Initial Registration Assessment, Research Proposal Example
Introduction
In a world bounded by the assumptive control of networked connections, it could be analyzed that defining internet as a major system of operation in the modern society is likely is indeed creating a major definition on how the world intends to welcome different aspects of development. However, being interconnected throughout the world has its pros and cons. One of the most defined conditions by which worldwide interconnection provides a great impact on how the world is the fact that the internet opens up several opportunities for individuals around the globe to define their careers and specifically the manner by which they handle their duties. For a fact, several companies have now engaged themselves in the process of operating online apart from the physical offices then are maintaining. This condition of operation-shifting has caused several organizations the possibility of expanding further outside of their main branches as they decide to reach out to other parts of the globe.
Engaging in such a process of operation often involves a specific condition by which data and information are stored and shared online. This means that both public and private information are being transferred and shared through the worldwide web between networked users. This particular process benefits the business operators especially when it comes to creating possible forms of operation in and out their physical branches. This approach would allow them to connect real time with all the other members of their organization from other parts of the world even beyond the issues of time discrepancies. True, as a result, faster and more accurate operations are given way. However, one aspect of the process is the disadvantage of having the information and data shared to be rather vulnerable from hackers; especially that it is stored and transferred online. This is why security issues often get the best out of the systems that are operating online especially when it comes to handling privately defined data that are supposed to be well protected from outside intruders.
To be able to establish a system of protection, several procedures such as data encryption has been developed. In the past, creating an encryption for particular individual documents alone is defined as a hard process to undergo. All the more when it comes to establishing a protection system that is supposed to create an unbreakable protocol to protect data in the midst of a wide-ranged arena of information open for public access. Among the most competent protection system that has been developed up to date is that of the WiMax data security system. Through the creation of an effective division of system protections, WiMax operational protection system intends to manage the information from the point of placing data online, storing it and sharing it to third party users and protect it from particular outside users who are not supposed to be able to access specifically confident data.
Aim
It is the primary aim of this research to establish confidence on WiMax and the compatibility it has with other programs that are operating through the internet. Considering that data protection is a serious issue that the world has to contend with at present, this research hopes to create a relatively clear definition of how WiMax tends to respond to the said need. Through creating a more reliable system of protection that organizations and individuals operating their businesses and other personal concerns through the internet would actually be able to benefit fully from, WiMax and its capabilities shall be explored further.
Objectives
It is the primary objective of this research to create a distinctive presentation on how WiMax operates to protect data online and serve the needs of the users of the net when it comes to being assured that the information they keep and share through the worldwide web would not be accessed by anyone unauthorized to do so. It is also the objective of this research to manifest the reliability of WiMax as a platform of protection that is especially compatible with IEEE, which is considered a general platform of online computing that is widely used today.
Overview of the PhD work
The research topic on WiMax security systems compatibility issue is considered to be a PhD work level of discussion especially that it involves a wide array of condition that directly affects the society at present. Issues considered under this umbrella of topic intend to create a more reliable system of networked computing that the society needs to be assured of today. With the wide array of impact that modern mobile-technology has on the world, it could not be denied that networking along with its pros and cons has already become a common ground of discussion among people today. Program developers are at some point in the need of creating a reliable system that would help network users to trust the system as a whole thus making conditions of protection more dependable especially for the sake of improving security services provided to users worldwide.
Overview about this report
This particular report shall try to examine the essential elements that make up the WiMax operational architecture that allows it to withstand massive online pressure especially when it comes to handling data that is supposed to be protected as they are being kept and shared through the internet. Relatively, through this report, a definite distinction on how WiMax’s particular characteristic allows it to provide ample response to the security needs of the people who utilize the internet for personal and/or organizational operations.
Brief of Report Content
- The WiMax architecture discussion section shall provide a definition on the actual architectural makeup of the program thus proving its capacity to protect information or data online.
- The section on IEEE 802.16 protocol layer shall define the necessity of assuming the security issues that are related to the IEEE 802.16 protocol layer thus better indicating the role of WiMax in the picture.
- The Encryption Protocol Update Section shall give a distinctive discussion on the different forms of encryption developed from the beginning of the computing era up to the current years of operation. This shall provide a good definition on how computing security operations have started and further improved through time.
WiMax Architecture
WiMax is basically a wireless broadband access technology. It is known for providing services that is close to WiFi networks. This particular service provides network connection to both all internet-enabled gadgets including modern mobile phones. The meaning of WiMax is noted as Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access. Hence, from such a name-description, it could be noted that this particular platform of modern technology enables people to connect with each other through the use of wirelessly defined digital communication systems. Intended for metropolitan area networks, WiMax allows for the wide-range of information exchange making it one of the largest platforms of modern networking approaches used today. Unlike WiFi, WiMax has a regulated environment which means that the process of information processing in the system is lessened yet is more protected compared to the open service provided through WiFi.
To make sure that the data passed on is well protected, WiMax initiates encryption automation that is equipped to be less vulnerable to hackers.
IEEE 802.16 protocol layer associated with Security issues
The following should be described fully!
In WiMax, most of security issues are addressed and handled in the MAC security sub-layer:
The last sub-layer of MAC layer is the Security Sub-layer which lies between the MAC CPS and the PHY layer, addressing the authentication, key establishment and exchange, encryption and decryption of data exchanged between MAC and PHY layers.
Security within the MAC layer is referred to as the security sublayer. The goal of this layer is to provide access control, authentication, secure key exchange, and encryption (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 199). Many of the respective parts of this system are interrelated as shown in the figure below,
(Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 199)
When parties establish a link, they are protected through protocols that ensure confidentiality and unique access of the authorized parties. The unique handshaking between the two entities; namely base station (BS) and subscriber station (SS), is done at the MAC layer through security sublayer, which is based on fundamental concepts of secure exchange (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 199).” It’s through simple fundamentals that multicast networks can expand and remain safe through the use of these secure sublayers.
Since WiMAX Security utilizes IP (Internet Protocol) as is its main transport tool, the handling management traffic and control/signaling is done through a network service provider. These providers must pay extra attention to IP-related security threats, as well as the implications of security for end client devices. This applies to the core network, application servers, and all spaces in between (Motorola, 3). Vulnerabilities that occur when exchanging data can lead to file corruptions or even hacking. “The need for strong security always needs to be anticipated. IEEE 802.16 working groups instilled a significant number of advanced security knowledge into WiMAX protocols. As Motorola notes, ”their philosophy has been to “build in” security instead of having to “bolt on” security at a later time (Motorola, p.3).” This is why WiMAX standards are so dsistinct in their format and structure. An essential aspect of high speed data exchange in the wireless industry has to do with customer satisfaction in trusting the security of the technology being used. WiMAX allows providers to hold their systems to a higher standard of security. WiMAX standard entails specific guidelines for secure improvements in areas like, subscriber device authentication , higher-level authentication for alternate users advanced data encryption over-the-air, and finally choices for protecting control signalling data. all this data converges on an IP-based and service orientated network (Motorola 2007,4). Data management during the process of exchange is one of the key aspects of security layers integrity. The other end of the spectrum relies on securing privacy through valid authentication techniques.
Privacy and Key Management Protocol Version 2 (PKMv2) is a core part of the IEEE approach to standards-based security. as a key management protocol that allows for crypto key exchange for authentication, encryption and protection of multicast and broadcast traffic (Motorolla 2007, 4).” To prevent any man in the middle hacking or other security attacks the WiMAX has a 3-way handshake scheme to support the optimization of the re-authentication methods for enhancing fast handovers in Mobile (Motorola 2007, 4).” The essential aspect to take into account here is that PKMv2 establishes what could be viewed as a virtual witness mediating the process of key exchange. In addition to this adding to more security, this also results in a collective data on authentication histories for system updates and improvements. Authentication relies on EAP for a scalable framework, because it allows networks to guarantee that end-user and subscriber end devices (MSS) are real consumers of network services and not corrupted or automated bots (Motorolla 2007, 4). The main benefit of high end authentication systems like PKMv2 is that they allow a multitude of people across large networks to interact and correspond securely on a trusted provider. By consistently making it possible for individuals to interact across one networks securely, it makes it possible for authenticated subscribers to associate with even more secure networks of that calibre. An example of this can be seen with how WiMAX functions with 3GPP.
3GPP operators have the ability to grant subscribers, who have been authenticated, access to 3GPP packet switch services (Motorola 2007, 5). Motorola notes that, According to the WiMAX Forum, documentation of 3GPP/WiMAX interworking, 3GPP operators can grant authenticated subscribers access to services in the 3GPP Packet Switched (PS) domain through a WiMAX Access Network. The WiMAX Access Network architecture can be integrated into the 3GPP core network environment using different configurations and integration options (Motorola 2007, 5).”Here it’s identified that when networks are secure and trusting of one another, there are a wide range of possibilities. A secure relationship of trust is vital between 3GPP and AAA in order for there to be an effective exchange of security, accounting data, and authorizations. In order for data traffic to function properly, security devices and tunnels are established between the WiMAX Access Network and the 3GPP Gateway (Motorolla 2007, 6). This represents the world of digital infrastructure and how they utilize networks to exchange data, without which no network could expand. The problem is there are a wide range of system vulnerabilities that can occur.
Comprehensive views of system vulnerabilities have been setup by Motorola Security Services (MSS) specifically to address the full spectrum of security factors involved in WiMAX. This has to be done as the actual process of maintaining security in a real world wireless network can present many unpredictable variables. As Motorola notes, “The mission-critical nature of WiMAX applications demands high levels of network security, but this is not possible unless security standards, technologies, processes and policies are all united in a holistic, real-world security architecture that can protect the WiMAX infrastructure from end to end and top to bottom (Motorola 2007, 7).” This is a problem. Online network culture does not adjust for anyone particular brand or method. For WiMax to be implemented effectively, its structural base must already be compatible to integrate with system accustomed to wired networks. It’s clear Motorola is already ware of some of these necessities, as polices are changing to make the system more accommodating to real world needs.
Improvements in policy have also posed a major advancement for WiMAX sublayer issues. Much of the potential threats that can be caused to the MAC and PHY layers, such as BS or attack from hacks are mitigated with new policy amendments. Amendments made to regulation 802.16-2004 and IEEE802.16e-2005, has resulted in more liberal policies for Motorola to implement enhancements. According to researchers, these improved regulations in protocol and policy have resulted in increased quality of service and security and the use of Scalable OFDMA, which has incited the public to name this system “Mobile WiMAX” ((Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 199). The fact that Motorola improves gradually their encryption and authentication policies as they progress and expand as a business has some ups and some potential downfalls. In one case, continuous improvement is a major factor in the process of expanding networking and as the market grows ever-more demanding of it mobile and telecommunication devices and global necessities increase, network security will become a more pressing matter. The concern Motorola should have is for their sustainability. The tech and web market is cyclical in general and the battle for Motorola and other wireless providers to stay up on trends is urgent and never ending. A mobile wireless provider can’t take breaks, or even power naps, which is why the trend to implement new policies, or encryption methods, while at the same time maintaining network integrity could be likened to juggling knives.
SA, as the above diagram shows is basically the source for authentication control. The data shows that there are three type of these, “Three types of SAs are defined [4,5]: primary, static, and dynamic. Each manageable SS establishes a Primary Security association during the initialization process. Static SAs are provisioned within the BS (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 200).” SA is an essential transitioning support for authentication engaging with PKI to effectively execute secure exchange. Public key infrastructure (PKI): Protocol For securely exchanging keying material, between a base station and a mobile station, The WiMAX standard uses the Privacy and Key Management The privacy key management (PKM) protocol is responsible for privacy, key management, and authorizing an SS to the BS (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 200).” The core aspect of privacy is identity authentication, as personality theft is still a major concern in the digital market. These systems are designed to secure against such activity, and limit the options available those that might attack, hack, or corrupt a network. This is why public keys and authorization keys are a critical part of WiMAX. As Motorola notes,“Once the user identity is validated, After user WiMAX uses public key to create the authorization key, and then sends itto the mobile station (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 200).”WiMAX uses the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) for valid user authentication processing. EAP is a framework that requires specific protocols and methods to ensure authentication is legitimate (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 200).
As the authors note cost efficiency is a key part of the problem which is why there may be a slow transition from traditional networking to WiMAX. They say, “As the latest 802.16/WiMax supports mobility and roaming, like those in cellular networks, cost-efficiency is a rising issue in terms of overhead in authentication. Authentication involves expensive cryptographic operation. In general, the more complex cryptography, the more computational (Kim n.d., 4).” If there is higher need for computation, that means processing speed will be more complex to satisfy without spending more and investing in system functionality. It also could mean early, third party applications integration could be limited. This is not good for expansion. “Naturally, a WiMax network will be interfaced with a core network, probably a converged all-IP network. Besides, many look forward to carrying other promising technologies such as VoIP, Video Conferencing, and IPTV through WiMax. It’s because a large portion of WiMax subscribers (probably enterprise users rather than consumers) would be potential users for those services as well. (Kim n.d., 4).”Here it’s clear that the initial issue with a transition over to WiMAX will ultimately be the demand for integrating other services.
It’s clear that WiMAX implementation will not be a simple transition as it’s taking on a major endeavor in replacing wired networks. Kim points out that, “while 802.16/WiMax is an appealing alternative to wired networks, there exist critical threats including jamming, eavesdropping and modification of management messages, masquerading as BS, and DoS attacks. Even though some issues are no longer valid since the recent amendments, some remain unsolved and need to be carefully reviewed to avoid the same mistake as 802.11/WiFi. (Kim n.d., 5).” There are still some potential pitfalls with transitioning over to this system. The main concern is obviously security. The world banking, telecommunication, and the bulk of global media factions are distributed online. Transitioning over to a new method of connection for many of these industries that have established significant web infrastructure for their operations could have drastic detrimental affects if not handled properly.
[Reference must be from IEEE or a book on WiMax!]
Encryption Protocols Update
People have always looked for ways to protect their valuable information from others. In older times, they would either make a simple pattern change to an alphabet or substitute other letters or numbers into written messages to protect private information. Thus, began the age of cryptography. Encryption component may be different in each encryption algorithm but they are all meant to protect private information and provide access to those only for whom the information was intended.
Overview
A security protocol represents an abstract protocol which performs functions related to security and implements cryptographic methods. When data is encoded through encryption then only computers having the appropriate decoder can read it and also use it. Encryption can be used by anyone who wants to safeguard files and electronic mails sent to friends and colleagues. The encryption key can tell the computer about what kind of computations are required for encrypting something or to decrypt something.
Comparison of existing encryption protocols
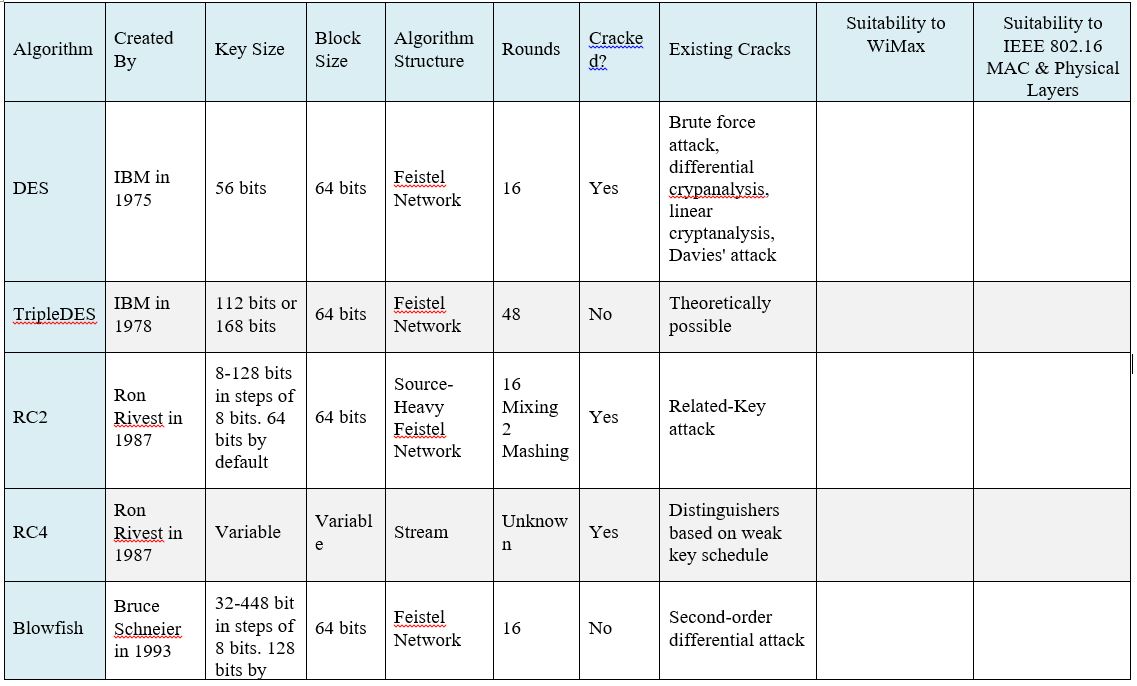
IBM developed Data Encryption Standard (DES) cipher in 1970’s. Data Encryption Standard Algorithm (DEA), a simple Fiestel network block cipher, uses 56 bit key length and 64 bit block size. DES cipher remained a standard among U.S. Government and other governments around the world until it became possible to crack it in less than twenty four hours using simple brute force attacks. Thus, DES is now considered outdated and less secure now.
In order to improve on DES, IBM developed the Triple Data Encryption Standard (TDES) in late 1970’s. Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA), which could be considered as three-times the DEA, replaces 56 bit key length in DES with 168 bit key lengths. This longer key length provides an effective defense against a brute force attack and despite being theoretically crackable, it is not practical to crack TDES using modern technology. Thus, a reputation of being fairly secure has made it a popular choice to process financial transactions.
Ron Rivest developed the “Rivest Cipher” or RC2 encryption algorithm in late 1980’s which uses 64 bit block size and variable key length. Originally created for Lotus to be used in their Lotus Notes messaging software, RC2 uses Fiestel network with 16 rounds of mixing and 2 rounds of mashing. RC2 was suited to its time and remained secret before becoming publicly available over the internet. RC2 can be cracked with 234 chosen plaintexts, thus, its status as a fairly easily cracked cipher makes it unsuitable for modern encryption needs.
Ron Rivest improved on RC2 with RC4, also known as ARC4 or ARCFOUR, where “A” stands for “alleged” as RC4 has never been released to the public and no one knows for sure how RC4 really looks like. RC4, a software stream cipher, is currently the standard encryption in SSL and WEP wireless applications and even though it is considered “secure enough”, it is vulnerable to crack due to not being consistently random for encryption purposes. Despite being better than RC2, RC4 is not suited to new applications which require higher levels of security.
Bruce Schneier developed the Blowfish cipher in early 1990’s which is a symmetric key block cipher that uses 64 bit block size and variable key length. With key lengths between 32 bits and 448 bits, Blowfish is a very secure cipher but it is being replaced by Twofish and Rijndael due to its small 64 bit block size. Blowfish is one of the fastest block ciphers to date but does slow considerably when changing keys which is why it is not used in some applications. Created with the intention of unrestricted and unlimited use by anyone, Blowfish continues to remain in the public domain.
Bruce Schneier improved upon Blowfish with another encryption tool Twofish which is also a symmetric key block cipher but uses larger block size of 128 bits and variable key sizes up to 256 bits. Though faster than Blowfish, Twofish is still slightly slower than Rijndael for 128 bit keys. But Twofish does have a speed advantage over Rijndael when it comes to 256 bit keys. Though considered a very strong encryption algorithm, Twofish remains vulnerable to a truncated differential cryptanalysis attack despite not being broken yet.
In 2002, the United States Government replaced outdated standard DES with Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) which is also known as Rijndael, named after Rijndael symmetric block cipher developed by two Belgian cryptographers Vincent Rijmen and Joan Daemen. Rijndael uses a block size of 128 bits with a variable key length of 128 bits to 256 bits. Instead of Feistel Network which is used by DES and other ciphers, Rijndael uses a substitution-permutation network. The substitution-permutation network not only makes Rijndael fast in both hardware and software applications and increases its appeal but Rijndael is also popular due to being easy to implement and requiring little memory.
The government uses Rijndael for both classified and non-classified information due to its reputation for being practically crack-proof. Though crack is theoretically possible, the state of technology has not reached there yet. Brute force attacks have been ineffective against Rijndael so far. Side channel attacks, which target implementations of cipher rather than cipher itself, indicate that crack can only be effective if they run on the same server where encryption is taking place.
The table below requires two more columns:
- Suitability to WiMax: Is this algorithm suitable to WiMax. This requires some reading about WiMax requirements
- Suitability to IEEE 802.16 MAC & Physical Layers: This is related to section 3. )
Comparison Table of Popular Encryption Algorithms
Conclusion
How the work so far is related to the PhD program … including:
What is the problem
In sum, the problem the data has shown must be resolved is the difficulty to create secure exchange across networks. For most these exchanges are based on trust of the integrity of the connection, but this concept becomes more complex when the model is multicast. One main problem this study has revealed is that, during the basic and primary connection, MAC management messages are transferred as plain-text without proper authentication. This, allows for management message to be hijacked over the air, or even attacked (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 201). Another issue of great concern has to do with how 802.16 uses the X.509 certificate. When attempting to recognize a genuine SS, this is the standard process for how PKI validates the certification path. This particular method uses RSA encryption with SHA-1 hashing. In most cases, the manufacturer pre-configures SS’s certificates (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 201). The problem is that this authentication scheme poses many potential threats. Because WiMAX supports authentication on the unilateral device level, address sniffing and spoofing make a SS masquerade attack more likely. This is because which can be implemented in a similar way as Wireless-fidelity (Wi-Fi) MAC filtering based on the hardware device address. Therefore, possible (Bogdanoski, Latkoski, Risteski, & Popovski, 2008, 201).”
What is/are new in this report that are not out there (of course reference to the above bulletin point a))
As the authors note, “The solution implemented in this research paper is based on [1] to use both timestamp and nonce for enhanced security to prevent from identified threats (Altaf, Javed , Naseer, & Latif, 2009, 105).” The research shows that this method provides the highest level of security, specifically when both timestamps and nonce are used parallel in collaboration with one another. The timestamp ensures that messages or recent, and nonce guarantees that all messages in question the reply to a prior message. This method also ensures in-depth security, especially in cases where hackers try to attack the system by synchronizing the clock with SS or BS (Altaf, Javed , Naseer, & Latif, 2009, 105).
The real solution to the problems is using a hybrid approach. The authors note that, “it is obvious that using the hybrid approach no illegitimate packet is accepted by the Base Station and also it identifies the interleaving attack while preventing the network from the suppress replay attack which leads us to conclude the effectiveness of hybrid approach (Altaf, Javed , Naseer, & Latif, 2009, 107).” While there will always be developing methods of
What is the next phase of this PhD program
Finally, as was previously mentioned, the world is bounded by network connections. And as the world grows more interconnected, there will be more benefits as well as greater potential pitfalls and setbacks. The real benefit of world interconnection through these networks is the ability for people to reinvent what is understood to be work, play, and life. As more companies expand to have telecommute departments, or solely function online, network security and secure authentication methods become a vital part of the process. This offers a priceless and virtually limitless opportunity for companies to expand, but it also puts an enormous strain on cyber security technicians, and technical support departments. I can also reshape the protocols of how retrieve information and exchange it. The next step depends on the next trend of the market. Emerging trends are aas cyclical as the mobile market itself, and in many ways it’s also very volatile as there are constant expansions in both for good and for bad. As systems like WiMax transition into their next phase of replacing wired networks, it’s vital that both security and cost efficiency maintain a priority in the development, testing, and implementation process. In the end the responsibility to keep private data secure while simultaneously expanding is doubled edged and not expected to be an easy process.
References
Altaf, Ayesha, Javed, M.Younus, Naseer, Sheraz, & Latif,Aisha. (2009). Performance Analysis of Secured Privacy and Key Management Protocol in IEEE 802.16e-2005. International Journal of Digital Content Technology and its Applications, Vol 3, Number 1, 103-109.
Bogdanoski, Mitko, Latkoski,Pero, Risteski, Alexandar, & Popovski, Borislav.(2008). IEEE 802.16 Security Issues: A Survey.In 16th Telecommunications Forum 2008. Serbia, November 25-27.199-202.
Kim, Hyung-Joon. (n.d.).IEEE 802.16/WiMax Security. New Jersey: Stevens Institute of Technology.
Motorola. (2007). WiMAX Security for Real-World Network Service Provider Deployments.
Nguyen,Trung. (2009). A survey of WiMAX security threats. http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse571-09/index.html

Time is precious
don’t waste it!

Plagiarism-free
guarantee

Privacy
guarantee

Secure
checkout

Money back
guarantee






