 All papers examples
All papers examples
Disciplines

- MLA
- APA
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- High School
- PhD
- Harvard
- Biology
- Art
- Drama
- Movies
- Theatre
- Painting
- Music
- Architecture
- Dance
- Design
- History
- American History
- Asian History
- Literature
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- English
- Linguistics
- Law
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Ethics
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Theology
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Economics
- Tourism
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- Psychology
- Sociology
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Anatomy
- Zoology
- Ecology
- Chemistry
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Geography
- Geology
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- Internet
- IT Management
- Web Design
- Mathematics
- Business
- Accounting
- Finance
- Investments
- Logistics
- Trade
- Management
- Marketing
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Technology
- Aeronautics
- Aviation
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Healthcare
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Journalism
- Public Relations
- Education
- Educational Theories
- Pedagogy
- Teacher's Career
- Statistics
- Chicago/Turabian
- Nature
- Company Analysis
- Sport
- Paintings
- E-commerce
- Holocaust
- Education Theories
- Fashion
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Science
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Paper Types

- Movie Review
- Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Assessment
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Case Study
- Coursework
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Essay
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Interview
- Lab Report
- Literature Review
- Marketing Plan
- Math Problem
- Movie Analysis
- Movie Review
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Online Quiz
- Outline
- Personal Statement
- Poem
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Quiz
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- Resume
- Speech
- Statistics problem
- SWOT analysis
- Term Paper
- Thesis Paper
- Accounting
- Advertising
- Aeronautics
- African-American Studies
- Agricultural Studies
- Agriculture
- Alternative Medicine
- American History
- American Literature
- Anatomy
- Anthropology
- Antique Literature
- APA
- Archaeology
- Architecture
- Art
- Asian History
- Asian Literature
- Astronomy
- Aviation
- Biology
- Business
- Canadian Studies
- Chemistry
- Chicago/Turabian
- Classic English Literature
- Communication Strategies
- Communications and Media
- Company Analysis
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Criminal Justice
- Dance
- Design
- Drama
- E-commerce
- Earth science
- East European Studies
- Ecology
- Economics
- Education
- Education Theories
- Educational Theories
- Engineering
- Engineering and Technology
- English
- Ethics
- Family and Consumer Science
- Fashion
- Finance
- Food Safety
- Geography
- Geology
- Harvard
- Healthcare
- High School
- History
- Holocaust
- Internet
- Investments
- IT Management
- Journalism
- Latin-American Studies
- Law
- Legal Issues
- Linguistics
- Literature
- Logistics
- Management
- Marketing
- Master's
- Mathematics
- Medicine and Health
- MLA
- Movies
- Music
- Native-American Studies
- Natural Sciences
- Nature
- Nursing
- Nutrition
- Painting
- Paintings
- Pedagogy
- Pharmacology
- PhD
- Philosophy
- Physics
- Political Science
- Psychology
- Public Relations
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Religion
- Science
- Shakespeare
- Social Issues
- Social Work
- Sociology
- Sport
- Statistics
- Teacher's Career
- Technology
- Theatre
- Theology
- Tourism
- Trade
- Undergraduate
- Web Design
- West European Studies
- Women and Gender Studies
- World Affairs
- World Literature
- Zoology
Improving Anticoagulation Control in Hospitalized Elderly Patients on Warfarin, Article Critique Example
Hire a Writer for Custom Article Critique
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.

Citation
Gouin-Thibault, Isabelle, et.al. (2010). “Improving anticoagulation control in hospitalized elderly patients on Warfarin.” Journal from the American Geriatrics Society. Vol. 58, page.242-7.
Topic
Topic and Major Objective of the Journal
The number of old age patients who need Warfarin therapy is rapidly increasing, because the aging factor of the people is causing escalation in the occurrence of venous thromboembolism and atrial fibrillation. Warfarin therapy is believed to have therapeutic index of narrow nature. So it has been believed that attaining effective but reliable anticoagulation is challenging, particularly for the patients that are frail elderly, who are at the great risk for bleeding. To reduce the risks linked with the anticoagulant treatment, anticoagulation health centers have been established and revealed to better results more than the care of standard level. Computer programs are usually practiced in anticoagulation health centers to determine the dosages of Warfarin but no computer programs particularly established for old age patients are, however the practice of particular algorithms for the initiation of treatment and detailed monitoring are suggested to old age patients to extend time spent within the ranges of therapeutic events.
The main objective of the study is to identify the effect of patient characteristics and of particular procedures that were established for managing the therapy called Warfarin in older people and incorporated in an in-house computer program related to the quality of anticoagulation.
Identify & define the important concepts focused on by the author. Are the definitions clear, in your opinion?
The main concept discussed in the article is named as International Normalized Ratio (INR) on the basis of which the concept of Warfarin induction algorithm particularly established for elderly inpatients. An INR is helpful in checking the effects of anticoagulant (blood thinning) medicines, for example Warfarin. People with atrial fibrillation usually take anticoagulant medicines to defend against clots that can result into the strokes. While using Warfarin, patients have to go for regular blood tests to check their INR. Same like as the patients understand the numbers of their blood pressure, they also must understand about the Warfarin dosage and their INR.
Theory/Research Methods
Is the author being guided by a particular theoretical perspective? If so, what is it & how does she/he use this theory to understand the problem?
A systematic approach and Rosendaal method has been followed to understand the problem by setting the criteria of eight factors and to know about the times spent within, above, and below the target INR range were calculated using the. The criteria used to evaluate and understand the quality of anticoagulation includes the percentages of time within the therapeutic INR range (2.5 + 0.5); the percentages of time within the INR range (2.5 + 0.7); the percentage of time with the values of INR < 2.0 and >3.0; values percentage of 4.0 and greater, reflecting over anticoagulation; the percentage of the value concerned with INR of 1.5 and less, reflecting sub-therapeutic levels; the time to the first INR value of 4.0 or greater; and the number of INR determinations per month.
Sampling criteria
Sample size
The sample size of the study was 307 patients out of 355 eligible students.
Characteristics of sample
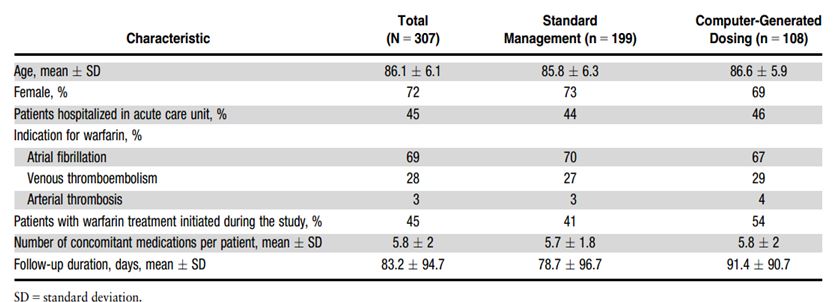
The 307 participants of the study had an average (mean) age of 86.1 + 6.1. The patients that were hospitalized treated with Warfarin therapy and with a therapeutic global normalized ratio consist on the range of 2.0 to 3.0. From the 307 patients, 108 were allocated to the CGD group and 199 to the SM group. The total 16 physicians participated in managing the patients of CGD group and 30 physicians were involved in treating the SM group. Over the period of 13-months, 6,009 INR determinations were carried out in the 307 participated patients. Adherence of the physicians working in CGD group to the dose recommendations were made through the software was 91%. Their main characteristics of the sample taken for this study are shown in the following table.
Sample mortality
The sample looks a valid sample because out of 355 patients 307 patients were selected because the remaining 48 aging patients had fewer than two INR determinations or the follow-up of less than 7 days, cannot meet the selection criteria for the final analysis and hence excluded from the study.
Methods used to obtain the sample (randomization, survey, field observation, etc.)
The survey method has been used to obtain the sample. A standardized computerized data collection survey form was given to each patient to record sex, age, suggestion for Warfarin therapy, treatment period, and the duration of follow-up. Major events of bleeding events were also re-corded as non-expected factor. The measurements of INRs throughout the period of study were taken from the database of laboratory.
Type of constant obtained
The comparison between the characteristics of patient and treatment of two groups were made using Student chi-square tests for qualitative variables and t-tests for quantitative variables. Univariate analyses were carried out, afterward the multivariable analyses to test relationships between the criteria of eight anticoagulation and six co-variables: sex, age, determination to Warfarin therapy, treatment duration, duration of follow-up, and model of care (CGD or SM).
Main Ideas
Summarize the findings. What are the results?
In accordance to the multivariate analysis, only follow-up duration and model of care autonomously influenced the control of anticoagulation; the ratio of duration within the range of therapeutic INR 2.0 to 3.0 was considerably more than in the patients of CGD group than the patients of SM group (59% vs. 48%, P=.004). When a greater INR range was evaluated (1.8-3.2), the ratio of duration within range was 73% versus 64% (P=.006) for CGD and SM groups respectively. The usage of the computer was linked with less days with INRs more than 3, a minor percentage of INRs of 4 or more than this, a longer duration to the first INR of 4.0 or more, and a less mean number of INRs per month than SM (all P<.01).
Are the results valid?
The results of the study are valid because despite the evidence that Warfarin is greatly effective in controlling the thromboembolism, it has not been used in elderly patients widely. Considerations about anticipated complexities with the control of anticoagulation and inducing events of bleeding have been recommended as determinants for not suggesting Warfarin therapy to elderly patients. However, few data is available to direct clinicians in prescribing the dosages of Warfarin for older adults.
Excepptional Events
Any findings were not expected? Are serendipitous findings described?
Throughout the period of study, seven patients from the 307 patients faced a nonfatal major and unexpected bleeding event. Three of them were belonged to CGD group and four were in the SM group. In four patients, the Warfarin therapy had been started throughout the study period. However, in all patients the Warfarin therapy was discontinued; one patient received vitamin K, and four of them needed blood transfusions.
Conclusions
What conclusions does the author(s) make? Are limitations discussed? Any suggestions for further study?
The author made the conclusion that, the current study, in which Warfarin management rules and procedures are proposed, provides the evidence that long-term rules and initiation regimen specifically associated to elderly patients who are managed in a computerized dosage program allow those elderly patients who were hospitalized to take benefit from a care quality as maximum as that of low age ambulatory patients.
The limitations of the study have also been discussed. The first limitation was that the size of sample taken was too small for an evaluation about the effects of CGD on patient results, but there is well-known agreement that the control of anticoagulation affects the results related to anticoagulation. And the second limitation that has been discussed was the absence of random allocation to the treatment groups. The suggestions that have been made for further study was the randomized selection of sample that could make produce the better results.
Do the data support the conclusions being made by the author?
The answer to this question is yes, because the great rate of INRs within the therapeutic range achieved with the help of software is especially remarkable as the patients in the present study were hospitalized and have more age than those patients participated in previous studies and thus were more prone to instability of anticoagulation due to comorbid and poly-pharmac conditions.
Reflection
Identify any missing elements of the study.
The missing element in the study is vitamin K antagonist therapy for stroke prophylaxis. Because, in a study that has been carried out in five countries to assess the control of anticoagulation in ambulatory patients with chronic atrial fibrillation, vitamin K antagonist therapy for stroke prophylaxis was the core element.
Any biases present?
The bias of this study is the selection of sample size because it has been believed that the randomized sampling could generate better results about the selected problems.
Is the description of the study sufficiently clear to allow replication?
However, the study lacks some important factors but the description of the study sufficiently clear to allow replication.
Will the research help in caring for patients in the hospital?
Initiation regimen and long-term rules that have specifically been developed and included in a computerized dosage program improve quality of anticoagulation in elderly inpatients, allowing them to benefit from a quality of care as high as that of younger ambulatory patients.
What could be done to improve the research?
The research could be improved by increasing the sample size and the methods to choose the sample. Moreover, the training of the physicians involved in the research for Warfarin dose management could probably improve the quality of research.
What was the most important in critiquing this article?
Although the authors of this study have done a great work, but when compared to the previous studies numerous things can be identified as a weak element of this research. For instance the research design was not too much clear that can attract the unique attention of the audiences.

Stuck with your Article Critique?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!

Time is precious
don’t waste it!
writing help!


Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee

