The Irrational Online Shopping Behavior of College Students, Research Proposal Example
A study on the irrational online shopping Behavior of college students based on perspectives of live-streaming Services Tmall and TikTok
Abstract
This paper evaluates irrational online shopping behaviors among college students with attention to live streaming platforms of TikTok and TMall. By looking at these two platforms, it would be possible to have an in-depth understanding of the extent to which irrational online shopping behaviors are manifested among students and the possible causes. By understanding the forces driving irrational consumption among college students, it would be possible to adopt the most appropriate strategies that will promote more responsible consumption behavior among college students. The significance of this study is that it will contribute to the body of knowledge of the strategies to improve financial management among students and also the quality of learning. The main objective of the study is to improve the shopping or consumption behaviors of college students. This paper uses the Motivation-Need Theory to explore the phenomenon in addition to McClelland’s Acquired Needs Theory.
Introduction
Consumption behavior among college students has increasingly become a concern to many scholars. Moon and Attiq (2018) provide an in-depth explanation of the need to evaluate the shopping behavior among students. The authors say that in many cases, college students are involved in compulsive buying that is characterized by the misuse of credit cards and depletion of limited resources at their disposal. Several factors influence the consumption choices of humans alike. Some factors lead to improper shopping behaviors that are unsustainable in the long run. Jung (2017) says that most students do not have a stable source of income, and their shopping and consumption behaviors directly impact the quality of their lives on campus. Money is a resource, and there is a need to use it prudently. Students can only have fruitful and comfortable, and successful. In their paper, Duroy et al. (2018) indicate that some shopping behaviors result from personality disorders, and they usually result in poor financial management skills that may have adverse effects on the quality of life of students. Different scholars have adopted varying approaches to examine the problem of brash consumerism among college students. Pradhan et al. (2018) look at the issue in the context of the misuse of credit cards. The authors indicate that the poor consumption choices among college students are often influenced by situational factors, including those occasioned by credit cards. This paper evaluates irrational online shopping behaviors among college students with attention to live streaming platforms of TikTok and TMall. By looking at these two platforms, it would be possible to have an in-depth understanding of the extent to which irrational online shopping behaviors are manifested among students and the possible causes. By understanding the forces driving irrational consumption among college students, it would be possible to adopt the most appropriate strategies that will promote more responsible consumption behavior among college students.
Background of the Study
Nasidi et al. (2021) describe how technological evolutions have impacted consumption behaviors among people in all corners of the world. The paper accurately states that the evolution of technology has made it possible for people to acquire the products that they need without necessarily visiting shopping centers. Today people can shop in the comfort of their homes. As a result of these advancements in technology, shopping has become more convenient and cost-effective. While these trends have had some positive impacts on the quality of shopping, they have also had some adverse effects. One of the most important effects of these changes is the development of irrational shopping behavior among many groups of people (Shareef et al., 2019). Irrational consumption behavior is harmful in many ways. The tendency may be an indication of a personality challenge, but it may also lead to adverse social, economic, and psychological challenges (D’Souza, 2018).
In an article, it is stated that “Changes in consumer behavior can occur for different reasons, including personal, economic, psychological, contextual, and social factors. However, in dramatic contexts such as a disease outbreak or a natural disaster, some factors, more than others, have a more significant impact on consumer behavior. Indeed, situations that potentially disrupt social lives, or threaten individuals’ health, have been proven to lead to strong behavioral changes” (Dicosta et al., 2021). From the statement, it is evident that irrational shopping is a dangerous practice that is capable of having adverse effects on the culprits when it is not contained. Students are vulnerable in several ways, and their uncontrolled spending may lead them to adverse mental health challenges. According to Muller et al. (2015), it is not only personal traits that encourage compulsive buying. Environmental issues such as advertising, peer pressure, and market stimuli, among other factors, significantly influence the consumption choices of students.
Palan et al. (2011) examine compulsive buying behavior among college students in the context of the use of credit cards. The author says that the problem of irrational shopping by American students has escalated and become a serious national issue. According to Palan et al. (2011), a lot of American students want to acquire products that are far beyond their capability with the aim of demonstrating power and status, thus fulfilling self-seeking needs. According to the paper, these consumption habits among college students are a cause of worry to educators across the country. The consumption behavior also worries parents and regulatory authorities.
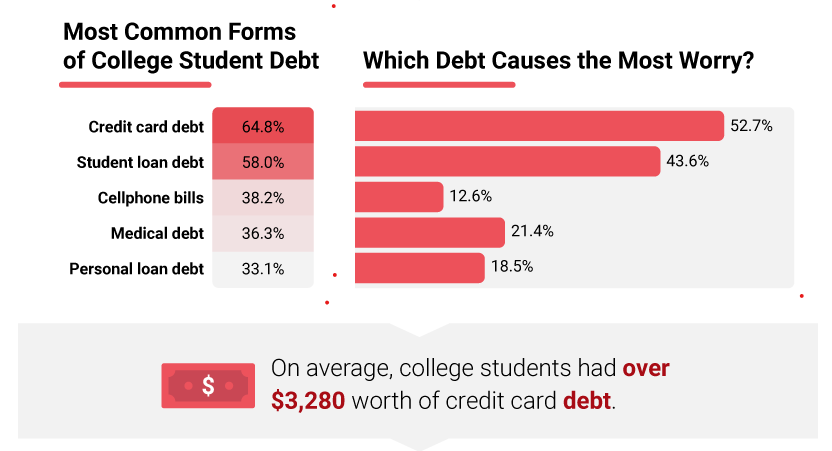
According to Palan et al. (2011), credit cards have played an important role in mediating undesirable consumption habits among American students. The paper says that in 2001, only 23% of freshmen reported to school with credit cards. However, by 2008, the number of freshmen who reported to college with credit cards increased to 39%. In the same period, the author says that credit card debt among American students rose to an average of $ 3,178. Most importantly, 82% of the students defaulted in repaying their debts (Palan et al., 2011). In the same study, the researcher found that college students depleted their resources not on basic things but on discretionary items such as entertainment, expensive clothes, and other luxuries. Students appear to be spending huge amounts of resources on items that are unnecessary and which add no value at all to their lives.
In the face of these challenges, there have been reasonable fears that irrational spending among college students has a tremendous impact on the quality of their learning. According to Gained et al. (2014), poor spending among college students affects their mental state, and this eventually impacts their learning activities. The authors indicate that to ensure quality learning among college students, it is critical to look at the critical issue of student spending. That forms the foundation of this paper.
Figure 1.0. Most common form of college debt. Source: College Finance, https://collegefinance.com/research/college-student-debt-and-credit-card-usage
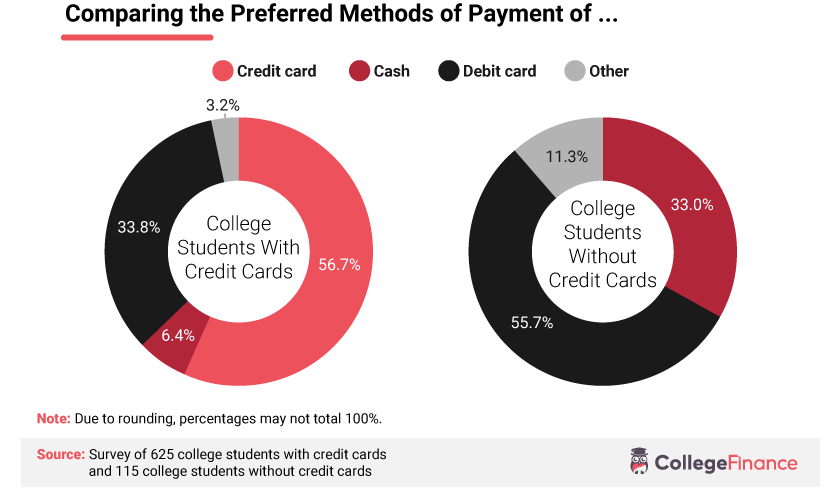
Figure 2.0: Methods of payment among college students Source: College Finance, https://collegefinance.com/research/college-student-debt-and-credit-card-usage
Problem Statements
Several factors affect the quality of learning among college students. Financial stability among students directly impacts their mental status. When students do not have money, they will be stressed, and this may cause them to drop out of school, or when they stay in school, they may not get the best out of their studies. While a lot of studies have been conducted on the problem of irrational shopping behavior among students, there has been little or limited examination of the contribution of emerging technologies such as TikTok and Tmall. When one examines these platforms, it is possible to obtain information on the shopping behaviors among college students, and this may make it possible to make an informed choice on how to approach the challenge. It is believed that by addressing the challenge of irrationals online shopping behavior of students, it will be possible to improve the quality of learning.
Research Questions
- To what extent do the live streaming services of TMall and TikTok reflect the irrational online shopping behavior among college students?
- How do live streaming services such as TikTok and TMall influence the consumption or online shopping behavior of college students?
- How do irrational online shopping behaviors among college students affect the quality of their learning?
- What may possible policy interventions be introduced to improve online shopping behavior among college students?
Research Objectives
Main objective
- The main objective of the study is to improve the shopping or consumption behaviors of college students.
Other objectives
- Another objective is to develop an understanding of the impact of live streaming services on the irrational online shopping behavior among college students.
- To develop interventions that will improve the online shopping behavior of college students.
- To help the government, parents, and other stakeholders to develop suitable interventions to improve spending and, as a result, improve the quality of learning among college students.
Significance of the Study
A lot of factors contribute to the success of students in their learning activities. The inability of students to have prudent financial management practices has affected the quality of their learning. The significance of this study is that it will contribute to the body of knowledge of the strategies to improve financial management among students and also the quality of learning. Presently, the world is undergoing a serious financial challenge, and many families are witnessing a significant decline in their disposable income. At this time, there is a pressing need to develop responsible financial management strategies. As long as a student are incapable of managing their resources prudently, it will be very difficult for them to achieve excellence. , this study will help to improve the quality of education by enhancing better financial management practices among students.
Definition of Key Terms
- Irrational: Not supported by logical reason. An irrational decision or action is that which is not founded on any logic and which would not have been made had reason been applied.
- Online shopping: this is a shopping activity that is carried out over some forms of technology such as an application or a website. Online shopping does not require shoppers to visit stores physically.
- TMall: This is a Chinese online business to consumer service retail outlet
- TikTok: This is a social media platform that focuses on sharing videos
- College students: students in various levels of their college education
- Financial management: strategies put in place to manage monetary resources
- Consumption behaviors: product purchasing and consumption tendencies of different people
Overview of the Theoretical Underpinning
Consumption is one of the most significant topics that characterize economic studies. Several theories have been developed to explain consumption behavior among populations. This paper is founded on Motivation-Need Theory. The motivation-need theory suggests that “people act to fulfill their needs based on a five-part priority system. The needs include, in order of importance: physiological (survival), safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization” (Solomon et al. 2012). Under this theory, it is assumed that people consume according to their unique needs. This theory is based on Maslow’s theory of the hierarchy of needs. According to Maslow, when humans are making consumption needs, there are five basic needs that they seek to fulfill. These needs are “physiological, safety, social, esteem and self-actualization” (Gunter & Furnham, 2014). The need to fulfill these needs usually imposes a lot of pressure on individuals since the satisfaction of these needs requires a lot of resources.
According to Maslow, human needs are not at the same level. There are some needs that are more basic than others, and they need to be fulfilled ahead of others (Joung & Park?Poaps, 2013). For example, a consumer may be faced with the option of buying a pair of shoes and buying food, but the money available may not be sufficient to acquire both of them. In the face of these circumstances, the individual will have to weigh what they may need ahead of the other. Prioritization is an important aspect of the motivation-needs theory. Since the resources are limited, individuals have to make a choice on what to acquire ahead of the other. It is said that “as the name of the theory indicates, Maslow believed that these needs exist in a hierarchical order. This progression principle suggests that lower-level needs must be met before higher-level needs. The deficit principle claims that once a need is satisfied, it is no longer a motivator because an individual will take action only to satisfy unmet needs” (Lockshin & Corsi, 2012). While there is a need for individual consumers to prioritize their product acquisition and choices, there is evidence that this is not always the case. There are people who do not plan their consumption according to their hierarchy of needs. For example, a person may have limited resources, but they choose to spend on entertainment rather than using the resources to pay for school fees.
McClelland’s Acquired Needs Theory is another theory that may be applied in the examination of the present phenomenon (Osemeke & Adegboyega, 2017). According to this theory, there are three basic needs of humans. The theory says that power, the need for affiliation, and the need for achievement. While these motivations are applicable majorly in the context of management, they may be useful in understanding human traits that influence their consumption behavior (Rybnicek et al., 2019).
Justification of Selected Theories
The two theories are important in understanding the factors or motivation for consumption. As indicated earlier, the Motivation-Need Theory is important in understanding the motivation for consumption choices among populations. Under this theory, it is assumed that people consume according to their unique needs. This theory is based on Maslow’s theory of the hierarchy of needs. According to Maslow, when humans are making consumption needs, there are five basic needs that they seek to fulfill (Schütte & Ciarlante, 2016). In the present study, the main objective is to understand the motivation of irrational online shopping behavior among college students. Thus, through this theory, it will be possible to understand the factors that influence the consumption behaviors among college students and develop interventions that may address the challenge.
McClelland’s Acquired Needs Theory is another theory that may be used in understanding the irrational shopping behavior among college students. In many cases, the theory is used in management circles, but it may also be used to understand the factors that influence people to consume some products (Ball, 2012). Applying this theory in the present case will allow the researcher to understand the characteristics of people that influence their consumption choices.
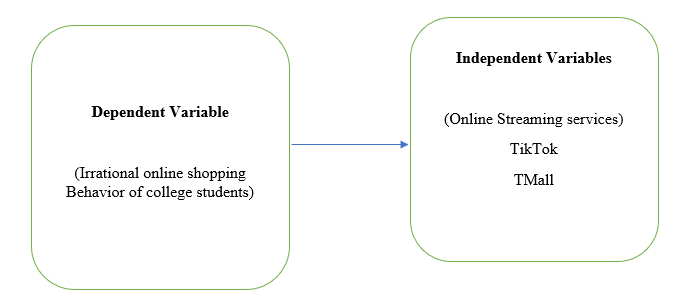
Proposed Framework and Conceptual Overview
Development of Hypotheses
- Online streaming services such as TikTok and TMall contribute to the irrational online shopping behavior among college students.
- There is no relationship between Online streaming services such as TikTok and TMall and irrational online shopping behavior among college students.
- There is an insignificant relationship between Online streaming services such as TikTok and TMall and the irrational online shopping behavior among college students.
- There is a significant relationship between Online streaming services such as TikTok and TMall and the irrational online shopping behavior among college students.
- It is impossible to determine if online streaming services such as TikTok and TMall contribute to the irrational online shopping behavior among college students.
Summary of Research Hypotheses
The hypotheses presented in the study evaluate the relationship between Online streaming services such as TikTok and TMall and irrational online shopping behavior among college students. Fundamentally, the hypotheses describe if these online streaming platforms have any relationship with the consumption trends among the students or they exist independently.
Proposal Summary
The problem of irrational shopping by American students has escalated and become a serious national issue. A lot of American students want to acquire products that are far beyond their capability with the aim of demonstrating power and status, thus fulfilling self-seeking needs. These consumption habits among college students are a cause of worry to educators across the country. The consumption behavior also worries parents and regulatory authorities. It is evident that irrational shopping is a dangerous practice that is capable of having adverse effects on the culprits when it is not contained. Students are vulnerable in several ways, and their uncontrolled spending may lead them to adverse mental health challenges. It is not only personal traits that encourage compulsive buying. Environmental issues such as advertising, peer pressure, and market stimuli, among other factors, significantly influence the consumption choices of students. This paper uses the Motivation-Need Theory to explore the phenomenon. This theory is based on Maslow’s theory of the hierarchy of needs. According to Maslow, when humans are making consumption needs, there are five basic needs that they seek to fulfill. Additionally, the paper uses McClelland’s Acquired Needs Theory to understand the various motivations of humans to consumption choices.
References
Ball, B. (2012). A summary of motivation theories. Retrieved on www. your coach. be> uploads, 3.
D’Souza, V. (2018). “Unethical advertising through social media”-A case study is investigating ethical marketing issues in the fast-food industry of Ireland (Doctoral dissertation, Dublin Business School).
Di Crosta A, Ceccato I, Marchetti D, La Malva P, Maiella R, Cannito L, et al. (2021) Psychological factors and consumer behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS ONE 16(8): e0256095. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256095
Duroy, D., Sabbagh, O., Baudel, A., & Lejoyeux, M. (2018). Compulsive buying in Paris psychology students: Assessment of DSM-5 personality trait domains. Psychiatry Research, 267, 182-186.
Fernandes, D., Lynch Jr, J. G., & Netemeyer, R. G. (2014). Financial literacy, financial education, and downstream financial behaviors. Management Science, 60(8), 1861-1883.
Gaines, A., Robb, C. A., Knol, L. L., & Sickler, S. (2014). Examining the role of financial factors, resources, and skills in predicting food security status among college students. International journal of consumer studies, 38(4), 374-384.
Gunter, B., & Furnham, A. (2014). Consumer profiles (RLE Consumer Behaviour): An introduction to psychographics. Routledge.
Joung, H. M., & Park?Poaps, H. (2013). Factors motivating and influencing clothing disposal behaviours. International Journal of consumer studies, 37(1), 105-111.
Jung, J. (2017). Impact of motives on impulsivity and compulsivity in compulsive buying behavior. Social Behavior and Personality: an international journal, 45(5), 705-718.
Lockshin, L., & Corsi, A. M. (2012). Consumer behaviour for wine 2.0: A review since 2003 and future directions. Wine Economics and Policy, 1(1), 2-23.
Moon, M. A., & Attiq, S. (2018). Compulsive buying behavior: Antecedents, consequences and prevalence in shopping mall consumers of an emerging economy. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences (PJCSS), 12(2), 548-570.
Müller, A., Mitchell, J. E., & de Zwaan, M. (2015). Compulsive buying. The American Journal on Addictions, 24(2), 132-137.
Nasidi, Q. Y., bin Ahmad, M. F., Garba, M., Hassan, I., & Gamji, M. B. (2021). Empirical investigation of factors affecting online shopping behavior. Laplace em Revista, 7(3D), 363-377.
Osemeke, M., & Adegboyega, S. (2017). Critical review and comparison between Maslow, Herzberg, and McClelland? s theory of needs. Funai Journal of Accounting, Business and Finance, 1(1), 161-173.
Palan, K. M., Morrow, P. C., Trapp, A., & Blackburn, V. (2011). Compulsive buying behavior in college students: the mediating role of credit card misuse. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 19(1), 81-96.
Pradhan, D., Israel, D., & Jena, A. K. (2018). Materialism and compulsive buying behaviour: The role of consumer credit card use and impulse buying. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics.
Rybnicek, R., Bergner, S., & Gutschelhofer, A. (2019). How individual needs influence motivation effects: a neuroscientific study on McClelland’s need theory. Review of Managerial Science, 13(2), 443-482.
Schütte, H., & Ciarlante, D. (2016). Consumer behaviour in Asia. Springer.
Shareef, M. A., Dwivedi, Y. K., Kumar, V., Davies, G., Rana, N., & Baabdullah, A. (2019). Purchase intention in an electronic commerce environment: A trade-off between controlling measures and operational performance. Information Technology & People.
Solomon, M., Russell-Bennett, R., & Previte, J. (2012). Consumer behaviour. Pearson Higher Education AU.

Time is precious
don’t waste it!

Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee