding is a technique which goes way beyond nutrion education.
Mothers need to develop strategies of placing the infant at the breast in facilitating feeding. This is the job of experienced nurse practitioners. WIC is a very important program that assists low income women with food for their children. On the other hand these findings about WIC staff may not be reliable enough for nursing practice because researchers did not say how many nurses were involved in the program and the extent they were used if at all.
References
Creswell, J. (2003). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publications.
Denzin, K., & Lincoln, Y. (Eds.). (2005). The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage
Lucas, R. (2012). Beyond the Existence Proof: Ontological Conditions, Epistemological Implications, and In-Depth Interview Research. California. Quality & Quantity.
Reifsnider, E. Gill, S. Villarreal, P., and Tinkle, M. (2003) Breastfeeding Attitudes of WIC Staff: A Descriptive Study. J Perinat Educ , 12(3), 7–15.
Thompson, D. (28th February, 2012). The Collapse of Print Advertising in 1 Graph. The Atlantic

Time is precious
don’t waste it!

Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee






